Abstract
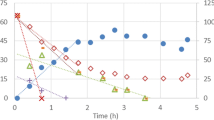
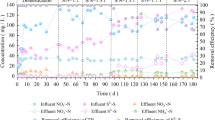
Inhibition of nitrification by sulfide was assessed using sludge obtained from a steady-state nitrifying reactor. Independent batch activity assays were performed with ammonium and nitrite as substrate, in order to discriminate the effect of sulfide on ammonium and nitrite oxidation. In the absence of sulfide, substrate affinity constants (K S,NH4 = 2.41 ± 0.11 mg N/L; K s, NO2 = 0.74 ± 0.03 mg N/L) and maximum specific rates (q max,NH4 = 0.086 ± 0.008 mg N/mg microbial protein h; q max,NO2 = 0.124 ± 0.001 mg N/mg microbial protein h) were determined. Inhibition of ammonium oxidation was no-competitive (inhibition constant (K i , NH4 ) of 2.54 ± 0.12 mg HS−-S/L) while inhibition of nitrite oxidation was mixed (competitive inhibition constant (K’ i , NO2 ) of 0.22 ± 0.03 mg HS−-S/L and no-competitive inhibition constant (K i , NO2 ) of 1.03 ± 0.06 mg HS−-S/L). Sulfide has greater inhibitory effect on nitrite oxidation than ammonium oxidation, and its presence in nitrification systems should be avoided to prevent accumulation of nitrite. By simulating the effect of sulfide addition in a continuous nitrifying reactor under steady-state operation, it was shown that the maximum sulfide concentration that the sludge can tolerate without affecting the ammonium consumption efficiency and nitrate yield is 1 mg HS−-S/L.




Similar content being viewed by others

References
Kuenen, J. G., & Robertson, L. A. (1994). Combined nitrification-denitrification processes. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 15, 109–117.
Spieck, E., Ehrich, S., Aamand, J., & Bock, E. (1998). Isolation and immunocytochemical location of the nitrite-oxidizing system in Nitrospira moscoviensis. Archives of Microbiology, 169, 225–230.
Arp, D. J., Sayavedra-Soto, L. A., & Hommes, N. G. (2002). Molecular biology and biochemistry of ammonia oxidation by Nitrosomonas europaea. Archives of Microbiology, 178, 250–255.
Bernet, N., & Spérandio, M. (2009). Principles of nitrifying processes. In F. J. Cervantes (Ed.), Environmental technologies to treat nitrogen pollution: principles of nitrifying processes (pp. 23–37). London: IWA.
Pérez-Alfaro, J. E., Buitrón, G., Gomez, J., Texier, A.-C., & Cuervo-López, F. M. (2013). Kinetic and physiological evaluation of ammonium and nitrite oxidation processes in presence of 2-chlorophenol. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 169, 990–1000.
Sears, K., Alleman, J. E., Barnard, J. L., & Oleszkiewicz, J. A. (2004). Impacts of reduced sulfur components on active and resting ammonia oxidizers. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 31, 369–378.
Singh, S. N., & Verma, A. (2007). The potential of nitrification inhibitors to manage the pollution effect of nitrogen fertilizers in agricultural and other soils: a review. Environmental Practice, 9, 266–279.
Texier, A.-C., Gómez, J., & Cuervo-López, F. M. (2013). Inhibitory, toxic and structure effects of toluene on microbial consortia involved in wastewater treatment. In M. C. Palminteri (Ed.), Toluene: chemical properties, applications and toxicology: Inhibitory, toxic and structure effects of toluene on microbial consortia involved in wastewater treatment (pp. 93–123). New York: Nova.
Nielsen, A. H., Vollertsen, J., & Hvitved-Jacobsen, T. (2006). Kinetics and stoichiometry of aerobic sulfide oxidation in wastewater from sewers-effects of pH and temperature. Water Environment Research, 78, 275–283.
Tang, K., Baskaran, V., & Nemati, M. (2009). Bacteria of the sulphur cycle: an overview of microbiology, biokinetics and their role in petroleum and mining industries. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 44, 73–94.
