Abstract
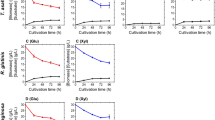
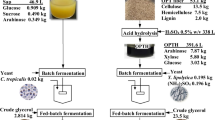
Limiting nitrogen supply has been routinely used as the master regulator to direct lipid biosynthesis. However, this strategy does not work with nitrogen-rich substrates, such as Jerusalem artichoke (JA), a fructose-based biomass, while it is difficult to obtain a high carbon-to-nitrogen (C/N) molar ratio. In this study, an alternative strategy to promote lipid accumulation by the oleaginous yeast Trichosporon fermentans CICC 1368 was developed by limiting phosphorous supply, and this strategy was implemented with JA hydrolysate as substrate. We showed that lipid accumulation was directly correlated with the C/P ratio of the culture media for T. fermentans. The time course of cell growth and lipid production was analyzed in a media with an initial C/P ratio of 6342, and the cellular lipid content could reach up to 48.5% of dry biomass. Moreover, JA hydrolysates were used as substrate for microbial lipid accumulation, under high C/P molar ratio condition, lipid yield, lipid content, and lipid coefficient increased by 10, 30, and 34%, respectively. It showed that by limiting phosphorus, the conversion of sugar into lipids can be improved effectively. Limiting phosphorus provides a promising solution to the problem of microbial lipid production with nitrogen-rich natural materials.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang, C., Chen, X. F., Xiong, L., Chen, X. D., Ma, L. L., & Chen, Y. (2013). Single cell oil production from low-cost substrates: the possibility and potential of its industrialization. Biotechnology Advances, 31, 129–139.
Jin, M., Slininger, P. J., Dien, B. S., et al. (2015). Microbial lipid-based lignocellulosic biorefinery: feasibility and challenges. Trends in Biotechnology, 33, 43–54.
Hu, C., Wu, S., Wang, Q., Jin, G., Shen, H., & Zhao, Z. K. (2011). Simultaneous utilization of glucose and xylose for lipid production by Trichosporon cutaneum. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 4, 25.
Liu, W., Wang, Y., Yu, Z., & Bao, J. (2012). Simultaneous saccharification and microbial lipid fermentation of corn stover by oleaginous yeast Trichosporon cutaneum. Bioresource Technology, 118, 13–18.
Yu, X. C., Zheng, Y. B., Dorgan, K. M., & Chen, S. L. (2011). Oil production by oleaginous yeasts using the hydrolysate from pretreatment of wheat straw with dilute sulfuric acid. Bioresource Technology, 102, 6134–6140.
Tsigie, Y. A., Wang, C. Y., Truong, C. T., & Ju, Y. H. (2011). Lipid production from Yarrowia lipolytica Po1g grown in sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate. Bioresource Technology, 102, 9216–9222.
Guo, L., Zhang, J., Hu, F., Dy Ryu, D., & Bao, J. (2013). Consolidated bioprocessing of highly concentrated Jerusalem artichoke tubers for simultaneous saccharification and ethanol fermentation. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 110, 2606–2615.
Ratledge, C., & Wynn, J. P. (2002). The biochemistry and molecular biology of lipid accumulation in oleaginous microorganisms. Advances in Applied Microbiology, 51, 1–51.
Braunwald, T., Schwemmlein, L., Graeff-Honninger, S., French, W. T., Hernandez, R., Holmes, W. E., & Claupein, W. (2013). Effect of different C/N ratios on carotenoid and lipid production by Rhodotorula glutinis. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 97, 6581–6588.
Li, Y. H., Zhao, Z. B., & Bai, F. W. (2007). High-density cultivation of oleaginous yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides Y4 in fed-batch culture. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 41, 312–317.
Wu, S., Hu, C., Jin, G., Zhao, X., & Zhao, Z. K. (2010). Phosphate-limitation mediated lipid production by Rhodosporidium toruloides. Bioresource Technology, 101, 6124–6129.
Huang, C., Zong, M. H., Wu, H., & Liu, Q. P. (2009). Microbial oil production from rice straw hydrolysate by Trichosporon fermentans. Bioresource Technology, 100, 4535–4538.
