Abstract
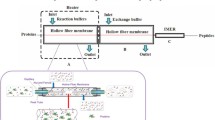
With the fast development of microalgal biofuel researches, the proteomics studies of microalgae increased quickly. A filter-aided sample preparation (FASP) method is widely used proteomics sample preparation method since 2009. Here, a method of microalgae proteomics analysis based on modified filter-aided sample preparation (mFASP) was described to meet the characteristics of microalgae cells and eliminate the error caused by over-alkylation. Using Chlamydomonas reinhardtii as the model, the prepared sample was tested by standard LC-MS/MS and compared with the previous reports. The results showed mFASP is suitable for most of occasions of microalgae proteomics studies.



Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Wisniewski, J. R., Zougman, A., Nagaraj, N., & Mann, M. (2009). Universal sample preparation method for proteome analysis. Nature Method, 6, 359–362.
Wang, J., Zhao, X., Zhao, Y., Ma, C., Zhong, R., Qian, X., & Ying, W. (2013). Influence of overalkylation in enzymatic digestion on the qualitative and quantitative analysis of proteins. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 31, 927–933.
Boja, E. S., & Fales, H. M. (2001). Overalkylation of a protein digest with iodoacetamide. Analytical Chemistry, 73, 3576–3582.
Zerges, W., & Hauser, C. (2009). In D. B. Stern & G. B. Witman (Eds.), The Chlamydomonas sourcebook (2nd ed., pp. 967–1025). London: Academic Press.
Vallon, O., & Spalding, M. H. (2009). In D. B. Stern & G. B. Witman (Eds.), The Chlamydomonas sourcebook (2nd ed., pp. 115–158). London: Academic Press.
Naumann, B., Busch, A., Allmer, J., Ostendorf, E., Zeller, M., Kirchhoff, H., & Hippler, M. (2007). Comparative quantitative proteomics to investigate the remodeling of bioenergetic pathways under iron deficiency in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proteomics, 7, 3964–3979.
Mastrobuoni, G., Irgang, S., Pietzke, M., Assmus, H. E., Wenzel, M., Schulze, W. X., & Kempa, S. (2012). Proteome dynamics and early salt stress response of the photosynthetic organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. BMC Genomics, 13, 215.
Fascellaro, G., Petrera, A., Lai, Z. W., Nanni, P., Grossmann, J., Burger, S., Biniossek, M. L., Gomez-Auli, A., Schilling, O., & Imkamp, F. (2016). Comprehensive proteomic analysis of nitrogen-starved Mycobacterium smegmatis delta pup reveals the impact of pupylation on nitrogen stress response. Journal of Proteome Research, 15, 2812–2825.
Eitzinger, N., Wagner, V., Weisheit, W., Geimer, S., Boness, D., Kreimer, G., & Mittag, M. (2015). Proteomic analysis of a fraction with intact eyespots of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and assignment of protein methylation. Frontiers in Plant Science, 6, 1085.
Harris, E. H. (2001). Chlamydomonas as a model organism. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 52, 363–406.
Schmidt, M., Gebner, G., Luff, M., Heiland, I., Wagner, V., Kaminski, M., Geimer, S., Eitzinger, N., Reibenweber, T., Voytsekh, O., Fiedler, M., Mittag, M., & Kreimer, G. (2006). Proteomic analysis of the eyespot of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii provides novel insights into its components and tactic movements. The Plant Cell, 18, 1908–1930.
Longworth, J., Noirel, J., Pandhal, J., Wright, P. C., & Vaidyanathan, S. (2012). HILIC- and SCX-based quantitative proteomics of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii during nitrogen starvation induced lipid and carbohydrate accumulation. Journal of Proteome Research, 11, 5959–5971.
Gillet, S., Decottignies, P., Chardonnet, S., & Le Marechal, P. (2006). Cadmium response and redoxin targets in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: a proteomic approach. Photosynthesis Research, 89, 201–211.
Sun, M. M., Sun, J., Qiu, J. W., Jing, H. M., & Liu, H. B. (2012). Characterization of the proteomic profiles of the brown tide alga Aureoumbra lagunensis under phosphate- and nitrogen-limiting conditions and of its phosphate limitation-specific protein with alkaline phosphatase activity. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 78, 2025–2033.
KIM, Y. K., YOO, W. I., LEE, S. H., & LEE, M. Y. (2005). Proteomic analysis of cadmium-induced protein profile alterations from marine alga Nannochloropsis oculata. Ecotoxicology, 14, 589–596.
Patel, A. K., Huang, E. L., Low-Decarie, E., & Lefsrud, M. G. (2015). Comparative shotgun proteomic analysis of wastewater-cultured microalgae: nitrogen sensing and carbon fixation for growth and nutrient removal in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Journal of Proteome Research, 14, 3051–3067.
Washburn, M. P., Wolters, D., & Yates 3rd, J. R. (2001). Large-scale analysis of the yeast proteome by multidimensional protein identification technology. Nature Biotechnology, 19, 242–247.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31470432) and Provincial Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning (No. 2014020090). The authors also want to express their thanks to Dr. Qin Hong Qing’s constructive discussions on the setting of the mass spectrum parameters.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Cao, X., Wang, Y. et al. A Method for Microalgae Proteomics Analysis Based on Modified Filter-Aided Sample Preparation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 183, 923–930 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2473-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2473-9