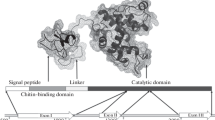
Abstract
Chitinases are glycosyl hydrolases that catalyze the hydrolysis of β-(1,4)-glycosidic bonds in chitin, the major structural polysaccharide presented in the cuticle and gut peritrophic matrix of insects. Two aspartate residues (D143, D145) and one tryptophan (W146) in the Lymantria dispar chitinase are highly conserved residues observed within the second conserved motif of the family 18 chitinase catalytic region. In this study, a chitinase cDNA, LdCht5, was cloned from L. dispar, and the roles of the three residues were investigated using site-directed mutagenesis and substituting them with three other amino acids. Seven mutant proteins, D143E, D145E, W146G, D143E/D145E, D143E/W146G, D145E/W146G, and D143E/D145E/W146G, as well as the wild-type enzyme, were produced using the baculovirus-insect cell line expression system. The enzymatic and kinetic properties of these mutant enzymes were measured using the oligosaccharide substrate MU-(GlcNAc)3. Among the seven mutants, the D145E, D143E/D145E, and D145E/W146G mutations kept some extant catalytic activity toward MU-(GlcNAc)3, while the D143E, W146G, D143E/W146G, and D143E/D145E/W146G mutant enzymes were inactivated. Compared with the mutant enzymes, the wild-type enzyme had higher values of k cat and k cat / K m. A study of the multiple point mutations in the second conserved catalytic region would help to elucidate the role of the critical residues and their relationships.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Matsuki, M., Kay, N., Serin, J., & Scott, J. K. (2011). Variation in the ability of larvae of phytophagous insects to develop on evolutionarily unfamiliar plants: a study with gypsy moth Lymantria dispar and eucalyptus. Agricultural and Forest Entomology, 13, 1–13.
Peric-Mataruga, V., Hackenberger, B., Vlahovic, M., Ilijin, L., & Mrdakovic, M. (2014). Potential improvement of Lymantria dispar L. management by quercetin. Archives of Biological Sciences, 66, 1125–1129.
Cao, C., Sun, L., Wen, R., Shang, Q., Ma, L., & Wang, Z. (2015). Characterization of the transcriptome of the asian gypsy moth Lymantria dispar identifies numerous transcripts associated with insecticide resistance. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 119, 54–61.
Sahai, A. S., & Manocha, M. S. (1993). Chitinases of fungi and plants: their involvement in morphogenesis and host-parasite interaction. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 11, 317–338.
Kern, M. F., Maraschin, S. F., Vom, E. D., Schrank, A., Vainstein, M. H., & Pasquali, G. (2010). Expression of a chitinase gene from Metarhizium anisopliae in tobacco plants confers resistance against Rhizoctonia solani. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 160, 1933–1946.
Tetreau, G., Cao, X., Chen, Y. R., Muthukrishnan, S., Jiang, H., & Blissard, G. W. (2015). Overview of chitin metabolism enzymes in Manduca sexta: identification, domain organization, phylogenetic analysis and gene expression. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 62, 114–126.
Zhang, J. Z., Zhang, X., Arakane, Y., Muthukrishnan, S., Kramer, K. J., & Ma, E. (2011). Identification and characterization of a novel chitinase-like gene cluster (Agcht5) possibly derived from tandem duplications in the African malaria mosquito, Anopheles gambiae. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 41, 521–528.
Kramer, K. J., & Koga, D. (1986). Insect chitin: physical state, synthesis, degradation and metabolic regulation. Insect Biochemistry, 16, 851–877.
Arakane, Y., & Muthukrishnan, S. (2010). Insect chitinase and chitinase-like proteins. Cellular & Molecular Life Sciences CMLS, 67, 201–216.
Kramer, K. J., & Muthukrishnan, S. (2005). Chitin metabolism in insects. In L. I. Gilbert, K. Iatrou, & S. S. Gill (Eds.), Comprehensive molecular insect science (Vol. 4, pp. 111–144). NY: Elsevier.
Merzendorfer, H. (2013). Insect-derived chitinases. In A. Vilcinskas (Ed.), Yellow biotechnology II insect biotechnology in plant protection and industry. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol (Vol. 136, pp. 19–50). Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Wu, Q., Liu, T., & Yang, Q. (2013). Cloning, expression and biocharacterization of OfCht5, the chitinase from the insect, Ostrinia furnacalis. Insect Sci., 20, 147–157.
Paek, A., Park, H. Y., & Jeong, S. E. (2012). Molecular cloning and functional expression of chitinase-encoding cDNA from the cabbage moth, Mamestra brassicae. Molecules and Cells, 33, 439–447.
Zhang, J. Z., Zhang, X., Arakane, Y., Muthukrishnan, S., Kramer, K. J., & Ma, E. (2011). Comparative genomic analysis of chitinase and chitinase-like genes in the African malaria mosquito (Anopheles gambiae). PloS One, 6, e19899.
Zhu, Q., Arakane, Y., Banerjee, D., Beeman, R. W., Kramer, K. J., & Muthukrishnan, S. (2008). Domain organization and phylogenetic analysis of the chitinase-like family of proteins in three species of insects. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 38, 452–466.
Xi, Y., Pan, P. L., Ye, Y. X., Yu, B., & Zhang, C. X. (2014). Chitin deacetylase family genes in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens, (Hemiptera: delphacidae). Insect Molecular Biology, 23, 695–705.
