Abstract
Golgi α-mannosidase II (GMII), a key glycosyl hydrolase in the N-linked glycosylation pathway, has been demonstrated to be closely associated with the genesis and development of cancer. In this study, we cloned cDNA-encoding Capra hircus GMII (chGMII) and expressed it in Pichia pastoris expression system. The chGMII cDNA contains an open reading frame of 3432 bp encoding a polypeptide of 1144 amino acids. The deduced molecular mass and pI of chGMII was 130.5 kDa and 8.04, respectively. The gene expression profile analysis showed GMII was the highest expressed gene in the spleen. The recombinant chGMII showed maximum activity at pH 5.4 and 42 °C and was activated by Fe2+, Zn2+, Ca2+, and Mn2+ and strongly inhibited by Co2+, Cu2+, and EDTA. By homology modeling and molecular docking, we obtained the predicted 3D structure of chGMII and the probable binding modes of chGMII-GnMan5Gn, chGMII-SW. A small cavity containing Tyr355 and zinc ion fixed by residues Asp290, His176, Asp178, and His570 was identified as the active center of chGMII. These results not only provide a clue for clarifying the catalytic mechanism of chGMII but also lay a theoretical foundation for subsequent investigations in the field of anticancer therapy for mammals.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhong, W., Kuntz, D. A., Ember, B., Singh, H., Moremen, K. W., Rose, D. R., & Boons, G. J. (2008). Probing the substrate specificity of Golgi alpha-mannosidase II by use of synthetic oligosaccharides and a catalytic nucleophile mutant. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 130, 8975–8983.
Feizi, T. (1985). Demonstration by monoclonal antibodies that carbohydrate structures of glycoproteins and glycolipids are onco-developmental antigens. Nature, 314, 53–57.
M. Misago, Y. F. Liao, S. Kudo, S. Eto, M. G. Mattei, K. W. Moremen & M. N. Fukuda (1995). Molecular cloning and expression of cDNAs encoding human alpha-mannosidase II and a previously unrecognized alpha-mannosidase IIx isozyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A, 92, 11766–11770.
van den Elsen, J. M., Kuntz, D. A., & Rose, D. R. (2001). Structure of Golgi alpha-mannosidase II: a target for inhibition of growth and metastasis of cancer cells. The EMBO Journal, 20, 3008–3017.
Dennis, J. W., & Laferte, S. (1985). Recognition of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides on murine tumor cells by natural killer cells. Cancer Research, 45, 6034–6040.
Kiyohara, T., Dennis, J. W., & Roder, J. C. (1987). Double restriction in NK cell recognition is linked to transmethylation and can be triggered by asparagine-linked oligosaccharides on tumor cells. Cellular Immunology, 106, 223–233.
Rose, D. R. (2012). Structure, mechanism and inhibition of Golgi alpha-mannosidase II. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 22, 558–562.
Thompson, A. J., Williams, R. J., Hakki, Z., Alonzi, D. S., Wennekes, T., Gloster, T. M., Songsrirote, K., Thomas-Oates, J. E., Wrodnigg, T. M., Spreitz, J., Stutz, A. E., Butters, T. D., Williams, S. J., & Davies, G. J. (2012). Structural and mechanistic insight into N-glycan processing by endo-alpha-mannosidase. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109, 781–786.
Polakova, M., Sestak, S., Lattova, E., Petrus, L., Mucha, J., Tvaroska, I., & Kona, J. (2011). Alpha-D-mannose derivatives as models designed for selective inhibition of Golgi alpha-mannosidase II. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 46, 944–952.
Kuntz, D. A., Nakayama, S., Shea, K., Hori, H., Uto, Y., Nagasawa, H., & Rose, D. R. (2010). Structural investigation of the binding of 5-substituted swainsonine analogues to Golgi alpha-mannosidase II. Chembiochem, 11, 673–680.
Kumar, N. S., Kuntz, D. A., Wen, X., Pinto, B. M., & Rose, D. R. (2008). Binding of sulfonium-ion analogues of di-epi-swainsonine and 8-epi-lentiginosine to Drosophila Golgi alpha-mannosidase II: the role of water in inhibitor binding. Proteins, 71, 1484–1496.
Moremen, K. W. (1989). Isolation of a rat liver Golgi mannosidase II clone by mixed oligonucleotide-primed amplification of cDNA. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 86, 5276–5280.
Moremen, K. W., & Robbins, P. W. (1991). Isolation, characterization, and expression of cDNAs encoding murine alpha-mannosidase II, a Golgi enzyme that controls conversion of high mannose to complex N-glycans. The Journal of Cell Biology, 115, 1521–1534.
Misago, M., Liao, Y. F., Kudo, S., Eto, S., Mattei, M. G., Moremen, K. W., & Fukuda, M. N. (1995). Molecular cloning and expression of cDNAs encoding human alpha-mannosidase II and a previously unrecognized alpha-mannosidase IIx isozyme. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 92, 11766–11770.
