Abstract
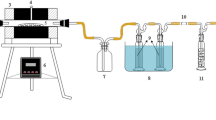
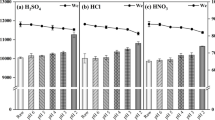
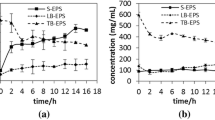
Waste-activated sludge (WAS) solubilized remarkably after enzymatic-enhanced anaerobic digestion, but its dewaterability was deteriorated. In this study, a novel method was performed to improve the dewaterability of enzymatic-enhanced anaerobic digestion sludge by adding CaCl2 (0.01~1.00 g/g total sludge). The capillary suction time (CST), moisture content, and filtrate turbidity were employed to characterize the dewaterability of WAS, and the possible mechanisms involved were clarified. The results showed the dewaterability did not worsen when CaCl2 was added before sludge digestion, and the CST, moisture content, and filtrate turbidity were notably reduced with the increase of CaCl2 dosage. It also shown that calcium ions played an important role in the bioflocculation of digested sludge by neutralizing negative charges on the surface of sludge. In addition, soluble protein initially lowered a little and then observably improved with the addition of CaCl2, while soluble carbohydrate was reduced sharply first and then bounced back afterwards. The interactions between calcium ions and the biopolymer further enhanced the dewatering of sludge through bridging of colloidal particles together.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouskova, A., Dohanyos, M., Schmidt, J. E., & Angelidaki, I. (2005). Strategies for changing temperature from mesophilic to thermophilic conditions in anaerobic CSTR reactors treating sewage sludge. Water Research, 39, 1481–1488.
Romano, R. T., Zhang, R. H., Teter, S., & McGarvey, J. A. (2009). The effect of enzyme addition on anaerobic digestion of Jose tall wheat grass. Bioresource Technology, 100, 4564–4571.
Phothilangka, P., Schoen, M. A., Huber, M., Luchetta, P., Winkler, T., & Wett, B. (2008). Prediction of thermal hydrolysis pretreatment on anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Water Science and Technology, 58, 1467–1473.
Tanaka, S., & Kamiyama, K. (2002). Thermochemical pretreatment in the anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Water Science and Technology, 46, 173–179.
Kang, X. R., Zhang, G. M., Chen, L., Dong, W. Y., & Tian, W. D. (2011). Effect of initial pH adjustment on hydrolysis and acidification of sludge by ultrasonic pretreatment. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 50, 12372–12378.
Yang, Q., Luo, K., Li, X. M., Wang, D. B., Zheng, W., Zeng, G. M., & Liu, J. J. (2010). Enhanced efficiency of biological excess sludge hydrolysis under anaerobic digestion by additional enzymes. Bioresource Technology, 101, 2924–2930.
Luo, K., Yang, Q., Yu, J., Li, X. M., Yang, G. J., Xie, B. X., Yang, F., Zheng, W., & Zeng, G. M. (2011). Combined effect of sodium dodecyl sulfate and enzyme on waste activated sludge hydrolysis and acidification. Bioresource Technology, 102, 7103–7110.
Cheng, J., Wang, L., Ji, Y., Zhu, N., & Kong, F. (2014). The influence of factors on dewaterability of one-stage autothermal thermophilic aerobically digested sludges. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 30, 639–647.
Houghton, J. I., Quarmby, J., & Stephenson, T. (2000). The impact of digestion on sludge dewaterability. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 78, 153–159.
Shao, L., He, P., Yu, G., & He, P. (2009). Effect of proteins, polysaccharides, and particle sizes on sludge dewaterability. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 21, 83–88.
Dursun, D., & Dentel, S. K. (2009). Toward the conceptual and quantitative understanding of biosolids conditioning: the gel approach. Water Science and Technology, 59, 1679–1685.
Tony, M. A., Zhao, Y. Q., Fu, J. F., & Tayeb, A. M. (2008). Conditioning of aluminium-based water treatment sludge with Fenton’s reagent: effectiveness and optimizing study to improve dewaterability. Chemosphere, 72, 673–677.
Wojciechowska, E. (2005). Application of microwaves for sewage sludge conditioning. Water Research, 39, 4749–4754.
Feng, X., Deng, J. C., Lei, H. Y., Bai, T., Fan, Q. J., & Li, Z. X. (2009). Dewaterability of waste activated sludge with ultrasound conditioning. Bioresource Technology, 100, 1074–1081.
Yuan, H. P., Zhu, N. W., & Song, F. (2011). Dewaterability characteristics of sludge conditioned with surfactants pretreatment by electrolysis. Bioresource Technology, 102, 2308–2315.
