Abstract
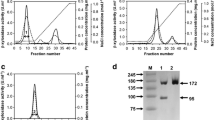
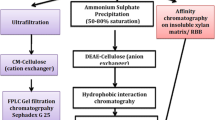
A locally isolated strain of Aspergillus niger van Tieghem was found to produce thermostable β-xylosidase activity. The enzyme was purified by cation and anion exchange and hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Maximum activity was observed at 70–75 °C and pH 4.5. The enzyme was found to be thermostable retaining 91 and 87% of its original activity after incubation for 72 h at 60 and 65 °C, respectively, with 52% residual activity detected after 18 h at 70 °C. Available data indicates that the purified β-xylosidase is more thermostable over industrially relevant prolonged periods at high temperature than those reported from other A. niger strains. Maximum activity was observed on p-nitrophenyl-β-d-xylopyranoside and the enzyme also hydrolysed p-nitrophenyl β-d-glucopyranoside and p-nitrophenyl α-l-arabinofuranoside. The purified enzyme acted synergistically with A. niger endo-1,4-β-xylanase in the hydrolysis of beechwood xylan at 65 °C. During hydrolysis of pretreated straw lignocellulose at 70 °C using a commercial lignocellulosic enzyme cocktail, inclusion of the purified enzyme resulted in a 19-fold increase in the amount of xylose produced after 6 h. The results observed indicate potential suitability for industrial application in the production of lignocellulosic bioethanol where thermostable β-xylosidase activity is of growing interest to maximise the enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulose.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taha, M., Foda, M., Shahsavari, E., Aburto-Medina, A., Adetutu, E., & Ball, A. (2016). Commercial feasibility of lignocellulose biodegradation: possibilities and challenges. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 38, 190–197.
Gomes, K. D., Maitan-Alfenas, G. P., de Andrade, L. G. A., Falkoski, D. L., Guimares, V. M., Alfenas, A. C., & de Rezende, S. T. (2017). Purification and characterization of xylanases from the fungus Chrysoporthe cubensis for production of xylooligosaccharides and fermentable sugars. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 182, 818–830.
Maitan-Alfenas, G. P., Visser, E. M., & Guimaraes, V. M. (2015). Enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass: converting food waste in valuable products. Current Opinion in Food Science, 1, 44–49.
Huberman, L. B., Liu, J., Qin, L. N., & Glass, N. L. (2016). Regulation of the lignocellulolytic response in filamentous fungi. Fungal Biology Reviews, 30, 101–111.
Van Dyk, J. S., & Pletschke, B. I. (2012). A review of lignocellulose bioconversion using enzymatic hydrolysis and synergistic cooperation between enzymes—factors affecting enzymes, conversion and synergy. Biotechnology Advances, 30, 1458–1480.
Qing, Q., & Wyman, C. E. (2011). Supplementation with xylanase and β-xylosidase to reduce xylo-oligomer and xylan inhibition of enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose and pretreated corn stover. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 4, 18.
Zhang, Z., Donaldson, A. A., & Ma, X. (2012). Advancements and future directions in enzyme technology for biomass conversion. Biotechnology Advances, 30, 913–919.
Bankeeree, W., Akada, R., Lotrakul, P., Punnapayak, H., & Prasongsuk, S. (2017). Enzymatic hydrolysis of black liquor xylan by a novel xylose-tolerant, thermostable β-xylosidase from a tropical strain of Aureobasidium pullulans CBS 135684. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology. Article in press. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2598-x.
Benassi, V. M., Silva, T. M. D., Pessela, B. C., Guisan, J. M., Mateo, C., Lima, M. S., Jorge, J. A., & Polizeli, M. D. L. T. M. (2013). Immobilization and biochemical properties of a β-xylosidase activated by glucose/xylose from Aspergillus niger USP-67 with transxylosylation activity. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 89, 93–101.
Terrasan, C. R. F., Romero-Fernandez, M., Orrego, A. H., Oliveira, S. M., Pessela, B. C., Carmona, E. C., & Guisan, J. M. (2017). Immobilization and stabilization of beta-xylosidases from Penicillium janczewskii. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 182, 349–366.
Sheng, P., Xu, J., Saccone, G., Li, K., & Zhang, H. (2014). Discovery and characterization of endo-xylanase and β-xylosidase from a highly xylanolytic bacterium in the hindgut of Holotrichia parallela larvae. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 105, 33–40.
