Abstract
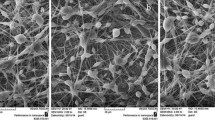
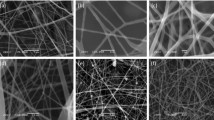
In this study, an antibacterial electrospun nanofibers for wound dressing application was successfully prepared from polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), Pluronic F127 (Plur), polyethyleneimine (PEI) blend solution with titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs). PVA–Plur–PEI nanofibers containing various ratios of TiO2 NPs were obtained. The formation and presence of TiO2 in the PVA–Plu–PEI/ TiO2 composite was confirmed by X-ray diffraction (XRD). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA), mechanical measurement, and antibacterial activity were undertaken in order to characterize the PVA–Plur–PEI/TiO2 nanofiber morphology and properties. The PVA–Plu–PEI nanofibers had a mean diameter of 220 nm, and PVA–Plur–PEI/TiO2 nanofibers had 255 nm. Moreover, the antimicrobial properties of the composite were studied by zone inhibition against Gram-negative bacteria, and the result indicates high antibacterial activity. Results of this antibacterial testing suggest that PVA–Plur–PEI/TiO2 nanofiber may be effective in topical antibacterial treatment in wound care; thus, they are very promising in the application of wound dressings.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramakrishna, S., Fujihara, K., Teo, W., Lim, T., & Ma, Z. (2005). An introduction to electrospinning and nanofibers (pp. 135–137). Singapore: World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte, Ltd.
Wendorff, J. H., Agarwal, S., & Greiner, A. (2012). Electrospinning: materials, in: processing, and applications. Germany: Wiley-VCH.
Fouda, M. G., El-Aassar, M. R., & Al-Deyab, S. S. (2013). Antimicrobial activity of carboxymethyl chitosan/polyethylene oxide nanofibers embedded silver nanoparticles. Carbohydrate Polymers, 92, 1012–1017.
Greiner, A., & Wendorff, J. H. (2007). Electrospinning: a fascinating method for the preparation of ultrathin fibers. Nanotechnology, 46, 5670–5703.
Pham, Q. P., Sharma, U., & Mikos, A. G. (2006). Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for tissue engineering applications: a review. Tissue Engineering, 12(5), 1197–1211.
Roshmi, T., Soumya, K. R., Jyothis, M., & Radhakrishnan, E. K. (2015). Electrospun polycaprolactone membrane incorporated with biosynthesized silver nanoparticles as effective wound dressing material. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 176(8), 2213–2224.
Yoshimoto, H., Shin, Y. M., Terai, H., & Vacanti, J. P. (2003). A biodegradable nanofiber scaffold by electrospinning and its potential for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials, 24, 2077–2082.
Agarwal, S., Wendorff, J. H., & Greiner, A. (2010). Chemistry on electrospun polymeric nanofibers: merely routine chemistry or a real challenge. Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 31, 1317–1331.
Nitanan, T., Akkaramongkolporn, P., Rojanarata, T., Ngawhirunpat, T., & Opanasopit, P. (2013). Neomycin-loaded poly(styrene sulfonic acid-co-maleic acid) (PSSA-MA)/polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) ion exchange nanofibers for wound dressing materials. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 448, 71–78.
Unnithana, A. R., Barakat, N. A. M., Pichiahd, P. B. T., Gnanasekarane, G., Nirmalab, R., Chad, Y.-S., Junge, C. H., El-Newehy, M., & Kim, H. Y. (2012). Wound-dressing materials with antibacterial activity from electrospun polyurethane–dextran nanofiber mats containing ciprofloxacin HCl. Carbohydrate Polymers, 90, 1786–1793.
Karami, Z., Rezaeian, I., Zahedi, P., & Abdollahi, M. (2013). Preparation and performance evaluations of electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone), poly(lactic acid), and their hybrid (50/50) nanofibrous mats containing thymol as an herbal drug for effective wound healing. Applied Polymer Science, 129, 756–766.
Lin, J., Li, C., Zhao, Y., Hu, J., & Zhang, L. M. (2012). Co-electrospun nanofibrous membranes of collagen and zein for wound healing. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 4, 1050–1057.
Merrell, J. G., McLaughlin, S. W., Tie, L., Laurencin, C. T., Chen, A. F., & Nair, L. S. (2009). Curcumin loaded poly(ε-caprolactone) nanofibers: diabetic wound dressing with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology, 36, 1149–1156.
Jin, G., Prabhakaran, M. P., Kai Dan Annamalai, S. K., Arunachalam, K. D., & Ramakrishna, S. (2013). Tissue engineered plant extracts as nanofibrous wound dressing. Biomaterials, 34, 724–734.
Son, B., Yeom, B.-Y., Song, S. H., Lee, C.-S., & Hwang, T. S. (2009). Antibacterial electrospun chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers containing silver nitrate and titanium dioxide. Applied Polymer Science, 111, 2892–2899.
Asran, A. S., Razghandi, K., Aggarwal, N., Michler, G. H., & Groth, T. (2010). Nanofibers from blends of polyvinyl alcohol and polyhydroxy butyrate as potential scaffold material for tissue engineering of skin. Biomacromolecules, 11, 3413–3421.
Abdelrahman, M. A., Samuel, M. H., & Orlando, J. R. (2014). Antimicrobial wound dressing nanofiber mats from multicomponent (chitosan/silver-NPs/polyvinyl alcohol) systems. Carbohydrate Polymers, 100, 166–178.
Sarhan, W. A., & Azzazy, M. E. (2015). High concentration honey chitosan electrospun nanofibers: biocompatibility and antibacterial effects. Carbohydrate Polymers, 122, 135–143.