Zhou, Z., Xing, C., An, Y., Hu, D., Qiao, W., & Wang, L. (2014). Inhibitory effects of sulfide on nitrifying biomass in the anaerobic–anoxic–aerobic wastewater treatment process. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 89, 214–219.
Bejarano Ortiz, D. I., Thalasso, F., Cuervo López, F. M., & Texier, A.-C. (2013). Inhibitory effect of sulfide on the nitrifying respiratory process. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 88, 1344–1349.
McCarty, G. W. (1999). Modes of action of nitrification inhibitors. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 29, 1–9.
Keener, W. K., & Arp, D. J. (1993). Kinetic studies of ammonia monooxygenase inhibition in Nitrosomonas europaea by hydrocarbons and halogenated hydrocarbons in an optimized whole-cell assay. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 59, 2501–2510.
Hyman, M. R., & Wood, P. M. (1985). Suicidal inactivation and labelling of ammonia mono-oxygenase by acetylene. Biochemical Journal, 227, 719–725.
Juliette, L. Y., Hyman, M. R., & Arp, D. J. (1993). Inhibition of ammonia oxidation in Nitrosomonas europaea by sulfur compounds: thioethers are oxidized to sulfoxides by ammonia monooxygenase. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 59, 3718–3727.
Gilch, S., Meyer, O., & Schmidt, I. (2009). A soluble form of ammonia monooxygenase in Nitrosomonas europaea. Biological Chemistry, 390, 863–873.
Meincke, M., Bock, E., Kastrau, D., & Kroneck, P. M. H. (1992). Nitrite oxidoreductase from Nitrobacter hamburgensis: redox centers and their catalytic role. Archives of Microbiology, 158, 127–131.
Artiga, P., González, F., Mosquera-Corral, A., Campos, J. L., Garrido, J. M., Ficara, E., & Méndez, R. (2005). Multiple analysis reprogrammable titration analyser for the kinetic characterization of nitrifying and autotrophic denitrifying biomass. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 26, 176–183.
Park, S., & Bae, W. (2009). Modeling kinetics of ammonium oxidation and nitrite oxidation under simultaneous inhibition by free ammonia and free nitrous acid. Process Biochemistry, 44, 631–640.
Liwarska-Bizukojc, E., & Bizukojc, M. (2012). A new approach to determine the kinetic parameters for nitrifying microorganisms in the activated sludge systems. Bioresource Technology, 109, 21–25.
Silva, C. D., Gómez, J., Houbron, E., Cuervo-López, F. M., & Texier, A.-C. (2009). p-Cresol biotransformation by a nitrifying consortium. Chemosphere, 75, 1387–1391.
Segel, I. H. (1993). Enzyme kinetics: behavior and analysis of rapid equilibrium and steady-state enzyme systems, Wiley-Interscience, New Ed edition.
Bartlett, J. K., & Skoog, D. A. (1954). Colorimetric determination of elemental sulfur in hydrocarbons. Analytical Chemistry, 26, 1008–1011.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., & Randall, R. J. (1951). Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 193, 265–275.
Khin, T., Gheewala, S. H., & Annachhatre, A. P. (2002). Modeling of nitrification inhibition with aniline in suspended-growth processes. Water Environment Research, 74, 531–540.
Noophan, P., Figueroa, L. A., & Munakata-Marr, J. (2004). Nitrite oxidation inhibition by hydroxylamine: experimental and model evaluation. Water Science and Technology, 50, 295–304.
Ginestet, P., Audic, J. M., Urbain, V., & Block, J. C. (1998). Estimation of nitrifying bacterial activities by measuring oxygen uptake in the presence of the metabolic inhibitors allylthiourea and azide. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 64, 2266–2268.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported financially by the Council of Science and Technology of Mexico (CONACYT) (Grant No. SEP-CONACYT-CB-2011-01-165174). Diego I. Bejarano Ortiz received a fellowship from CONACYT (211547).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bejarano-Ortiz, D.I., Huerta-Ochoa, S., Thalasso, F. et al. Kinetic Constants for Biological Ammonium and Nitrite Oxidation Processes Under Sulfide Inhibition. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 177, 1665–1675 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1844-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1844-3