Abstract
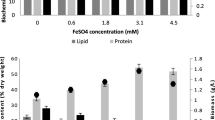
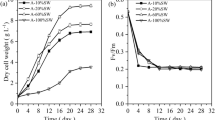
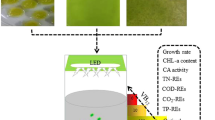
The effects of nitrogen (N) and/or phosphorus (P) starvation on the biochemical composition of native microalgae Chlorella spp. polyculture obtained from the phycoremediation of swine wastewaters were investigated. Microalgae-specific growth rate of 1.2 day−1 was achieved (30.3 mg L−1 day−1). PO4 −2 and NH3 were completely removed from swine digestate effluent after 3 and 11 days, respectively. Microalgae harvested immediately after nutrient removal showed high protein (56–59 %) and carbohydrate (25–34 %) but low lipid (1.8–3 %) contents. Depletion of N or P alone stimulated carbohydrate production at the expenses of proteins. Significant lipid accumulation from 3 % ± 0.5 to 16.3 % ± 0.8 was reached only after 25 days following N and P starvation as demonstrated by Nile red-stained cells. Regarding to the effects of harvesting methods on cellular biochemical composition, circumstantial evidences indicate that coagulation–flocculation with tannin may lead to lower protein and lipid amounts but increased carbohydrate content (p < 0.01) as compared to centrifugation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mezzari, M. P., Da Silva, M. L. B., Nicoloso, R. S., Ibelli, A. M. G., Bortoli, M., Viancelli, A., & Soares, H. M. (2013). Assessment of N2O emission from a photobioreactor treating ammonia-rich swine wastewater digestate. Bioresource Technology, 149, 327–332. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2013.09.065.
Wang, H., Xiong, H., Hui, Z., & Zeng, X. (2012). Mixotrophic cultivation of Chlorella pyrenoidosa with diluted primary piggery wastewater to produce lipids. Bioresource Technology, 104, 215–220. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2011.11.020.
Prajapati, S. K., Kaushik, P., Malik, A., & Vijay, V. K. (2013). Phycoremediation and biogas potential of native algal isolates from soil and wastewater. Bioresource Technology, 135, 232–238.
Choi, H. J., Seung, C., & Lee, M. (2014). Effect of the N/P ratio on biomass productivity and nutrient removal from municipal wastewater. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 38, 761–766. doi:10.1007/s00449-014-1317-z.
Choi, H. J. (2014). Effect of optical panel distance in a photobioreactor for nutrient removal and cultivation of microalgae. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 30, 2015–2023. doi:10.1007/s11274-014-1626-z.
Gupta, P. L., & Choi, S. L. H. (2015). A mini review: photobioreactors for large scale algal cultivation. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 31(9), 1409–1417. doi:10.1007/s11274-015-1892-4.
Rasala, B. A., & Mayfield, S. P. (2014). Photosynthetic biomanufacturing in green algae: production of recombinant proteins for industrial, nutritional, and medical uses. Photosynthesis Research, 123(3), 227–239.
Zhu, S., Huang, W., Xu, J., Wang, Z., Xu, J., & Yuan, Z. (2014). Metabolic changes of starch and lipid triggered by nitrogen starvation in the microalga Chlorella zofingiensis. Bioresource Technology, 152, 292–298. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2013.10.092.
Ho, S. H., Huang, S. W., Chen, C. Y., Hasunuma, T., Kondo, A., & Chang, J. S. (2013). Characterization and optimization of carbohydrate production from an indigenous microalga Chlorella vulgaris FSP-E. Bioresource Technology, 135, 157–165.
Ho, S. H., Chen, C. Y., & Chang, J. S. (2012). Effect of light intensity and nitrogen starvation on CO2 fixation and lipid/carbohydrate production of an indigenous microalga Scenedesmus obliquus CNW-N. Bioresource Technology, 113, 244–252.
Khalil, Z. I., Asker, M. M. S., El-Sayed, S., & Kobbia, I. A. (2010). Effect of pH on growth and biochemical responses of Dunaliella bardawil and Chlorella ellipsoidea. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 26(7), 1225–1231.
Roleda, M. Y., Slocombe, S. P., Leakey, R. J. G., Day, J. G., Bell, E. M., & Stanley, M. S. (2013). Effects of temperature and nutrient regimes on biomass and lipid production by six oleaginous microalgae in batch culture employing a two-phase cultivation strategy. Bioresource Technology, 129, 439–449.