Moreno, I., González-González, V., & Romero-García, J. (2011). Control release of lactate dehydrogenase encapsulated in poly (vinyl alcohol) nanofibers via electrospinning. European Polymer Journal, 47, 1264–1272.
Zulkifli, F. H., Shahitha, F., Yusuff, M. M., Hamidon, N. N., & Chahal, S. (2013). Cross-linking effect on electrospun hydroxyethyl cellulose/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibrous scaffolds. Procedia Engineering, 53, 689–695.
Schmolka, I. R. (1972). Artificial skin I. Preparation and properties of pluronic F-127 gels for treatment of burns. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 6, 571–582.
Gombotz, W. R., & Pettit, D. K. (1995). Biodegradable polymers for protein and peptide drug delivery. Journal of Bioconjugate Chem, 6, 332–351.
Jushasz, J., Lenaerts, V., Taymond, P., & Ong, H. (1989). Diffusion of rat atrial natriuretic factor in thermoreversible poloxamer gels. Biomaterials, 10, 265–268.
Viegas, T.X., Reeve, L.E., and Levinson, R.S. (1994). U.S. Patent, 5,306,501.
Viegas, T.X., Reeve, L.E., & Henry, R.L. (1994). U.S. patent, 5,346,703,.
El-Aassar, M. R. (2013). Functionalized electrospun nanofibers from poly (AN-co-MMA) for enzyme immobilization. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 85, 140–148.
El-Aassar, M. R., Al-Deyab, S. S., & Kenawy, E. (2013). Covalent immobilization of β-galactosidase onto electrospun nanofibers of poly (AN-co-MMA) copolymer. Applied Polymer Science, 127, 1873–1884.
Wist, J., Sanabria, J., Dierolf, C., Torres, W., & Pulgarin, C. (2004). Evaluation of photocatalytic disinfection of crude water for drinking water production. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 147, 241–246.
Grassian, V. H., Oshaughnessy, P. T., Adamcakova-Dodd, A., Pettibone, J. M., & Thorne, P. S. (2007). Inhalation exposure study of titanium dioxide nanoparticles with a primary particle size of 2 to 5 nm. Environmental Health Perspectives, 115, 397–402.
Borenfreund, E., & Puerner, J. A. (1985). Toxicity determinedin vitro by morphological alterations and neutral red absorption. Toxicology Letters, 24, 119–124.
Bechert, T., Steinrücke, P., & Guggenbichler, J. P. (2000). A new method for screening anti-infective biomaterials. Journal of Natural Medicines, 6, 1053–1056.
Kitkulnumchai, Y., Ajavakom, A., & Sukwattanasinitt, M. (2008). Treatment of oxidized cellulose fabric with chitosan and its surface activity towards anionic reactive dyes. Cellulose, 15, 599–608.
Thamaphat, K., Limsuwan, P., & Ngotawornchai, B. (2008). Phase characterization of TiO2 powder by XRD and TEM. Journal of Natural Sciences, 42, 357–361.
Shalumon, K. T., Binulal, N. S., Selvamurugan, N., Nair, S. V., Menon, D., & Furuike, T. (2009). Electrospinning of carboxymethyl chitin/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Carbohydrate Polymers, 77, 863–869.
Cetiner, S., Kalaoglu, F., Karakas, H., & Sarac, A. S. (2010). Electrospun nanofibers of polypyrrole-poly(acrylonitrile-co-vinyl acetate). Textile Research Journal, 80, 1784–1792.
Hsu, S. H., Chou, C. W., & Tseng, S. M. (2004). Enhanced thermal and mechanical properties in polyurethane/Au nanocomposites. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, 289, 1096–1101.
Shi, H., Magaye, R., Castranovaand, V., & Zhao, J. (2013). Titanium dioxide nanoparticles: a review of current toxicological data. Particle and Fiber Toxicology, 10, 15.
Lee, S., Pereira, B. P., & Yusof, N. (2009). Unconfined compression properties of a porous poly(vinyl alcohol)-chitosan-based hydrogel after hydration. Acta Biomaterialia, 5, 1919–1925.
Chuang, W., Young, T., Yao, C., & Chiu, W. (1999). Properties of the poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan blend and its effect on the culture of fibroblast in vitro. Biomaterials, 20, 1479–1487.
Ramovatar, M., Kumari, K., & Paulraj, R. (2015). Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in testicular cells of male wistar rat. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 175(2), 825–840.
Shah, M. S. A., Nag, M., Kalagara, T., Singh, S., & Manorama, S. V. (2008). Silver on PEG-PU TiO2 polymer nanocomposite films; an excellent system for antibacterial applications. Materials Chemistry, 20, 2455–2460.
Weir, E., Lawlor, A., Whelan, A., & Regan, F. (2008). The use of nanoparticles in anti-microbial materials and their characterization. Analyst, 133, 835–845.
Roy, S. C., Varghese, O. K., Paulose, M., & Grimes, C. A. (2010). Toward solar fuels: photocatalytic conversion of carbon dioxide to hydrocarbons. ACS Nano, 4, 1259–1278.
Vincent, M. G., John, P. N., Narayanan, P. M., Vani, C., & Sevanan, M. (2014). In vitro study on the efficacy of zinc oxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles against metallo beta-lactamase and biofilm producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Applied Pharmaceutical Science, 4, 41–46.
Santhoshkumar, T., Rahuman, A., Jayaseelan, G., & Rajakumar, G. (2015). Green synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Psidium guajava extract and its antibacterial and antioxidant properties. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine, 7(12), 968–976.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by postdoc Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China Grant No is (2015 M57145)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Aassar, M.R., El fawal, G.F., El-Deeb, N.M. et al. Electrospun Polyvinyl Alcohol/ Pluronic F127 Blended Nanofibers Containing Titanium Dioxide for Antibacterial Wound Dressing. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 178, 1488–1502 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1962-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1962-y