Abstract
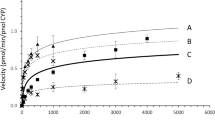
Genetic polymorphism of the cytochrome P450 (CYP) genes particularly affects CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 to a functionally relevant extent, and it is therefore crucial to elucidate the enzyme kinetic and molecular basis for altered catalytic activity of these allelic variants. This study explored the expression and function of the reported alleles CYP2D6*2, CYP2D6*10, CYP2D6*17, CYP2C19*23, CYP2C19*24, and CYP2C19*25 with respect to gene polymorphisms. Site-directed mutagenesis (SDM) was carried out to generate these six alleles. After DNA sequencing, the CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 wild types alongside with their alleles were each independently co-expressed with NADPH-CYP oxidoreductase (OxR) in Escherichia coli. The expressed proteins were analyzed using Western blotting, reduced carbon monoxide (CO) difference spectral scanning, and cytochrome c reductase assay. Results from Western blot revealed the presence of all CYP wild-type and allelic proteins in E. coli membrane fractions. The reduced CO difference spectra scanning presented the distinct peak of absorbance at 450 nm, and the cytochrome c reductase assay has confirmed that spectrally active OxR was expressed in each protein preparation. As a conclusion, the results obtained from this study have proven the CYP variants to be immunoreactive and spectrally active and are suitable for use to examine biotransformation and interaction mechanism of the enzymes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang, G. W., & Kam, P. C. A. (1999). The physiological and pharmacological roles of cytochrome P450 isoenzymes. Anaesthesia, 54(1), 42–50.
Rowland, P., Blaney, F. E., Smyth, M. G., Jones, J. J., Leydon, V. R., Oxbrow, A. K., Lewis, C. J., Tennant, M. G., Modi, S., Eggleston, D. S., Chenery, R. J., & Bridges, A. M. (2006). Crystal structure of human cytochrome P450 2D6. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281(11), 7614–7622.
Abraham, B. K., & Adithan, C. (2001). Genetic polymorphism of CYP2D6. Indian Journal of Pharmacology, 33, 147–169.
Ingelman-Sundberg, M., Sim, S. C., Gomez, A., & Rodriquez-Antona, C. (2007). Influence of cytochrome P450 polymorphisms on drug therapies: pharmacogenetic, pharmacoepigenetic and clinical aspects. Pharmacolology and Therapeutics, 116(3), 496–526.
Guengerich, F. P. (2010). Cytochrome P450 enzymes. In C. A. McQueen (Ed.), Comprehensive toxicology (2nd ed., pp. 41–76). Kidlington: Elsevier Ltd..
Meyer, J. M., & Rodvold, K. A. (1996). Drug bioinformation by the cytochrome P-450 enzyme system. Infections in Medicine, 13(452), 463–464 523.
Eichelbaum, M., Ingelman-Sundberg, M., & Evans, W. E. (2006). Pharmacogenomics and individualized drug therapy. Annual Review of Medicine, 57(1), 119–137.
Nelson, D. R., Koymans, L., Kamataki, T., Stegeman, J. J., Feyereisen, R., Waxman, D. J., Waterman, M. R., Gotoh, O., Coon, M. J., Estabrook, R. W., Gunsalus, I. C., & Nebert, D. W. (1996). The P450 superfamily: update on new sequences, gene mapping, accession numbers and nomenclature. Pharmacogenetics, 1, 1–42.
Ingelman-Sundberg, M. (2005). Genetic polymorphisms of cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6): clinical consequences, evolutionary aspects and functional diversity. Pharmacogenomics Journal, 5(1), 6–13.
Wang, J. F., Zhang, C. C., Chou, K. C., & Wei, D. Q. (2009). Structure of cytochrome P450s and personalized drug. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 16(2), 232–244.
Nelson, D. R., & Nebert, D. W. (2011). Cytochrome P450 (CYP) gene superfamily in eLS (pp. 1–13). Chichester: John Wiley& Sons Ltd..
Zhou, Q., Yu, X. M., Lin, H. B., Wang, L., Yun, Q. Z., Hu, S. N., & Wang, D. M. (2009). Genetic polymorphism, linkage disequilibrium, halotype structure and novel allele analysis of CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 in Han Chinese. Pharmacogenomics Journal, 9(6), 380–394.
Beverage, J. N., Sissung, T. M., Sion, A. D., Romano, F., & William, D. (2007). CYP2D6 polymorphisms and the impact on tamoxifen therapy. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 96(9), 2224–3221.
Carter, P. (1986). Site-directed mutagenesis. Journal of Biochemistry, 237(1), 1–7.
