Abstract
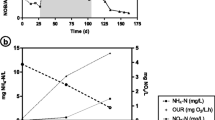
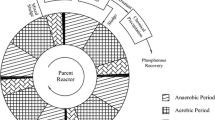
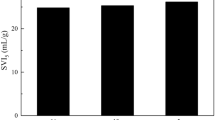
In an anaerobic/aerobic/anoxic (A/O/A) sequencing batch reactor (SBR), non-filamentous bulking sludge granulated after the adjustment of cycle duration and influent composition directed by pH, oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) and dissolved oxygen (DO). The turning points and plateaux of pH, ORP and DO profiles indicated the end of biochemical reactions, such as chemical oxygen demand (COD) consumption, P release, ammonium oxidation, P uptake and denitrification. The difference of nutrient concentration between the beginning and turning points represented the actual treatment capability of the sludge. Non-filamentous bulking with SVI30 of 255 mL g−1 resulted in a huge biomass loss. After regulation, the cycle duration was shortened from 310 to 195 min without unnecessary energy input. In addition, the settling ability was obviously improved as SVI30 reduced to 28 mL g−1. Moreover, matured granules with an average diameter of 600 μm were obtained after 45 days, and simultaneous COD, ammonium and phosphate (P) removal was also realized after granulation.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adav, S. S., Lee, D. J., Show, K. Y., & Tay, J. H. (2008). Aerobic granular sludge: recent advances. Biotechnol Advance, 26, 411–423.
Kishida, N., Kim, J., Tsuneda, S., & Sudo, R. (2006). Anaerobic/oxic/anoxic granular sludge process as an effective nutrient removal process utilizing denitrifying polyphosphate-accumulating organisms. Water Research, 40, 2303–2310.
Zhang, H. M., Dong, F., Jiang, T., Wei, Y., Wang, T., & Yang, F. L. (2011). Aerobic granulation with low strength wastewater at low aeration rate in A/O/A SBR reactor. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 49, 215–222.
Adav, S. S., Lee, D. J., & Lai, J. Y. (2009). Treating chemical industries influent using aerobic granular sludge: recent development. Journal of Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 40, 333–336.
Lee, D. J., Chen, Y. Y., Show, K. Y., Whiteley, C. G., & Tay, J. H. (2010). Advances in aerobic granule formation and granule stability in the course of storage and reactor operation. Biotechnology Advances, 28, 919–934.
Tay, J. H., Liu, Q. S., & Liu, Y. (2001). The effects of shear force on the formation, structure and metabolism of aerobic granules. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 57, 227–233.
Moy, B. Y. P., Tay, J. H., Toh, S. K., Liu, Y., & Tay, S. T. L. (2002). High organic loading influences the physical characteristics of aerobic sludge granules. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 34, 407–412.
Qin, L., Liu, Y., & Tay, J. H. (2004). Effect of settling time on aerobic granulation in sequencing batch reactor. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 21, 47–52.
Mosquera-Corral, A., De Kreuk, M., Heijnen, J., & Van Loosdrecht, M. (2005). Effects of oxygen concentration on N-removal in an aerobic granular sludge reactor. Water Research, 39, 2676–2686.
Li, Z., Kuba, T., & Kusuda, T. (2006). The influence of starvation phase on the properties and the development of aerobic granules. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 38, 670–674.
Kong, Y., Liu, Y. Q., Tay, J. H., Wong, F. S., & Zhu, J. (2009). Aerobic granulation in sequencing batch reactors with different reactor height/diameter ratios. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 45, 379–383.
Verawaty, M., Pijuan, M., Yuan, Z., & Bond, P. (2012). Determining the mechanisms for aerobic granulation from mixed seed of floccular and crushed granules in activated sludge wastewater treatment. Water Research, 46, 761–771.
Li, A. J., & Li, X. Y. (2009). Selective sludge discharge as the determining factor in SBR aerobic granulation: numerical modelling and experimental verification. Water Research, 43, 3387–3396.
Pijuan, M., Werner, U., & Yuan, Z. (2011). Reducing the startup time of aerobic granular sludge reactors through seeding floccular sludge with crushed aerobic granules. Water Research, 45, 5075–5083.
Amaral, A. L., Mesquita, D. P., & Ferreira, E. C. (2013). Automatic identification of activated sludge disturbances and assessment of operational parameters. Chemosphere, 91, 705–710.
Montoya, T., Borrás, L., Aguado, D., Ferrer, J., & Seco, A. (2008). Detection and prevention of enhanced biological phosphorus removal deterioration caused by Zoogloea overabundance. Environmental Technology, 29, 35–42.
Novak, L., Larrea, L., Wanner, J., & Garcia-Heras, J. (1993). Non-filamentous activated sludge bulking in a laboratory scale system. Water Research, 27, 1339–1346.
Novak, L., Larrea, L., Wanner, J., & Garcia-Heras, J. (1994). Non-filamentous activated sludge bulking caused by Zoogloea. Water Science and Technology, 29, 301–304.
Peng, Y., Gao, C., Wang, S., Ozaki, M., & Takigawa, A. (2003). Non-filamentous sludge bulking caused by a deficiency of nitrogen in industrial wastewater treatment. Water Science and Technology, 47, 289–295.
Chen, Y., Peng, Y. Z., Liu, M., Gan, Y. P., & Wang, S. Y. (2005). Non-filamentous activated sludge bulking in SBR treating the domestic wastewater. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 25, 105–108.
