Abstract
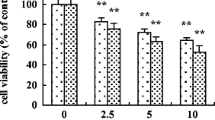
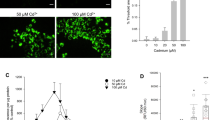
In this report, we have investigated the role of copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn) in oxidative stress induced by cadmium (Cd) in C6 cells. Cells were exposed to 20 μM Cd, 500 μM Cu, and 450 μM Zn for 24 h. Then, toxic effects, cellular metals levels, oxidative stress parameters, cell death, as well as DNA damage were evaluated. Cd induced an increase in cellular Cd, Cu, and Zn levels. This results not only in the inhibition of GSH-Px, GRase, CAT, and SOD activities but also in ROS overproduction, oxidative damage, and apoptotic cell death not related to Cu and Zn mechanisms. The thiol groups and GSH levels decreased, whereas the lipid peroxidation and DNA damage increased. The toxicity of Zn results from the imbalance between the inhibition of antioxidant activities and the induction of MT synthesis. The increase in Cu and Zn levels could be explained by the disruption of specific transporter activities, Cd interference with signaling pathways, and metal displacement. Our results suggest that the alteration of Cu and Zn homeostasis is involved in the oxidative stress induced by Cd.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- Cd:
-
Cadmium
- Cu:
-
Copper
- Zn:
-
Zinc
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- GSH-Px:
-
Glutathione peroxydase
- GRase:
-
Glutathione reductase
- GSH:
-
Reduced glutathione
- GSSG:
-
Oxized glutathione
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- MT:
-
Metallothioneins
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
- BCA:
-
Bicinchoninic acid
- BHT:
-
3,5-Di-tert-4butylhydroxytoluene
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- DTNB:
-
5,5′-Dithionitrobenzoic acid
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid
- NADPH:
-
Nicotinamide dinucleotide phosphate
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- TBARs:
-
Thiobarbituric acid reactants
- TNB:
-
5-Thio-2-nitrobenzoic acid
- ABTS:
-
2,2′-Azino-di-[3-ethylbenzthiazoline-sulfonate(6)]
References
Latinwo LM, Badisa VL, Ikediobi CO et al (2006) Effect of cadmium-induced oxidative stress on antioxidative enzymes in mitochondria and cytoplasm of CRL-1439 rat liver cells. Int J Mol Med 18:477–481
Barazani O, Dudai N, Khadka UR et al (2004) Cadmium accumulation in Allium schoenoprasum L. grown in an aqueous medium. Chemosphere 57:1213–1218
Waalkes MP (2000) Cadmium carcinogenesis in review. J Inorg Biochem 79:241–244
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100:57–70
Ercal N, Gurer-Orhan H, Aykin-Burns N (2001) Toxic metals and oxidative stress. Part I: mechanisms involved in metal-induced oxidative damage. Curr Top Med Chem 1:529–539
Bravard A, Vacher M, Gouget B et al (2006) Redox regulation of human OGG1 activity in response to cellular oxidative stress. Mol Cell Biol 26:7430–7436
Shih CM, Ko WC, Wu JS et al (2004) Mediating of caspase-independent apoptosis by cadmium through the mitochondria–ROS pathway in MRC-5 fibroblasts. J Cell Biochem 91:384–397
Takeda A (2000) Movement of zinc and its functional significance in the brain. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 34:137–148
Franklin RB, Costello LC (2009) The important role of the apoptotic effects of zinc in the development of cancers. J Cell Biochem 106:750–757
Slamon ND, Mead C, Morgan C et al (2005) The involvement of calcium in the protective and toxic (nonlinear) responses of rodent and human astroglial cells. Nonlinearity Biol Toxicol Med 3:79–95
Xu B, Chen S, Luo Y et al (2011) Calcium signaling is involved in cadmium-induced neuronal apoptosis via induction of reactive oxygen species and activation of MAPK/mTOR network. PLoS One 6:e19052
Southon A, Burke R, Norgate M et al (2004) Copper homoeostasis in Drosophila melanogaster S2 cells. Biochem J 383:303–309
Belyaeva EA, Dymkowska D, Wieckowski MR et al (2008) Mitochondria as an important target in heavy metal toxicity in rat hepatoma AS-30D cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 231:34–42