Herlitze, S., & Koenen, M. (1990). A general and rapid mutagenesis methods using polymerase chain reaction. Gene, 91(1), 143–147.
Niwa, T., Murayama, N., & Yamazaki, H. (2011). Comparison of cytochrome P450 2D6 and variants in terms of drug oxidation rates and substrate inhibition. Current Drug Metabolism, 12(5), 412–435.
Bradford, L. D. (2002). CYP2D6 alleles frequency in European Caucasians, Asians, Africans and their descendants. Pharmacogenomics, 45, 229–243.
Oscarson, M., Hidestrand, M., Johansson, I., & Ingelman-Sundberg, M. (1997). A combination of mutation in the CYP2D6*17 (CYP2D6Z) allele causes alterations in enzyme function. Molecular Pharmacology, 52(6), 1034–1040.
Senda, C., Yamaura, Y., Kobayashi, K., Fujii, H., Minami, H., Sasaki, Y., Igarashi, T., & Chiba, K. (2001). Influence of the CYP2D6*10 allele on the metabolism of mexiletine by human liver microsomes. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 52(1), 100–103.
Hanioka, N., Okumura, Y., Saito, Y., Hichiya, H., Soyama, A., Saito, K., Ueno, K., Sawada, J., & Narimatsu, S. (2006). Catalytic roles of CYP2D6.10 and CYP2D6.36 enzymes in mexiletine metabolism: in vitro functional analysis of recombinant proteins expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemical Pharmacology, 71(9), 1386–1395.
Sakuyama, K., Sasaki, T., Ujiie, S., Obata, K., Mizugaki, M., Ishikawa, M., & Hiratsuka, M. (2008). Functional characterization of 17 CYP2D6 allelic variants (CYP2D6.2, 10, 14A-B, 18, 27, 36, 39, 47-51, 53-55, and 57). Drug Metabolism and Disposition, 36(12), 2460–2467.
Liang, B., Zhan, Y., Wang, Y., Gu, E., Dai, D., Cai, J., & Hu, G. (2016). Effect of 24 cytochrome P450 2D6 variants found in the Chinese population on atomoxetine metabolism in vitro. Pharmacology, 97(1-2), 78–83.
Tiong, K. H., Yiap, B. C., Tan, E. L., Ismail, R., & Ong, C. E. (2010). Molecular cloning and functional analysis of cytochrome P450 2A6 (CYP2A6). Asia Pacific Journal of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, 18, 351–357.
Pan, Y., Abd-Rashid, B. A., Ismail, Z., Ismail, R., Mak, J. W., & Ong, C. E. (2011). Heterologous expression of human cytochromes P450 2D6 and 3A4 in Escherichia coli and their functional characterization. Protein Journal, 30(8), 581–591.
Lau, P. S., Leong, K. V., Ong, C. E., Dong, A. N., & Pan, Y. (2017). In vitro functional characterisation of cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C19 allelic variants CYP2C19*23 and CYP2C19*24. Biochemical Genetics, 55(1), 48–62.
Sandhu, P., Baba, T., & Guengerich, F. P. (1993). Expression of modified cytochrome P450 2C10 (2C9) in Escherichia coli, purification, and reconstitution of catalytic activity. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 306(2), 443–450.
Richardson, T. H., Jung, F., Griffin, K. J., Wester, M., Raucy, J. L., Kemper, B., Bornheim, L. M., Hassett, C., Omiecinski, C. J., & Johnson, E. F. (1995). A universal approach to the expression of human and rabbit cytochrome P450s of the 2C subfamily in Escherichia coli. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 323(1), 87–96.
Shen, A. L., Porter, T. D., Wilson, T. E., & Kasper, C. B. (1989). Structural analysis of the FMN binding domain of NADPH-cytochrome P-450 oxidoreductase by site-directed mutagenesis. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 264(13), 7584–7589.
Boye, S. L., Kerdpin, O., Elliot, D. J., Miners, J. O., Kelly, L., McKinnon, R. A., Bhasker, C. R., Yoovathaworn, K., & Birkett, D. J. (2004). Optimizing bacterial expression of catalytically active human cytochromes P450: comparison of CYP2C8 and CYP2C9. Xenobiotica, 34(1), 49–60.
Pritchard, M. P., Glancey, M. J., Blake, J. A. R., Gilham, D. E., Burchell, B., Wolf, C. R., & Friedberg, T. (1998). Functional co-expression of CYP2D6 and human NADPH cytochrome P450 reductase in Escherichia coli. Pharmacogenetics, 8(1), 33–42.