Zhu, L. Y., Zong, M. H., & Wu, H. (2008). Efficient lipid production with Trichosporon fermentans and its use for biodiesel preparation. Bioresource Technology, 99, 7881–7885.
Meesters, P., Huijberts, G. N. M., & Eggink, G. (1996). High cell density cultivation of the lipid accumulating yeast Cryptococcus curvatus using glycerol as a carbon source. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 45, 575–579.
Gong, Z., Wang, Q., Shen, H., Hu, C., Jin, G., & Zhao, Z. K. (2012). Co-fermentation of cellobiose and xylose by Lipomyces starkeyi for lipid production. Bioresource Technology, 117, 20–24.
Chen, P. S., Toribara, T. Y., & Warner, H. (1956). Microdetermina of phosphorus. Analytical Chemistry, 28, 1756–1758.
Wang, H. X., Qin, L., Wang, Y., Zhou, D. Y., Song, S., Wang, X. S., & Zhu, B. W. (2014). Effects of heating conditions on fatty acids and volatile compounds in foot muscle of abalone Haliotis discus hannai Ino. Fisheries Science, 80, 1097–1107.
Li, D. M., Zhou, D. Y., Zhu, B. W., et al. (2013). Effects of krill oil intake on plasma cholesterol and glucose levels in rats fed a high-cholesterol diet. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 93, 2669–2675.
Papanikolaou, S., Galiotou-Panayotou, M., Fakas, S., Komaitis, M., & Aggelis, G. (2007). Lipid production by oleaginous Mucorales cultivated on renewable carbon sources. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology, 109, 1060–1070.
Yanyan, H. U. A., Xin, Z., Jin, Z., Sufang, Z., & Zongbao, Z. (2007). Lipid production by Rhodosporidium toruloides using Jerusalem artichoke tubers. J Chin Biotechnol, 27, 59–63.
Zhang, Z., Zhang, X., & Tan, T. (2014). Lipid and carotenoid production by Rhodotorula glutinis under irradiation/high-temperature and dark/low-temperature cultivation. Bioresource Technology, 157, 149–153.
Dey, P., Banerjee, J., & Maiti, M. K. (2011). Comparative lipid profiling of two endophytic fungal isolates—Colletotrichum sp. and Alternaria sp. having potential utilities as biodiesel feedstock. Bioresource Technology, 102, 5815–5823.
Wu, S., Zhao, X., Shen, H., Wang, Q., & Zhao, Z. K. (2011). Microbial lipid production by Rhodosporidium toruloides under sulfate-limited conditions. Bioresource Technology, 102, 1803–1807.
Ashekuzzaman, S. M., & Jiang, J. Q. (2014). Study on the sorption-desorption-regeneration performance of Ca-, Mg- and CaMg-based layered double hydroxides for removing phosphate from water. Chemical Engineering Journal, 246, 97–105.
Xia, Z., Li, L., Feng, S., Cheng, H., & Wei, H. (2016). Clarifying the remelt syrup of brown granulated sugar by phosphate flocculating process. Chem Ind Eng Prog, 35, 2015–2020.
Wang, Y., Gong, Z., Yang, X., Shen, H., Wang, Q., Wang, J., & Zhao, Z. K. (2015). Microbial lipid production from pectin-derived carbohydrates by oleaginous yeasts. Process Biochemistry, 50, 1097–1102.
Liu, B., & Zhao, Z. (2007). Biodiesel production by direct methanolysis of oleaginous microbial biomass. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 82, 775–780.
Vicente, G., Bautista, L. F., Rodriguez, R., et al. (2009). Biodiesel production from biomass of an oleaginous fungus. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 48, 22–27.
Acknowledgements
Financial support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31501464), the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (20170540057), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2016M591419), and the Educational Commission of Liaoning Province of China (2016J018) is greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, R., Wu, X., Liu, S. et al. Efficient Conversion of Fructose-Based Biomass into Lipids with Trichosporon fermentans Under Phosphate-Limited Conditions. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 184, 113–123 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2536-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2536-y