Abstract
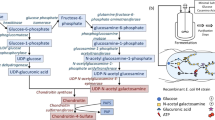
Bioengineered heparin is being investigated as a potential substitute for the animal-sourced anticoagulant drug. One step in the current process to prepare bioengineered heparin involves the conversion of N-sulfo heparosan, rich in → 4)GlcNS(1 → 4) GlcA(1 → sequences (where S is sulfo, GlcN is α-d-glucosamine, and GlcA is β-d-glucuronic acid), to a critical intermediate, rich in → 4)GlcNS(1 → 4) IdoA2S(1 → sequences (where S is sulfo and IdoA is α-l-iduronic acid), using 2-O-sulfotransferase (2-OST) and C5 epimerase (C5-epi). Until now, these heparan sulfate biosynthetic enzymes have been expressed in Escherichia coli grown in shake flask culture as fusion proteins. The current study is focused on the high cell density fed-batch cultivation of recombinant E. coli strains expressing both enzymes. We report the high productivity expression of active 2-OST and C5-epi enzymes of 6.0 and 2.2 mg/g dry cell weight, respectively.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Linhardt, R. J. (2003). Heparin: structure and activity. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 46, 2551–2554.
Liu, H., Zhang, Z., & Linhardt, R. J. (2009). Lessons learned from the contamination of heparin. Natural Product Reports, 26, 313–321.
Wang, Z., Yang, B., Zhang, Z., Ly, M., Takieddin, M., Mousa, S., Liu, J., Dordick, J. S., & Linhardt, R. J. (2011). Control of the heparosan N-deacetylation leads to an improved bioengineered heparin. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 91, 91–99.
Wang, Z., Ly, M., Zhang, F., Zhong, W., Suen, A., Dordick, J. S., & Linhardt, R. J. (2010). E. coli K5 fermentation and the preparation of heparosan, a bioengineered heparin precursor. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 107, 964–973.
Burkart, M. D., Izumi, M., Chapman, E., Lin, C., & Wong, C. (2000). Regeneration of PAPS for enzymatic synthesis of sulfated oligosaccharides. Journal of Organic Chemistry, 65, 5565–5574.
Paul, P., Liu, J., Dordick, J. S., & Linhardt, R. J. (2012). Recent advances in sulfotransferase enzyme activity assays. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 403, 1491–1500.
Sterner, E., Li, L., Paul, P., Beaudet, J. M., Liu, J., Linhardt, R. J., & Dordick, J. S. (2014). Assays for determining heparan sulfate and heparin O-sulfotransferase activity and specificity. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 406, 525–536.
Chen, J., Avci, F. Y., Muñoz, E. M., McDowell, L. M., Chen, M., Pedersen, L. C., Zhang, L., Linhardt, R. J., & Liu, J. (2005). Enzymatic redesigning of biologically active heparan sulfate. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 42817–42825.
Munoz, E., Xu, D., Avci, F., Kemp, M., Liu, J., & Linhardt, R. J. (2006). Enzymatic synthesis of heparin related polysaccharides on sensor chips: rapid screening of heparin–protein interactions. Biochemical Biophysical Research Communications, 339, 597–602.
Matsui, T., Sato, H., Yamamuro, H., Shinzato, N., Matsuda, H., Misawa, S., & Sato, S. (2008). High cell density cultivation of recombinant E. coli for hirudin variant 1 production by temperature shift controlled by pUC18-based replicative origin. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 80, 779–783.
Li, K., Bethea, H. N., & Liu, J. (2010). Using engineered 2-O-sulfotransferase to determine the activity of heparan sulfate C5-epimerase and its mutants. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 285, 11106–11113.
Yang, B., Weyers, A., Baik, J. Y., Sterner, E., Sharfstein, S., Mousa, S. A., Zhang, F., Dordick, J. S., & Linhardt, R. J. (2011). Ultra-performance ion-pairing liquid chromatography with on-line electrospray ion trap mass spectrometry for heparin disaccharide analysis. Analytical Biochemistry, 415, 59–66.
Restaino, O. F., Bhaskar, U., Paul, P., Li, L., De Rosa, M., Dordick, J. S., & Linhardt, R. J. (2013). High cell density cultivation of a recombinant E. coli strain expressing a key enzyme in bioengineered heparin production. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 97, 3893–3900.
Nakano, K., Rischke, M., Sato, S., & Maèrkl, H. (1997). Influence of acetic acid on the growth of Escherichia coli K12 during high-cell-density cultivation in a dialysis reactor. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 48, 597–601.
Yoon, S. K., Kang, W. K., & Park, T. H. (1994). Fed-batch operation of recombinant Escherichia coli containing trp promoter with controlled specific growth rate. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 43, 995–999.
Konstantinov, K., Kishimoto, M., Seki, T., & Yoshida, T. (1990). A balanced DO-stat and its application to the control of acetic acid excretion by recombinant Escherichia coli. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 36, 750–758.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge funding from the NIH in the form of grant HL096972, from the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 31171737 and the PRC grant 210208310507 supporting the visit of Jianhua Zhang, and from the Bioengineered Heparin Consortium.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Suflita, M., Li, G. et al. High Cell Density Cultivation of Recombinant Escherichia coli Strains Expressing 2-O-Sulfotransferase and C5-Epimerase for the Production of Bioengineered Heparin. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175, 2986–2995 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1466-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1466-1