Omura, T., & Sato, R. (1964). The carbon monoxide-binding pigment of liver microsomes: 1. Evidence for its hemoprotein nature. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 239, 2370–2378.
Phillips, A. H., & Langdon, R. G. (1962). Hepatic triphosphopyridine nucloetide-cytochrome c reductase: Isolation, characterization, and kinetic studies. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 237, 2652–2660.
Masubuchi, Y., Igarashi, S., Suzuki, T., Horie, T., & Narimatsu, S. (1996). Imipramine-induced inactivation of a cytochrome P450 2D enzyme in rat liver microsomes: in relation to covalent binding of its reactive intermediate. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 279(2), 724–731.
Gillam, E. M., Baba, T., Kim, B.-R., Ohmori, S., & Guengerich, F. P. (1993). Expression of modified human cytochrome P450 3A4 in Escherichia coli and purification and reconstitution of the enzyme. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 305(1), 123–131.
Blake, J. A., Pritchard, M., Ding, S., Smith, G., Burchell, B., Wolf, C. R., & Friedberg, T. (1996). Coexpression of a human P450 (CYP3A4) and P450 reductase generates a highly functional monooxygenase system in Escherichia coli. FEBS Letters, 397(2-3), 210–214.
Crettol, S., Petrovic, N., & Murray, M. (2010). Pharmacogenetics of phase I and phase II drug metabolism. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 16(2), 204–219.
Ma, Q., & Lu, A. Y. H. (2011). Pharmacogenetics, pharmacogenomics, and individualized medicine. Pharmacological Reviews, 63(2), 437–459.
Chaudhry, S. R., Muhammad, S., Eidens, M., Klemm, M., Khan, D., Efferth, T., & Weisshaar, M. P. (2014). Pharmacogenetics prediction of individual variability in drug response base on CYP2D6, CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 genetic polymorphism. Current Drug Metabolism, 15(7), 711–718.
Buzková, H., Pechandova, K., Slanar, O., & Perlík, F. (2006). Genetic polymorphism of cytochrome P450 and methods for its determination. Prague Medical Report, 107(4), 383–393.
Yamazaki, H., Nakamura, M., Komatsu, T., Ohyama, K., Hatanaka, N., Asahi, S., Shimada, N., Guengerich, F. P., Shimada, T., Nakajima, M., & Yokoi, T. (2002). Roles of NADPH-P450 reductase and apo- and holo-cytochrome b5 on xenobiotic oxidations catalyzed by 12 recombinant human cytochrome P450s expressed in membranes of Escherichia coli. Protein Expression and Purification, 24(3), 329–337.
Zelasko, S., Palaria, A., & Das, A. (2013). Optimization to achieve high-level expression of cytochrome P450 proteins using Escherichia coli expression system. Protein Expression and Purification, 92(1), 77–87.
Waterman, M. R., Jenkins, C. M., & Pikileva, I. (1995). Genetically engineered bacterial cells and applications. Toxicology Letters, 82, 807–813.
Guengerich, F. P., Martin, M. V., Guo, Z., & Chun, Y. J. (2009). Purification of functional recombinant P450s from bacteria. Methods in Enzymology, 272, 1245–1251.
Vermilion, J. L., & Coon, M. J. (1978). Purified liver microsomal NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase: spectral characterization of oxidation-reduction states. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 253(8), 2694–2704.
McGinnity, D. F., Griffin, S. J., Moody, G. C., Voice, M., Hanlon, S., Friedberg, T., & Riley, R. J. (1999). Rapid characterization of the major drug-metabolizing human hepatic cytochrome P450 enzyme expressed in Escherichia coli. Drug Metabolism and Disposition, 27(9), 1017–1023.
Acknowledgements
We express our gratitude to the Monash University Malaysia (Monash Seed Grant under the Bioactive Compounds Research Strength), the Ministry of Science, Technology & Innovation (grant no. 02-02-10-SF0077), and the Ministry of Higher Education (grant no. FRGS/1/2014/SKK03/MUSM/02/1) for funding and supporting this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Fig. 1S
Representative reduced CO difference spectra showing expression of the (a) CYP2D6 wild type (CYP2D6*1) together with its alleles, and (b) CYP2C19 wild type (CYP2C19*1) with its alleles in E. coli membranes. (GIF 4009 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, A.N., Pan, Y., Palanisamy, U.D. et al. Site-Directed Mutagenesis of Cytochrome P450 2D6 and 2C19 Enzymes: Expression and Spectral Characterization of Naturally Occurring Allelic Variants. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 186, 132–144 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-018-2728-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-018-2728-0