Strasser, R., Schoberer, J., Jin, C., Glossl, J., Mach, L., & Steinkellner, H. (2006). Molecular cloning and characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana Golgi alpha-mannosidase II, a key enzyme in the formation of complex N-glycans in plants. The Plant Journal, 45, 789–803.
Foster, J. M., Yudkin, B., Lockyer, A. E., & Roberts, D. B. (1995). Cloning and sequence analysis of GmII, a Drosophila melanogaster homologue of the cDNA encoding murine Golgi alpha-mannosidase II. Gene, 154, 183–186.
Jarvis, D. L., Bohlmeyer, D. A., Liao, Y. F., Lomax, K. K., Merkle, R. K., Weinkauf, C., & Moremen, K. W. (1997). Isolation and characterization of a class II alpha-mannosidase cDNA from lepidopteran insect cells. Glycobiology, 7, 113–127.
Paschinger, K., Hackl, M., Gutternigg, M., Kretschmer-Lubich, D., Stemmer, U., Jantsch, V., Lochnit, G., & Wilson, I. B. (2006). A deletion in the golgi alpha-mannosidase II gene of Caenorhabditis elegans results in unexpected non-wild-type N-glycan structures. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281, 28265–28277.
Rabouille, C., Kuntz, D. A., Lockyer, A., Watson, R., Signorelli, T., Rose, D. R., van den Heuvel, M., & Roberts, D. B. (1999). The Drosophila GMII gene encodes a Golgi alpha-mannosidase II. Journal of Cell Science, 112(Pt 19), 3319–3330.
Qiu, X., Li, D., Cui, J., Liu, Y., & Wang, X. (2014). Molecular cloning, characterization and expression analysis of melanotransferrin from the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Molecular Biology Reports, 41, 3781–3791.
Feng, X., Yu, X., Pang, M., Liu, H., & Tong, J. (2015). Molecular characterization and expression of three preprosomatostatin genes and their association with growth in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. Part B, Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, 182, 37–46.
Fazel, R., Zarei, N., Ghaemi, N., Namvaran, M. M., Enayati, S., Mirabzadeh Ardakani, E., Azizi, M., & Khalaj, V. (2014). Cloning and expression of Aspergillus flavus urate oxidase in Pichia pastoris. Springerplus, 3, 395.
Hossain, M. A., Nakano, R., Nakamura, K., Hossain, M. T., & Kimura, Y. (2010). Molecular characterization of plant acidic alpha-mannosidase, a member of glycosylhydrolase family 38, involved in the turnover of N-glycans during tomato fruit ripening. Journal of Biochemistry, 148, 603–616.
Joshi, S., & Satyanarayana, T. (2014). Optimization of heterologous expression of the phytase (PPHY) of Pichia anomala in P. pastoris and its applicability in fractionating allergenic glycinin from soy protein. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 41, 977–987.
Xiangya, K., Jiangye, Z., Ying, W., Jianfei, L., & Qinfan, L. (2014). Molecular characterization of Capra hircus lysosomal alpha-mannosidase and potential mutant site for the therapy of locoweed poisoning. Acta Biochimica Polonica, 61, 77–84.
Kiefer, F., Arnold, K., Kunzli, M., Bordoli, L., & Schwede, T. (2009). The SWISS-MODEL repository and associated resources. Nucleic Acids Research, 37, D387–D392.
Trott, O., & Olson, A. J. (2010). AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 31, 455–461.
Altmann, F., & Marz, L. (1995). Processing of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides in insect cells: evidence for alpha-mannosidase II. Glycoconjugate Journal, 12, 150–155.
Kaushal, G. P., Szumilo, T., Pastuszak, I., & Elbein, A. D. (1990). Purification to homogeneity and properties of mannosidase II from mung bean seedlings. Biochemistry, 29, 2168–2176.
Ren, J., Castellino, F. J., & Bretthauer, R. K. (1997). Purification and properties of alpha-mannosidase II from Golgi-like membranes of baculovirus-infected Spodoptera frugiperda (IPLB-SF-21AE) cells. The Biochemical Journal, 324(Pt 3), 951–956.
Shah, N., Kuntz, D. A., & Rose, D. R. (2008). Golgi alpha-mannosidase II cleaves two sugars sequentially in the same catalytic site. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105, 9570–9575.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Shaanxi Province Program for Science and Technology Research Development Plan (2014k01-17-02) of China and the central university basic scientific research operation cost special fund subsidizes (ZD2012009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplemental Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
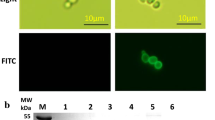
Intracellular and extracellular expression of chGMII. Lanes M, protein standard; 1–6, intracellular expression of chGMII in different pH; 7 and 14, intracellular and extracellular expression of negative control; 8–13, extracellular expression products in different pH. (GIF 1.95 mb)
ESM 2
Raw real-time PCR data of Fig. 1a (XLS 115 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Zhang, J., Lai, B. et al. Cloning, Expression, and Characterization of Capra hircus Golgi α-Mannosidase II. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 177, 1241–1251 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1810-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1810-0