Abstract
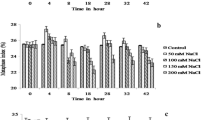
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and malondialdehyde (MDA) in plant cell are thought to be important inducible factors of cell apoptosis if excessively accumulated in cells. To elucidate the metabolic mechanism of MDA production and scavenging in the cytoplasmic male-sterile (CMS) rice, CMS line and maintainer were employed for studying the relationship at different developmental stages by marking upmost pulvinus interval method of experiment. The results showed that the panicles and leaves of the CMS line had a noticeable higher MDA content than those of maintainer line at all five stages that had been investigated (p < 0.05). MDA content in the CMS line in the flag leaves of auricle in the distance 0 mm stage (the meiosis stage) was the highest of the five stages. The increase of MDA contents in sterile panicles and leaves had inducible effects on the enzymic activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and peroxidase (POD). However, at the abortion peak stage, MDA was excessively accumulated and antioxidant enzymic activity reduced significantly, resulting in the generation and scavenging of MDA out of balance.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Linke, & Bomer, J. (2005). Mitochondrion, 5, 389–402.
Foyer, C. H., & Noctor, G. (2000). New Phytologist, 146, 359–388.
Esposito, L. A., Melov, S., Panov, A., Cottrell, B. A., & Wallace, D. C. (1999). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 96, 4820–4825.
Rudneva, I. I. (1999). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. C, 112, 265–271.
Arora, A., Sairam, R. K., & Srivastava, G. C. (2002). Current Science Association, 82(10), 1227–1238.
Chen, X. F., & Liang, C. Y. (1991). Acta Phytophysiological Sinica, 17, 44–48.
Li, S. Q., Wan, C. X., Kong, J., Zhang, Z. J., Li, Y. S., & Zhu, Y. G. (2004). Functional Plant Biology, 31, 369–376.
Kerim, T., Imin, N., Weinman, J. J., & Barry, G. (2003). Proteomics, 3, 738–751.
Hodges, D. M., Delong, J. M., Forney, C. F., & Prange, R. K. (1999). Planta, 207, 604–611.
Wang, A. G., Luo, G. H., Shao, C. B., & Guo, J. Y. (1983). Acta Phytophysiological Sinica, 9, 77–84.
Kochba, J., Lave, E. S., & Spiegel-Roy, P. (1977). Plant and Cell Physiology, 18, 463–467.
Jiang, Jin, Wu, Tao, F. (1982). Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai. pp. 36–38.
Touzet, P., & Budar, F. (2004). Trends in Plant Science, 9, 568–570.
Jiang, P., Zhang, X., Zhu, Y., Zhu, W., Xie, H., & Wang, X. (2007). Plant Cell Reports, 26, 1627–1634.
Deng, M. H., Wen, J. F., Zou, X. X., He, C. Z., Liu, Z. M., & Zhou, Q. C. (2009). Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University, 24(1), 22–25.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 10505018) and the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province of the People’s Republic of China (No. 091100110401).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Dai, X., Li, L. et al. Metabolism of Reactive Oxygen Species in Cytoplasmic Male Sterility of Rice by Marking Upmost Pulvinus Interval. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175, 1263–1269 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1346-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1346-8