Ruangsomboon, S., Ganmanee, M., & Choochote, S. (2013). Effects of different nitrogen, phosphorus, and iron concentrations and salinity on lipid production in newly isolated strain of the tropical green microalga, Scenedesmus dimorphus KMITL. Journal of Applied Phycology, 25(3), 867–874.
Sun, X., Cao, Y., Xu, H., Liu, Y., Sun, J., Qiao, D., & Cao, Y. (2014). Effect of nitrogen-starvation, light intensity and iron on triacylglyceride/carbohydrate production and fatty acid profile of Neochloris oleoabundans HK-129 by a two-stage process. Bioresource Technology, 155, 204–212. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2013.12.109.
Lowrey, J., Brooks, M. S., & McGinn, P. J. (2014). Heterotrophic and mixotrophic cultivation of microalgae for biodiesel production in agricultural wastewaters and associated challenges. Journal of Applied Phycology, 27(4), 1–14. doi:10.1007/s10811-014-0459-3.
Lee, S. J., Kim, S. B., Kim, J. E., Kwon, G. S., Yoon, B. D., & Oh, H. M. (1998). Effects of harvesting method and growth stage on the flocculation of the green alga Botryococcus braunii. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 27(1), 14–18.
Liang, K., Zhang, Q., Gu, M., & Cong, W. (2013). Effect of phosphorus on lipid accumulation in freshwater microalga Chlorella sp. Journal of Applied Phycology, 25(1), 311–318.
Li, Y., Han, F., Xu, H., Mu, J., Chen, D., Feng, B., & Zeng, H. (2014). Potential lipid accumulation and growth characteristic of the green alga Chlorella with combination cultivation mode of nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P). Bioresource Technology, 174, 24–32. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2014.09.142.
Coward, T., Lee, J. G. M., & Caldwell, G. S. (2014). Harvesting microalgae by CTAB-aided foam flotation increases lipid recovery and improves fatty acid methyl ester characteristics. Biomass and Bioenergy, 67, 354–362.
Borges, L., Morón-Villarreyes, J. A., D’Oca, M. G. M., & Abreu, P. C. (2011). Effects of flocculants on lipid extraction and fatty acid composition of the microalgae Nannochloropsis oculata and Thalassiosira weissflogii. Biomass and Bioenergy, 35(10), 4449–4454.
Bonato, A.L.V., do Valle, C.B., Jank, L., Resende, R.M.S., & Leguizamon, G.O.C. (2002). Extração de DNA genômico de Brachiaria e Panicum maximum. Campo Grande, MS, BRAZIL. doi: ISSN 1516–9308.
White, T. J., Bruns, T., Lee, S., & Taylor, J. (1990). Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications, 18, 315–322.
Koetschan, C., Hackl, T., Müller, T., Wolf, M., Förster, F., & Schultz, J. (2012). ITS2 database IV: interactive taxon sampling for internal transcribed spacer 2 based phylogenies. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 63(3), 585–588. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2012.01.026.
Hall, J. D., Fucikova, K., Lo, C., Lewis, L. A., & Karol, K. G. (2010). An assessment of proposed DNA barcodes in freshwater green algae. Cryptogamie Algologie, 31(4), 529–555.
APHA. (2012). Standard methods for the examination for water and wastewater. (D. American Water Works Association, Washington, Ed.) (22nd Ed.).
Porra, R. J., Thompson, W. a., & Kriedemann, P. E. (1989). Determination of accurate extinction coefficients and simultaneous equations for assaying chlorophylls a and b extracted with four different solvents: verification of the concentration of chlorophyll standards by atomic absorption spectroscopy. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics, 975(3), 384–394. doi:10.1016/S0005-2728(89)80347-0.
Held, P., & Raymond, K. (2011). Determination of algal cell lipids using Nile red—using microplates to monitor neutral lipids in Chlorella vulgaris. Biofuel Research, 8, 1–5.
Mezzari, M. P., da Silva, M. L. B., Pirolli, M., Perazzoli, S., Steinmetz, R. L. R., Nunes, E. O., & Soares, H. M. (2014). Assessment of a tannin-based organic polymer to harvest Chlorella vulgaris biomass from swine wastewater digestate phycoremediation. Water Science and Technology, 70(5), 888–894.