Rakotoarivonina, H., Revol, P. V., Aubry, N., & Rémond, C. (2016). The use of thermostable bacterial hemicellulases improves the conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to valuable molecules. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 100, 7577–7590.
Qing, Q., Yang, B., & Wyman, C. E. (2010). Xylooligomers are strong inhibitors of cellulose hydrolysis by enzymes. Bioresource Technology, 101, 9624–9630.
Xin, D., Sun, Z., Viikari, L., & Zhang, J. (2015). Role of hemicellulases in production of fermentable sugars from corn stover. Industrial Crops and Products, 74, 209–217.
Dumon, C., Song, L., Bozonnet, S., Faure, R., & O'Donohue, M. J. (2012). Progress and future prospects for pentose-specific biocatalysts in biorefining. Process Biochemistry, 47, 346–357.
Gírio, F. M., Fonseca, C., Carvalheiro, F., Duarte, L. C., Marques, S., & Bogel-Lukasik, R. (2010). Hemicelluloses for fuel ethanol: a review. Bioresource Technology, 101, 4775–4800.
Hu, J., Arantes, V., & Saddler, J. N. (2011). The enhancement of enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic substrates by the addition of accessory enzymes such as xylanase: is it an additive or synergistic effect? Biotechnology for Biofuels, 4, 36.
Harris, P. V., Xu, F., Kreel, N. E., Kang, C., & Fukuyama, S. (2014). New enzyme insights drive advances in commercial ethanol production. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 19, 162–170.
Gonçalves, G. A. L., Takasugi, Y., Jia, L., Mori, Y., Noda, S., Tanaka, T., Ichinose, H., & Kamiya, N. (2015). Synergistic effect and application of xylanases as accessory enzymes to enhance the hydrolysis of pretreated bagasse. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 72, 16–24.
Ye, Y., Li, X., Cao, Y., Du, J., Chen, S., & Zhao, J. (2017). A β-xylosidase hyper-production Penicillium oxalicum mutant enhanced ethanol production from alkali-pretreated corn stover. Bioresource Technology, 245, 734–742.
Bhalla, A., Bansal, N., Kumar, S., Bischoff, K. M., & Sani, R. K. (2013). Improved lignocellulose conversion to biofuels with thermophilic bacteria and thermostable enzymes. Bioresource Technology, 128, 751–759.
Viikari, L., Vehmaanpera, J., & Koivula, A. (2012). Lignocellulosic ethanol: from science to industry. Biomass and Bioenergy, 46, 13–24.
Kazeem, M. O., Shah, U. K. M., Baharuddin, A. S., & AbdulRahman, N. A. (2017). Prospecting agro-waste cocktail: supplementation for cellulase production by a newly isolated thermophilic B. licheniformis 2D55. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 182, 1318–1340.
Skovgaard, P. A., & Jorgensen, H. (2013). Influence of high temperature and ethanol on thermostable lignocellulolytic enzymes. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 40, 447–456.
He, H. Y., Qin, Y. L., Li, N., Chen, G. G., & Liang, Z. Q. (2015). Purification and characterization of a thermostable hypothetical xylanase from Aspergillus oryzae HML366. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 175, 3148–3161.
Lin, C. Y., Shen, Z. C., & Qin, W. S. (2017). Characterization of xylanase and cellulase produced by a newly isolated Aspergillus fumigatus N2 and its efficient saccharification of barley straw. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 182, 559–569.
Knob, A., Terrasan, C. R. F., & Carmona, E. C. (2010). β-Xylosidases from filamentous fungi: an overview. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 26, 389–407.