Kheradmand F, Nourmohammadi I, Modarressi MH et al (2010) Differential gene- expression of metallothionein 1M and 1G in response to zinc in sertoli TM4 cells. Iran Biomed J 14:9–15
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Nzengue Y, Steiman R, Garrel C et al (2008) Oxidative stress and DNA damage induced by cadmium in the human keratinocyte HaCaT cell line: role of glutathione in the resistance to cadmium. Toxicology 243:193–206
Nzengue Y, Steiman R, Guiraud P (2008) Characterization of the cell death induced by cadmium in HaCaT and C6 cell lines. Free Radic Res 42:142–153
Mouret S, Favier A, Beani JC et al (2007) Differential p53-mediated responses to solar-simulated radiation in human papillomavirus type 16-infected keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol 16:476–484
Nzengue Y, Lefebvre E, Cadet J et al (2009) Metallothionein expression in HaCaT and C6 cell lines exposed to cadmium. J Trace Elem Med Biol 23:314–323
Suwalsky M, Villena F, Norris B et al (2004) Cadmium-induced changes in the membrane of human erythrocytes and molecular models. J Inorg Biochem 98:1061–1066
Rousselet E, Richaud P, Douki T et al (2008) A zinc-resistant human epithelial cell line is impaired in cadmium and manganese import. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 230:312–319
Sensi SL, Yin HZ, Carriedo SG et al (1999) Preferential Zn2+ influx through Ca2+- permeable AMPA/kainate channels triggers prolonged mitochondrial superoxide production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:2414–2419
Wang Y, Fang J, Leonard SS et al (2004) Cadmium inhibits the electron transfer chain and induces reactive oxygen species. Free Radic Biol Med 36:1434–1443
Choi CY, An KW, Nelson ER et al (2007) Cadmium affects the expression of metallothionein (MT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX) mRNA in goldfish, Carassius auratus. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 145:595–600
Lazarova M, Labaj J, Eckl P et al (2006) Comparative evaluation of DNA damage by genotoxicants in primary rat cells applying the comet assay. Toxicol Lett 164:54–62
Kumari MV, Hiramatsu M, Ebadi M (2000) Free radical scavenging actions of hippocampal metallothionein isoforms and of antimetallothioneins: an electron spin resonance spectroscopic study. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 46:627–636
Angeloff A, Dubey I, Pratviel G et al (2001) Characterization of a 5′-aldehyde terminus resulting from the oxidative attack at C5′ of a 2-deoxyribose on DNA. Chem Res Toxicol 14:1413–1420
Krezel A, Maret W (2007) Different redox states of metallothionein/thionein in biological tissue. Biochem J 402:551–558
Kang YJ (2006) Metallothionein redox cycle and function. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 231:1459–1467
Aydin HH, Celik HA, Deveci R et al (2003) Characterization of the cellular response during apoptosis induction in cadmium-treated Hep G2 human hepatoma cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 95:139–153
Waisberg M, Joseph P, Hale B et al (2003) Molecular and cellular mechanisms of cadmium carcinogenesis. Toxicology 192:95–117
Boehning D, Patterson RL, Sedaghat L et al (2003) Cytochrome c binds to inositol (1,4,5) trisphosphate receptors, amplifying calcium-dependent apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol 5:1051–1061
Zhou T, Jia X, Chapin RE et al (2004) Cadmium at a non-toxic dose alters gene expression in mouse testes. Toxicol Lett 154:191–200
Acknowledgments
We thank Malika Kadri-Dakir, Sandra Grange, and Angèle Krawiec for their technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nzengue, Y., Steiman, R., Rachidi, W. et al. Oxidative Stress Induced by Cadmium in the C6 Cell Line: Role of Copper and Zinc. Biol Trace Elem Res 146, 410–419 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-9265-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-9265-9