Abstract
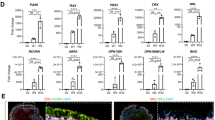
The purpose of this study was to evaluate retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells’ behavior in alginate beads that establish 3D environment for cellular growth and mimic extracellular matrix versus the conventional 2D monolayer culture. RPE cells were encapsulated in alginate beads by dripping alginate cell suspension into CaCl2 solution. Beads were suspended in three different media including Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM)/F12 alone, DMEM/F12 supplemented with 10 % fetal bovine serum (FBS), and DMEM/F12 supplemented with 30 % human amniotic fluid (HAF). RPE cells were cultivated on polystyrene under the same conditions as controls. Cell phenotype, cell proliferation, cell death, and MTT assay, immunocytochemistry, and real-time RT-PCR were performed to evaluate the effect of alginate on RPE cells characteristics and integrity. RPE cells can survive and proliferate in alginate matrixes. Immunocytochemistry analysis exhibited Nestin, RPE65, and cytokeratin expressions in a reasonable number of cultured cells in alginate beads. Real-time PCR data demonstrated high levels of Nestin, CHX10, RPE65, and tyrosinase gene expressions in RPE cells immobilized in alginate when compared to 2D monolayer culture systems. The results suggest that alginate can be used as a reliable scaffold for maintenance of RPE cells’ integrity and in vitro propagation of human retinal progenitor cells for cell replacement therapies in retinal diseases.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Strauss, O. (2005). Physiological Reviews, 85, 845–881.
Martínez- Morales, J. R., Rodrigo, I., & Bovolenta, P. (2004). Bioessays, 26, 766–777.
Davidson, A. E., Millar, I. D., Urquhart, J. E., Burgess-Mullan, R., Shweikh, Y., Parry, N. O., Sullivan, J., Maher, G. J., McKibbin, M., Downes, S. M., Lotery, A. J., Jacobson, S. G., Brown, P. D., Black, G. C., & Manson, F. D. (2009). The American Journal of Human Genetics, 85, 581–592.
Liang, F. Q., & Godley, B. F. (2003). Experimental Eye Research, 76, 397–403.
Sanie-Jahromi, F., Ahmadieh, H., Soheili, Z. S., Davari, M., Ghaderi, S., Kanavi, M. R., Samiei, S., Deezagi, A., Pakravesh, J., & Bagheri, A. (2012). BMC Research Notes, 5, 182.
Lamba, D., Karl, M., & Reh, T. (2008). Cell Stem Cell, 2, 538–549.
Binder, S., Stanzel, B. V., Krebs, I., & Glittenberg, C. (2007). Progress in Retinal and Eye Research, 26, 516–554.
Radtke, N. D., Seiler, M. J., Aramant, R. B., Petry, H. M., & Pidwell, D. J. (2002). American Journal of Ophthalmology, 133, 544–550.
Baker, P. S., & Brown, G. C. (2009). Current Opinion in Ophthalmology, 20, 175–181.
Idelson, M., & Reubinoff, B. (2012). Stem Cells and Cancer Stem Cells, 6, 87–99.
Idelson, M., Alper, R., Obolensky, A., Ben-Shushan, E., Hemo, I., Yachimovich-Cohen, N., Khaner, H., Smith, Y., Wiser, O., Gropp, M., Cohen, M. A., Even-Ram, S., Berman-Zaken, Y., Matzrafi, L., Rechavi, G., Banin, E., & Reubinoff, B. (2009). Cell Stem Cell, 5, 396–408.
Ahmad, I. (2001). Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 42, 2743–2748.
Fodor, W. L. (2003). Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology, 1, 102.
Ito, A., Hibino, E., Kobayashi, C., Terasaki, H., Kagami, H., Ueda, M., Kobayashi, T., & Honda, H. (2005). Tissue Engineering, 11, 489–496.
Drury, J. L., & Mooney, D. J. (2003). Biomaterials, 24, 4337–4351.
Tabata, Y. (2009). Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 6, S311–S324.
Dawson, E., Mapili, G., Erickson, K., Taqvi, S., & Roy, K. (2008). Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 60, 215–228.
Ghidoni, I., Chlapanidas, T., Bucco, M., Crovato, F., Marazzi, M., Vigo, D., Torre, M. L., & Faustini, M. (2008). Cytotechnology, 58, 49–56.
Rinaudo, M. (2007). Polymer International, 57, 397–430.
Kuo, C. K., & Ma, P. X. (2007). Biomaterials, 22, 511–521.
Lamba, D. A., Gust, J., & Reh, T. A. (2009). Cell Stem Cell, 4, 73–79.
Hirami, Y., Kada, F., Takahashi, K., Okita, K., Yamanaka, S., Ikeda, H., Yoshimura, N., & Takahashi, M. (2009). Neuroscience Letters, 458, 126–131.
Akrami, H., Soheili, Z. S., Khalooghi, K., Ahmadieh, H., Rezaie-Kanavi, M., Samiei, S., Davari, M., Ghaderi, S., & Sanie-Jahromi, F. (2009). Journal of Ophthalmic and Vision Research, 4, 134–141.
Amemiya, K., Haruta, M., Takahashi, M., Kosaka, M., & Eguchi, G. (2004). Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 316, 1–5.
Engelhardt, M., Bogdahn, U., & Aigner, L. (2005). Brain Research, 1040, 98–111.
Liang, L., Yan, R. T., Ma, W., Zhang, H., & Wang, S. Z. (2006). Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 47, 5066–5074.
Park, S. J., Yoon, W. G., Song, J. S., Jung, H. S., Kim, C. J., Oh, S. Y., Yoon, B. H., Jung, G., Kim, H. J., & Nirasawa, T. (2005). Proteomics, 6, 349–363.
Cho, C. K., Shan, S. J., Winsor, E. J., & Diamandis, E. P. (2007). Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 6, 1406–1415.
Ghaderi, S., Soheili, Z. S., Ahmadieh, H., Davari, M., Jahromi, F. S., Samie, S., Rezaie-Kanavi, M., Pakravesh, J., & Deezagi, A. (2011). Stem Cells and Development, 20, 1615–1625.
Justice, B. A., Badr, N. A., & Felder, R. A. (2009). Drug Discovery Today, 14, 102–107.
Azuma, N., Tadokoro, K., Asaka, A., Yamada, M., Yamaguchi, Y., Handa, H., Matsushima, S., Watanabe, T., Kida, Y., Ogura, T., Torii, M., Shimamura, K., & Nakafuku, M. (2005). Human Molecular Genetics, 14, 1059–1068.
Hsieh, Y. W., & Yang, X. J. (2009). Neural Development, 4, 1–19.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heidari, R., Soheili, ZS., Samiei, S. et al. Alginate as a Cell Culture Substrate for Growth and Differentiation of Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175, 2399–2412 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1431-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1431-z