Chu, F. F., Chu, P. N., Cai, P. J., Li, W. W., Lam, P. K. S., & Zeng, R. J. (2013). Phosphorus plays an important role in enhancing biodiesel productivity of Chlorella vulgaris under nitrogen deficiency. Bioresource Technology, 134, 341–346.
Chu, F. F., Chu, P. N., Shen, X. F., Lam, P. K. S., & Zeng, R. J. (2014). Effect of phosphorus on biodiesel production from Scenedesmus obliquus under nitrogen-deficiency stress. Bioresource Technology, 152, 241–246.
Ho, S. H., Nakanishi, A., Ye, X., Chang, J. S., Hara, K., Hasunuma, T., & Kondo, A. (2014). Optimizing biodiesel production in marine Chlamydomonas sp. JSC4 through metabolic profiling and an innovative salinity-gradient strategy. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 7(1), 97. doi:10.1186/1754-6834-7-97.
Roopnarain, A., Gray, V. M., & Sym, S. D. (2014). Phosphorus limitation and starvation effects on cell growth and lipid accumulation in Isochrysis galbana U4 for biodiesel production. Bioresource Technology, 156, 408–411.
AOCS. (2013). Official methods and recommended practices of the AOCS. (D. Firestone, Ed.) (6th ed.). Champaign: American Oil Chemists’ Society.
AOAC. (1990). Official methods of analysis of AOAC International. (Kenneth Helrich, Ed.) (15th ed.). Washington: Association of Official Analytical Chemists.
BCAA. (2009). Ash or mineral matter. In Brazilian Compendium of Animal Nutrition (p. 204). São José do Rio Preto, SP, Brazil.
Bi, Z., & He, B. B. (2013). Characterization of microalgae for the purpose of biofuel production. Transactions of the ASABE, 56(4), 1529–1539.
Pancha, I., Chokshi, K., George, B., Ghosh, T., Paliwal, C., Maurya, R., & Mishra, S. (2014). Nitrogen stress triggered biochemical and morphological changes in the microalgae Scenedesmus sp. CCNM 1077. Bioresource Technology, 156, 146–154. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.025.
Ikaran, Z., Suárez-Alvarez, S., Urreta, I., & Castañón, S. (2015). The effect of nitrogen limitation on the physiology and metabolism of Chlorella vulgaris var L3. Algal Research, 10, 134–144. doi:10.1016/j.algal.2015.04.023.
Bondioli, P., Della Bella, L., Rivolta, G., Chini Zittelli, G., Bassi, N., Rodolfi, L., Casini, D., Prussi, M., Chiaramonti, D., & Tredici, M. R. (2012). Oil production by the marine microalgae Nannochloropsis sp. F&M-M24 and Tetraselmis suecica F&M-M33. Bioresource Technology, 114, 567–572.
Peccia, J., Haznedaroglu, B., Gutierrez, J., & Zimmerman, J. B. (2013). Nitrogen supply is an important driver of sustainable microalgae biofuel production. Trends in Biotechnology, 31(3), 134–138.
Bellou, S., Baeshen, M. N., Elazzazy, A. M., Aggeli, D., Sayegh, F., & Aggelis, G. (2014). Microalgal lipids biochemistry and biotechnological perspectives. Biotechnology Advances, 32(6), 1476–1493. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2014.10.003.
Zhao, Y., Yu, Z., Song, X., & Cao, X. (2009). Biochemical compositions of two dominant bloom-forming species isolated from the Yangtze River Estuary in response to different nutrient conditions. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 368(1), 30–36.
Said, H. A. (2009). Changes in levels of cellular constituents of Dunaliella parva associated with inorganic phosphate depletion. Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research, 4(2), 44–49.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by CAPES-EMBRAPA (#001/2011) and EMBRAPA (#02.12.08.004.00.05). We thank Dr. Mariana Groke for the photomicrographs and Dr. Bruno dos Santos A. F. Brazil for microalgae identification.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michelon, W., Da Silva, M.L.B., Mezzari, M.P. et al. Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus on Biochemical Composition of Microalgae Polyculture Harvested from Phycoremediation of Piggery Wastewater Digestate. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 178, 1407–1419 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1955-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1955-x