de Vries, R. P., Riley, R., Wiebenga, A., Aguilar-Osorio, G., Amillis, S., Uchima, C. A., Anderluh, G., Asadollahi, M., Askin, M., Barry, K., Battaglia, E., Bayram, O., Benocci, T., Braus-Stromeyer, S. A., Caldana, C., Cánovas, D., Cerqueira, G. C., Chen, F., Chen, W., Choi, C., Clum, A., dos Santos, R. A. C., de Lima Damásio, A. R., Diallinas, G., Emri, T., Fekete, E., Flipphi, M., Freyberg, S., Gallo, A., Gournas, C., Habgood, R., Hainaut, M., Harispe, M. L., Henrissat, B., Hildén, K. S., Hope, R., Hossain, A., Karabika, E., Karaffa, L., Karányi, Z., Kraševec, N., Kuo, A., Kusch, H., LaButti, K., Lagendijk, E. L., Lapidus, A., Levasseur, A., Lindquist, E., Lipzen, A., Logrieco, A. F., MacCabe, A., Mäkelä, M. R., Malavazi, I., Melin, P., Meyer, V., Mielnichuk, N., Miskei, M., Molnár, A. P., Mulé, G., Ngan, C. Y., Orejas, M., Orosz, E., Ouedraogo, J. P., Overkamp, K. M., Park, H. S., Perrone, G., Piumi, F., Punt, P. J., Ram, A. F. J., Ramón, A., Rauscher, S., Record, E., Riaño-Pachón, D. M., Robert, V., Röhrig, J., Ruller, R., Salamov, A., Salih, N. S., Samson, R. A., Sándor, E., Sanguinetti, M., Schütze, T., Sepčić, K., Shelest, E., Sherlock, G., Sophianopoulou, V., Squina, F. M., Sun, H., Susca, A., Todd, R. B., Tsang, A., Unkles, S. E., van de Wiele, N., van Rossen-Uffink, D., de Castro Oliveira, J. V., Vesth, T. C., Visser, J., Yu, J. H., Zhou, M., Andersen, M. R., et al. (2017). Comparative genomics reveals high biological diversity and specific adaptations in the industrially and medically important fungal genus Aspergillus. Genome Biology, 18, 28.
Benoit, I., Culleton, H., Zhou, M., DiFalco, M., Aguilar-Osorio, G., Battaglia, E., Bouzid, O., Brouwer, C. P. J. M., El-Bushari, H. B. O., Coutinho, P. M., Gruben, B. S., Hildén, K. S., Houbraken, J., Barboza, L. A. J., Levasseur, A., Majoor, E., Mäkelä, M. R., Narang, H. M., Trejo-Aguilar, B., Van Den Brink, J., VanKuyk, P. A., Wiebenga, A., McKie, V., McCleary, B., Tsang, A., Henrissat, B., & De Vries, R. P. (2015). Closely related fungi employ diverse enzymatic strategies to degrade plant biomass. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 8, 107.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227, 680–685.
Miller, G. L. (1959). Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Analytical Chemistry, 31, 426–428.
Diaz, A. B., Blandino, A., Webb, C., & Caro, I. (2016). Modelling of different enzyme productions by solid-state fermentation on several agro-industrial residues. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 100, 9555–9566.
Liguori, R., Amore, A., & Faraco, V. (2013). Waste valorization by biotechnological conversion into added value products. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 97, 6129–6147.
Díaz-Malváez, F. I., García-Almendárez, B. E., Hernández-Arana, A., Amaro-Reyes, A., & Regalado-González, C. (2013). Isolation and properties of β-xylosidase from Aspergillus niger GS1 using corn pericarp upon solid state fermentation. Process Biochemistry, 48, 1018–1024.
Somera, A. F., Pereira, M. G., Guimarães, L. H. S., Polizeli, M. L. T. M., Terenzi, H. F., Furriel, R. P. M., & Jorge, J. A. (2009). Effect of glycosylation on the biochemical properties of β-xylosidases from Aspergillus versicolor. Journal of Microbiology, 47, 270–276.
La Grange, D. C., Pretorius, I. S., Claeyssens, M., & Van Zyl, W. H. (2001). Degradation of xylan to D-xylose by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae coexpressing the Aspergillus niger β-Xylosidase (xlnD) and the Trichoderma reesei xylanase II (xyn2) genes. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67, 5512–5519.
Bosetto, A., Justo, P. I., Zanardi, B., Venzon, S. S., Graciano, L., dos Santos, E. L. and de Cássia Garcia Simão, R. (2016) Research progress concerning fungal and bacterial β-xylosidases. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 178, 766–795.
Pedersen, M., Lauritzen, H. K., Frisvad, J. C., & Meyer, A. S. (2007). Identification of thermostable β-xylosidase activities produced by Aspergillus brasiliensis and Aspergillus niger. Biotechnology Letters, 29, 743–748.
Amaro-Reyes, A., García-Almendárez, B. E., Vázquez-Mandujano, D. G., Amaya-Llano, S., Castaño-Tostado, E., Guevara-González, R. G., Loera, O., & Regalado, C. (2011). Homologue expression of a β-xylosidase from native Aspergillus niger. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 38, 1311–1319.
