Abstract
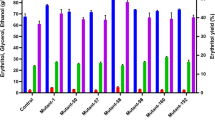
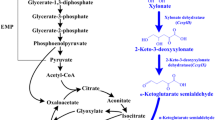
The biotransformation of xylose, the second most abundant sugar, has been a hot topic in recent years. In this work, Aureobasidium pullulans CGMCC3.0837 was subjected to UV mutagenesis to improve its erythritol production from xylose. The erythritol production of the obtained mutant ER35 was 50.92 % (17.28 g/L) higher than that of the parent strain. Response surface methodology was applied to optimize the medium composition. Yeast extract, KH2PO4, and citric acid were the key factors influencing erythritol synthesis, and the optimal concentrations were 17.82, 0.76, and 6.60 g/L, respectively. Under the optimized conditions, 31.75 and 31.42 g/L erythritol were obtained in shake flasks and in a 5-L fermentor, respectively. ER35 also showed a good consuming ability on xylose mother liquor with a final erythritol production of 26.35 g/L. This report provided insights into the potential of A. pullulans for the production of erythritol using xylose as a carbon source.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Olinger, P. M., & Velasco, V. S. (1996). Opportunities and advantages of sugar replacement. Cereal Foods World, 41, 110–117.
Bernt, W. O., Borzelleca, J. F., Flamm, G., & Munro, I. C. (1996). Erythritol: a review of biological and toxicological studies. Regulatory Toxicology & Pharmacology, 24, 191–197.
Boesten, D. M. P. H. J., den Hartog, G. J. M., de Cock, P., Douwina, B., Angela, B., & Aalt, B. (2015). Health effects of erythritol. Nutrafoods, 14, 3–9.
Park, Y. C., Lee, D. Y., Lee, D. H., & Kim, H. J. (2005). Proteomics and physiology of erythritol-producing strains. Journal of Chromatography B Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical & Life Sciences, 815, 251–260.
Marimuthu, J., Kyoung-Mi, L., Manish Kumar, T., Jung-Soo, K., Paramasamy, G., Sang-Yong, K., et al. (2009). Isolation of a novel high erythritol-producing Pseudozyma tsukubaensis and scale-up of erythritol fermentation to industrial level. Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology, 83, 225–231.
Kim, S. Y., Lee, K. H., Kim, J. H., & Oh, D. K. (1997). Erythritol production by controlling osmotic pressure in Trigonopsis variabilis. Biotechnology Letters, 19, 727–729.
Rymowicz, W. R. A., & Marcinkiewicz, M. (2009). High-yield production of erythritol from raw glycerol in fed-batch cultures of Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnology Letters, 31, 377–380.
Ryu, Y. W., Park, C. Y., Park, J. B., Kim, S. Y., & Seo, J. H. (2000). Optimization of erythritol production by Candida magnoliae in fed-batch culture. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 25, 100–103.
Vijaikishore, P., & Karanth, N. G. (1986). Factors affecting glycerol production by Pichia farinosa under alkaline conditions. Applied Biochemistry & Biotechnology, 13, 189–205.
Mirończuk, A. M., Rakicka, M., Biegalska, A., Rymowicz, W., & Dobrowolski, A. (2015). A two-stage fermentation process of erythritol production by yeast Y. lipolytica from molasses and glycerol. Bioresource Technology, 198, 445–455.
Kobayashi, Y., Iwata, H., Mizushima, D., Ogihara, J., & Kasumi, T. (2015). Erythritol production by Moniliella megachiliensis using nonrefined glycerol waste as carbon source. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 60(5), 475–480.
Chen, Y., Huang, W., Fu, G., Guo, J., Liu, M., Guo, X., et al. (2015). A genetic transformation protocol for the xylose-fermenting yeast Spathaspora passalidarum. Engineering in Life Sciences, 15, 550–555.
Chen, Y., Guo, J., Li, F., Liu, M., Zhang, X., Guo, X., et al. (2014). Production of pullulan from xylose and hemicellulose hydrolysate by Aureobasidium pullulans AY82 with pH control and DL-dithiothreitol addition. Biotechnology & Bioprocess Engineering, 19, 282–288.
Savergave, L. S., Gadre, R. V., Vaidya, B. K., & Narayanan, K. (2011). Strain improvement and statistical media optimization for enhanced erythritol production with minimal by-products from Candida magnoliae mutant R23. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 55, 92–100.
Yoon, S., Hong, E., Kim, S., Lee, P., Kim, M., Yang, H., et al. (2011). Optimization of culture medium for enhanced production of exopolysaccharide from Aureobasidium pullulans. Bioprocess & Biosystems Engineering, 35, 167–172.
Jiang, L. (2010). Optimization of fermentation conditions for pullulan production by Aureobasidium pullulan using response surface methodology. Carbohydrate Polymers, 79, 414–417.
Yang, L. B., Zhan, X. B., Zhu, L., Gao, M. J., & Lin, C. C. (2015). Optimization of a low-cost hyperosmotic medium and establishing the fermentation kinetics of erythritol production by Yarrowia lipolytica from crude glycerol. Preparative Biochemistry & Biotechnology.
Haaland, P. D. (Ed.). (1989). Separating signals from the noise. Experimental design inbiotechnology (pp. 61–83). New York: Marcel Dekker.
Ghezelbash, G. R., Nahvi, I., & Emamzadeh, R. (2014). Improvement of erythrose reductase activity, deletion of by-products and statistical media optimization for enhanced erythritol production from Yarrowia lipolytica mutant 49. Current Microbiology, 69, 149–157.
Cheng, H., Wang, B., Lv, J., Jiang, M., Lin, S., & Deng, Z. (2011). Xylitol production from xylose mother liquor: a novel strategy that combines the use of recombinant Bacillus subtilis and Candida maltose. Microbial Cell Factories, 10, 1039–1043.
Zhilin, L., Han, X., Weihong, J., Yu, J., & Sheng, Y. (2013). Improvement of solvent production from xylose mother liquor by engineering the xylose metabolic pathway in Clostridium acetobutylicum EA 2018. Applied Biochemistry & Biotechnology, 171, 555–568.
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by the “Twelfth Five-Year” National Science and technology project in rural areas (grant no. 2012AA101805).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, J., Li, J., Chen, Y. et al. Improving Erythritol Production of Aureobasidium pullulans from Xylose by Mutagenesis and Medium Optimization. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 180, 717–727 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2127-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2127-3