Li, D., Zhang, J., Yan, W., Liu, X., Ma, E., & Yi, S. (2015). Two chitinase 5 genes from Locusta migratoria: molecular characteristics and functional differentiation. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 58, 46–54.
Zhu, Q. (2007). PhD thesis, Characterization of families of chitinase genes & proteins from Tribolium castaneum, Drosophila melanogaster and Anopheles gambiae. Kansas State University, Kansas, USA.
Fan, X. J., Mi, Y. X., Ren, H., Zhang, C., Li, Y., & Xian, X. X. (2015). Cloning and functional expression of a chitinase cDNA from the apple leaf miner moth Lithocolletis ringoniella. Biochemistry, 80, 242–250.
Zhang, H., Huang, X., Fukamizo, T., Muthukrishnan, S., & Kramer, K. J. (2002). Site-directed mutagenesis and functional analysis of an active site tryptophan of insect chitinase. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 32, 1477–1488.
Lu, Y., Zen, K. C., Muthukrishnan, S., & Kramer, K. J. (2002). Site-directed mutagenesis and functional analysis of active site acidic amino acid residues D142, D144 and E146 in Manduca sexta (tobacco hornworm) chitinase. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 32, 1369–1382.
Li, Y. L., Song, H. F., Zhang, X. Y., Li, D. Q., Zhang, T. T., Ma, E. B., & Zhang, J. Z. (2016). Heterologous expression and characterization of two chitinase 5 enzymes from the migratory locust Locusta migratoria. Insect Sci., 23, 406–416.
Shinoda, T., Kobayashi, J., Matsui, M., & Chinzei, Y. (2001). Cloning and functional expression of a chitinase cDNA from the common cutworm, Spodoptera litura, using a recombinant baculovirus lacking the virus-encoded chitinase gene. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 31, 521–532.
Britton, H. T. S., & Robinson, R. A. (1931). Universal buffer solutions and the dissociation constant of veronal. Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed), 458, 1456–1462.
Ahmad, T., Rajagopal, R., & Bhatnagar, R. K. (2003). Molecular characterization of chitinase from polyphagous pest Helicoverpa armigera. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 310, 188–195.
Papanikolau, Y., Prag, G., Tavlas, G., Vorgias, C. E., Oppenheim, A. B., & Petratos, K. (2001). High resolution structural analyses of mutant chitinase a complexes with substrates provide new insight into the mechanism of catalysis. Biochemistry, 40, 11338–11343.
Watanabe, T., Uchida, M., Kobori, K., & Tanaka, H. (1994). Site-directed mutagenesis of the Asp-197 and Asp-202 residues in chitinase A1 of Bacillus circulans WL-12. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 58, 2283–2285.
Lin, F. P., Chen, H. C., & Lin, C. S. (1999). Site-directed mutagenesis of asp313, glu 315 and asp 391 residues in chitinase of Aeromonas caviae. International Union of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology Life, 48, 199–204.
Thomas, C. J., Gooday, G. W., King, L. A., & Possee, R. D. (2000). Mutagenesis of the active site coding region of the Autographa californica nucleopolyhedrovirus chiA gene. Journal of General Virology, 81, 1403–1411.
Huang, X., Zhang, H., Zen, K. C., Muthukrishnan, S., & Kramer, K. J. (2000). Homology modeling of the insect chitinase catalytic domain-oligosaccharide complex and the role of a putative active site tryptophan in catalysis. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 30, 107–117.
Watanabe, T., Kobori, K., Miyashita, K., Fujii, T., Sakai, H., & Uchida, M. (1993). Identification of glutamic acid 204 and aspartic acid 200 in chitinase A1 of Bacillus circulans WL-12 as essential residues for chitinase activity. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 268, 18567–18572.
Tull, D., & Withers, S. G. (1994). Mechanisms of cellulases and xylanases: a detailed kinetic study of the exo-beta-1, 4-glycanase from Cellulomonas fimi. Biochemistry, 33, 6363–6370.
Joshi, M. D., Hedberg, A., & Mcintosh, L. P. (1997). Complete measurement of the pKa values of the carboxyl and imidazole groups in Bacillus circulans xylanase. Prorein Science, 6, 2667–2670.
Gopalakrishnan, B., Muthukrishnan, S., & Kramer, K. J. (1995). Baculovirus mediated expression of a Manduca sexta, chitinase gene: properties of the recombinant protein. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 25, 255–265.
Arakane, Y., Zhu, Q., Matsumiya, M., Muthukrishnan, S., & Kramer, K. J. (2003). Properties of catalytic, linker and chitin-binding domains of insect chitinase. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 33, 631–648.
Zhu, Q., Arakane, Y., Beeman, R. W., Kramer, K. J., & Muthukrishnan, S. (2008). Characterization of recombinant chitinase-like proteins of Drosophila melanogaster and Tribolium castaneum. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 38, 467–477.
Du, X., & Liang, Y. (2004). Improved thermal stability of langmuir-blodgett films through an intermolecular hydrogen bond and metal complex. Journal of Chemical Physics, 120, 379.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31101490) and Key Research and Development Project of Shanxi Province (Grant No. 201603D321094).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, XJ., Yang, C., Zhang, C. et al. Cloning, Site-Directed Mutagenesis, and Functional Analysis of Active Residues in Lymantria dispar Chitinase. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 184, 12–24 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2524-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2524-2