Choengpanya, K., Arthornthurasuk, S., Wattana-Amorn, P., Huang, W. T., Plengmuankhae, W., Li, Y. K., & Kongsaeree, P. T. (2015). Cloning, expression and characterization of β-xylosidase from Aspergillus niger ASKU28. Protein Expression and Purification, 115, 132–140.
Delcheva, G., Dobrev, G., & Pishtiyski, I. (2008). Performance of Aspergillus niger B 03 β-xylosidase immobilized on polyamide membrane support. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 54, 109–115.
Wongwisansri, S., Promdonkoy, P., Matetaviparee, P., Roongsawang, N., Eurwilaichitr, L., & Tanapongpipat, S. (2013). High-level production of thermotolerant β-xylosidase of Aspergillus sp. BCC125 in Pichia pastoris: characterization and its application in ethanol production. Bioresource Technology, 132, 410–413.
Anand, A., Kumar, V., & Satyanarayana, T. (2013). Characteristics of thermostable endoxylanase and β-xylosidase of the extremely thermophilic bacterium Geobacillus thermodenitrificans TSAA1 and its applicability in generating xylooligosaccharides and xylose from agro-residues. Extremophiles, 17, 357–366.
Zhang, S., Wang, H., Shi, P., Xu, B., Bai, Y., Luo, H., & Yao, B. (2014). Cloning, expression, and characterization of a thermostable β-xylosidase from thermoacidophilic Alicyclobacillus sp. A4. Process Biochemistry, 49, 1422–1428.
Martins, M. P., Ventorim, R. Z., Coura, R. R., Maitan-Alfenas, G. P., Alfenas, R. F., & Guimarães, V. M. (2018). The β-xylosidase from Ceratocystis fimbriata RM35 improves the saccharification of sugarcane bagasse. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 13, 291–298.
Saha, B. C. (2001). Purification and characterization of an extracellular β-xylosidase from a newly isolated Fusarium verticillioides. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 27, 241–245.
Matsuo, M., Fujie, A., Win, M., & Yasui, T. (1987). Four types of β-xylosidases from Penicillium wortmanni IFO 7237. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 51, 2367–2379.
Rubingh, D. N. (1996). The influence of surfactants on enzyme activity. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science, 1, 598–603.
Rizzatti, A. C. S., Jorge, J. A., Terenzi, H. F., Rechia, C. G. V., & Polizeli, M. L. T. M. (2001). Purification and properties of a thermostable extracellular β-D-xylosidase produced by a thermotolerant Aspergillus phoenicis. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 26, 156–160.
Kitamoto, N., Yoshino, S., Ohmiya, K., & Tsukagoshi, N. (1999). Sequence analysis, overexpression, and antisense inhibition of a β-xylosidase gene, xylA, from Aspergillus oryzae KBN616. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 65, 20–24.
Wakiyama, M., Yoshihara, K., Hayashi, S., & Ohta, K. (2008). Purification and properties of an extracellular β-xylosidase from Aspergillus japonicus and sequence analysis of the encoding gene. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 106, 398–404.
Selig, M. J., Knoshaug, E. P., Decker, S. R., Baker, J. O., Himmel, M. E., & Adney, W. S. (2008). Heterologous expression of Aspergillus niger β-D-xylosidase (XlnD): characterization on lignocellulosic substrates. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 146, 57–68.
Yuan, Y., Hu, Y., Zhang, H., Leng, J., Li, F., Zhao, X., Gao, J., & Zhou, Y. (2016). Characterization of a recombinant multifunctional glycoside hydrolase family 3 β-xylosidase/α-l-arabinofuranosidase/β-glucosidase from Cellulosimicrobium cellulans sp. 21. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 131, 65–72.
Yao, R. M., Hou, W. L., & Bao, J. (2017). Complete oxidative conversion of lignocellulose derived non-glucose sugars to sugar acids by Gluconobacter oxydans. Bioresource Technology, 244, 1188–1192.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Irish Environmental Protection Agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boyce, A., Walsh, G. Purification and Characterisation of a Thermostable β-Xylosidase from Aspergillus niger van Tieghem of Potential Application in Lignocellulosic Bioethanol Production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 186, 712–730 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-018-2761-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-018-2761-z