Abstract
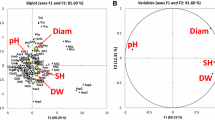
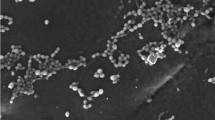
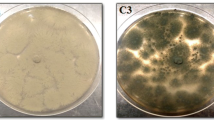
Soil is a sink of pesticide residues as well as microorganisms. Fungi are well known for solubilization of inorganic phosphates, and this activity of fungal isolates may be affected by the presence of pesticide residues in the soil. In the present study, five generically different fungal isolates, viz. Aspergillus niger JQ660373, Aspergillus flavus, Penicillium aculeatum JQ660374, Fusarium pallidoroseum and Macrophomina sp., were tested and compared for their phosphate-solubilizing ability in the absence and presence of monocrotophos (500 mg L−1). After 168 h of incubation, four times high amount of tricalcium phosphate was solubilized by isolates in the growth medium containing monocrotophos in comparison to control (without monocrotophos). Concurrently, 78 % of the applied monocrotophos was degraded by these fungal isolates. Kinetics of phosphate solubilization shifted from logarithmic to power model in the presence of monocrotophos. Similarly, the phosphatase activity was also found significantly high in the presence of monocrotophos. The combined order of phosphate solubilization as well as monocrotophos degradation was found to be A. niger JQ660373 > P. aculeatum JQ660374 > A. flavus > F. pallidoroseum > Macrophomina sp. On the contrary, phosphate solubilization negatively correlated with the pH of the growth medium. Hence, it could be concluded that these fungal species efficiently solubilize inorganic phosphates and monocrotophos poses a positive effect on their ability and in turn degraded by them. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report on P solubilization by Macrophomina sp. and F. pallidoroseum.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pandey, S., & Singh, D. K. (2004). Chemistry, 55(2), 197–205.
Bakalivanov, D. (1990). Pochvoznanie-i-Agrokhimiya, 25(5), 56–61.
Cernakova, M. (1993). Folia, 38(4), 331–334.
Binner, R., Berendes, K. H., Felgentreu, D., Friesland, H., & Glitschka, M. (1999). Nachrichtenblatt-des-Deutschen-Pflanzenschutzdienstes, 51(9), 227–237.
Das, A. C., & Mukherjee, D. (1998). World Journal of Microbiology, 14(6), 903–906.
Dordevic, S., Sestovic, M., Raicevic, V., & Dordevic, A. (1998). Pesticide, 13(4), 281–288.
Lee, P. W., Fukuto, J. M., Hernandez, H., & Stearns, S. M. (1990). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 38, 567–573.
Kucey, R. M. N. (1988). Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 68, 261–270.
Goldstein, A. H., & Liu, S. T. (1987). Bioresource Technology, 5, 72–74.
Goldstein, A. H., Rogers, R. D., & Mead, G. (1993). Bioresource Technology, 11, 1250–1254.
Halder, A. K., Mishra, A. K., & Chakarbarthy, P. K. (1991). Indian Journal of Experimental Biology, 29, 28–31.
Abd-Alla, M. H. (1994). Letters in Applied Microbiology, 18, 294–296.
Whitelaw, M. A. (2000). Advances in Agronomy, 69, 99–151.
Minaxi, & Saxena, J. (2010). BioControl, 55(6), 799–810.
Banik, S. (1983). Zentralblatt für Mikrobiologie, 138, 209–216.
Berthelin, F., Leyval, C., Laheurte, F., & De-Giudici, P. (1991). Special publication series of the British Ecological Society, No. 10. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific.
Rodriguez, H., & Fraga, R. (1999). Biotechnol Adv, 17, 319–339.
Barroso, C. V., Pereira, G. T., & Nahas, E. (2006). Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 37, 434–438.
Son, H. J., Park, G. T., Cha, M. S., & Heo, M. S. (2006). Bioresource Technology, 97, 204–210.
Rangaswamy, V., & Venkateswarlu, K. (1992). Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 49(6), 797–804.
Edi-Premono, M., Moawad, A. M., & Vlek, P. L. G. (1996). Indonesian Journal of Agricultural Science, 11, 13–23.
Murphy, J., & Riley, J. P. (1962). Analytica Chimica Acta, 27, 31–36.
Tham, S.-J., Chang, C.-D., Huang, H. J., & Lee, Y.-F. (2010). Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 74(4), 727–735.
Panhwar, Q. A., Radziah, O., Sariah, M., & Ismail, M. R. (2009). International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 6, 667–673.
Janghel, E. K., Rai, J. K., Rai, M. K., & Gupta, V. K. (2006). Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society, 53, 343–347.
Doyle, J. J., & Doyle, J. L. (1987). Phytochemical Bulletin, 19, 11–15.
Gomashe, V. A., Sabina, S. S., & Dharmik, G. P. (2012). International Journal of Science Innovations and Discovery, 2(2), 310–315.
Pradhan, N., & Sukla, L. B. (2005). African Journal of Biotechnology, 5(10), 850–854.
Sanjotha, P., Mahantesh, P., & Patil, C. S. (2011). International Journal of Microbiology Research, 3(1), 56–58.
Bhadbhade, B. J., Sarnaik, S. S., & Kanekar, P. P. (2002). Journal of Applied Microbiology, 93, 224–234.
Bhalerao, S. T., & Puranik, R. P. (2009). International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 63, 503–508.
Cunningham, J. E., & Kuiack, C. (1992). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 58(5), 1451–1458.
Dutton, V. M., & Evans, C. S. (1996). Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 42(9), 881–895.
Nahas, E. (1996). World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 12(6), 567–572.
Jones, D. L. (1998). Plant and Soil, 205(1), 25–44.
Richardson, A. E., Hadobas, P. A., & Hayes, J. E. (2000). Plant, Cell and Environment, 23(4), 397–405.
Tarafdar, J. C., Bareja, M., & Panwar, J. (2003). Indian Journal of Microbiology, 43(1), 27–32.
Aseri, G. K., Jain, N., & Tarafdar, J. C. (2009). American-Eurasian Journal of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, 5(4), 564–570.
Goldstein, A. H. (1986). American Journal of Alternative Agriculture, 1, 51–57.
Rodriguez, H., Gonzalez, T., Selman, G. (2000) Journal of Biotechnology, 84: 155–161.
George, T., Gregory, P., Wood, M., Read, D., & Buresh, R. (2002). Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 34, 1487–1494.
Nenwani, V., Doshi, P., Saha, T., & Rajkumar, S. (2010). Journal of Yeast and Fungal Research, 1(1), 009–014.
Ohtake, H., Kato, J., Kuroda, A., Taguchi, K., & Sakai, Y. (1996). In T. Nakazawa, K. Furukawa, D. Haas, & S. Silver (Eds.), Molecular biology and biotechnology (pp. 188–194). Washington DC: American Society for Microbiology.
Acknowledgments
Authors gratefully acknowledge Prof. Aditya Shastri, Vice Chancellor, Banasthali University for the financial support through the Department of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Banasthali University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jain, R., Garg, V. & Saxena, J. Effect of an Organophosphate Pesticide, Monocrotophos, on Phosphate-Solubilizing Efficiency of Soil Fungal Isolates. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175, 813–824 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1309-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1309-0