Raynaud, M., Vaxelaire, J., Olivier, J., Dieudé-Fauvel, E., & Baudez, J. C. (2012). Compression dewatering of municipal activated sludge: effects of salt and pH. Water Research, 46, 4448–4456.
Sobeck, D. C., & Higgins, M. J. (2002). Examination of three theories for mechanisms of cation-induced bioflocculation. Water Research, 36, 527–538.
Pevere, A., Guibaud, G., van Hullebusch, E. D., Boughzala, W., & Lens, P. N. L. (2007). Effect of Na+ and Ca2+ on the aggregation properties of sieved anaerobic granular sludge. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 306, 142–149.
Guan, B. H., Yu, J., Fu, H. L., Guo, M. H., & Xu, X. H. (2012). Improvement of activated sludge dewaterability by mild thermal treatment in CaCl2 solution. Water Research, 46, 425–432.
Bruus, J. H., Nielsen, P. H., & Keiding, K. (1992). On the stability of activated sludge flocs with implications to dewatering. Water Research, 26, 1597–1604.
Zhou, J., Donald, S. M., Harlan, G. K., & William, D. R. (2002). Effects of temperatures and extracellular proteins on dewaterability of thermophilically digested biosolids. Journal of Environmental Engineering and Science, 1, 6.
Li, X. Y., & Yang, S. F. (2007). Influence of loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on the flocculation, sedimentation and dewaterability of activated sludge. Water Research, 41, 1022–1030.
Bougrier, C., Delgenes, J. P., & Carrere, H. (2008). Effects of thermal treatments on five different waste activated sludge samples solubilisation, physical properties and anaerobic digestion. Chemical Engineering Journal, 139, 236–244.
Neyens, E., Baeyens, J., Dewil, R., & De heyder, B. (2004). Advanced sludge treatment affects extracellular polymeric substances to improve activated sludge dewatering. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 106, 83–92.
Yu, G. H., He, P. J., & Shao, L. M. (2010). Novel insights into sludge dewaterability by fluorescence excitation-emission matrix combined with parallel factor analysis. Water Research, 44, 797–806.
Novak, J. T., Agerbæk, M. L., Sørensen, B. L., & Hansen, J. A. (1999). Conditioning, filtering, and expressing waste activated sludge. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 125, 816–824.
Scholz, M. (2005). Review of recent trends in capillary suction time (CST) dewaterability testing research. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 44, 8157–8163.
Peng, G., Ye, F., & Li, Y. (2011). Comparative investigation of parameters for determining the dewaterability of activated sludge. Water Environment Research, 83, 667–671.
Teo, K. C., Xu, H. L., & Tay, J. H. (2000). Molecular mechanism of granulation. II: proton translocating activity. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 126, 411–418.
Mikkelsen, L. H., & Keidinkg, K. (2002). Physico-chemical characteristics of full scale sewage sludges with implications to dewatering. Water Research, 36, 2451–2462.
Liu, J. Y., Zhao, G. F., Duan, C., Xu, Y. F., Zhao, J., Deng, T., & Qian, G. R. (2011). Effective improvement of activated sludge dewaterability conditioning with seawater and brine. Chemical Engineering Journal, 168, 1112–1119.
Mikkelsen, L. H. (2003). Applications and limitations of the colloid titration method for measuring activated sludge surface charges. Water Research, 37, 2458–2466.
Kara, F., Gurakan, G. C., & Sanin, F. D. (2008). Monovalent cations and their influence on activated sludge floc chemistry, structure, and physical characteristics. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 100, 231–239.
Chu, C. P., & Lee, D. J. (2001). Experimental analysis of centrifugal dewatering process of polyelectrolyte flocculated waste activated sludge. Water Research, 35, 2377–2384.
Ye, F. X., Ye, Y. F., & Li, Y. (2011). Effect of C/N ratio on extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) and physicochemical properties of activated sludge flocs. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 188, 37–43.
Dey ES, Szewczyk E, Wawrzynczyk J, Norrlow O (2006) A novel approach for characterization of exopolymeric material in sewage sludge. Journal of Residuals Science and Technology 3:97-103
Yu, J., Guo, M. H., Xu, X. H., & Guan, B. H. (2014). The role of temperature and CaCl2 in activated sludge dewatering under hydrothermal treatment. Water Research, 50, 10–17.
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by a project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51308076), the Science and Technology Project of Hunan Province (No. 2014FJ3063), and the Key Laboratory of Renewable Energy Electric-Technology of Hunan Province (No. 2012ZNDL007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, K., Yang, Q., Li, Xm. et al. Effect of Calcium Ions on Dewaterability of Enzymatic-Enhanced Anaerobic Digestion Sludge. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 176, 2346–2357 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1722-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1722-z