Mesquita, D. P., Amaral, A. L., & Ferreira, E. C. (2011). Identifying different types of bulking in an activated sludge system through quantitative image analysis. Chemosphere, 85, 643–652.
Jin, B., Wilen, B. M., & Lant, P. (2003). A comprehensive insight into floc characteristics and their impact on compressibility and settleability of activated sludge. Chemical Engineering Journal, 95, 221–234.
Guo, J., Peng, Y., Yang, X., Gao, C., & Wang, S. (2013). Combination process of limited filamentous bulking and nitrogen removal via nitrite for enhancing nitrogen removal and reducing aeration requirements. Chemosphere, 91, 68–75.
APHA (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed., ). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Li, X., & Yang, S. (2007). Influence of loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on the flocculation, sedimentation and dewaterability of activated sludge. Water Research, 41, 1022–1030.
Loewus, F. A. (1952). Improvement in anthrone method for determination of carbohydrates. Analytical Chemistry, 24, 219–219.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., & Randall, R. J. (1951). Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 193, 265–275.
Peng, Y. Z., Wu, C. Y., Wang, R. D., & Li, X. L. (2011). Denitrifying phosphorus removal with nitrite by a real-time step feed sequencing batch reactor. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 86, 541–546.
Wu, C., Peng, Y., Wang, S., Li, X., & Wang, R. (2011). Effect of sludge retention time on nitrite accumulation in real-time control biological nitrogen removal sequencing batch reactor. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 19, 512–517.
Yu, R. F., Liaw, S. L., Chang, C. N., Lu, H. J., & Cheng, W. Y. (1997). Monitoring and control using on-line ORP on the continuous-flow activated sludge batch reactor system. Water Science and Technology, 35, 57–66.
Chen, K. C., Chen, C. Y., Peng, J. W., & Houng, J. Y. (2002). Real-time control of an immobilized-cell reactor for wastewater treatment using ORP. Water Research, 36, 230–238.
Ra, C. S., Lo, K. V., Shin, J. S., Oh, J. S., & Hong, B. J. (2000). Biological nutrient removal with an internal organic carbon source in piggery wastewater treatment. Water Research, 34, 965–973.
Chang, C. H., & Hao, O. J. (1996). Sequencing batch reactor system for nutrient removal: ORP and pH profiles. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 67, 27–38.
Wentzel, M., Lötter, L., Loewenthal, R., & Marais, G. (1986). Metabolic behaviour of Acinetobacter spp. in enhanced biological phosphorus removal-a biochemical model. Water S A, 12, 209–224.
Zhang, C. Y., Zhang, H. M., & Yang, F. L. (2014). Optimal cultivation of simultaneous ammonium and phosphorus removal aerobic granular sludge in A/O/A sequencing batch reactor and the assessment of functional organisms. Environmental Technology, 35, 1979–1988.
Wang, Y., Guo, G., Wang, H., Stephenson, T., Guo, J., & Ye, L. (2013). Long-term impact of anaerobic reaction time on the performance and granular characteristics of granular denitrifying biological phosphorus removal systems. Water Research, 47, 5326–5337.
Yang, S. F., Tay, J. H., & Liu, Y. (2004). Inhibition of free ammonia to the formation of aerobic granules. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 17, 41–48.
Liu, Y. Q., & Tay, J. H. (2007). Characteristics and stability of aerobic granules cultivated with different starvation time. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 75, 205–210.
Bassin, J., Pronk, M., Kraan, R., Kleerebezem, R., & Van Loosdrecht, M. (2011). Ammonium adsorption in aerobic granular sludge, activated sludge and anammox granules. Water Research, 45, 5257–5265.
Bassin, J. P., Kleerebezem, R., Dezotti, M., & van Loosdrecht, M. C. M. (2012). Simultaneous nitrogen and phosphate removal in aerobic granular sludge reactors operated at different temperatures. Water Research, 46, 3805–3816.
Zeng, R., Yuan, Z., Van Loosdrecht, M. C. M., & Keller, J. (2002). Proposed modifications to metabolic model for glycogen-accumulating organisms under anaerobic conditions. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 80, 277–279.
Zeng, R. J., Lemaire, R., Yuan, Z., & Keller, J. (2003). Simultaneous nitrification, denitrification, and phosphorus removal in a lab-scale sequencing batch reactor. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 84, 170–178.
De Kreuk, M., & Van Loosdrecht, M. (2004). Selection of slow growing organisms as a means for improving aerobic granular sludge stability. Water Science and Technology, 49, 9–17.
Liu, Y., Yang, S. F., & Tay, J. H. (2004). Improved stability of aerobic granules by selecting slow-growing nitrifying bacteria. Journal of Biotechnology, 108, 161–169.
Tu, X., Song, Y., Yu, H., Zeng, P., & Liu, R. (2012). Fractionation and characterization of dissolved extracellular and intracellular products derived from floccular sludge and aerobic granules. Bioresource Technology, 123, 55–61.
Wang, Z. C., Gao, M. C., She, Z. L., Wang, S., Jin, C., Zhao, Y., Yang, S., & Guo, L. (2015). Effects of salinity on performance, extracellular polymeric substances and microbial community of an aerobic granular sequencing batch reactor. Separation and Purification Technology, 144, 223–231.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Open Project of State Key Laboratory of Urban Water Resource and Environment (Grant No. ESK201301) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Zhang, H. & Yang, F. Granulation of Non-filamentous Bulking Sludge Directed by pH, ORP and DO in an Anaerobic/Aerobic/Anoxic SBR. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 178, 184–196 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1867-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1867-9