Abstract
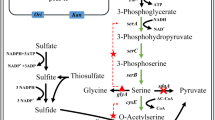
The direct fermentative production of l-serine from sugar has attracted increasing attention. Corynebacterium glutamicum SYPS-062 can directly convert sugar to l-serine. In this study, the effects of exogenous and endogenous regulation of cofactor folate on C. glutamicum SYPS-062 growth and l-serine accumulation were investigated. For exogenous regulation, the inhibitor (sulfamethoxazole) or precursor (p-aminobenzoate) of folate biosynthesis was added to the medium, respectively. For endogenous regulation, the gene (pabAB) that encodes the key enzyme of folate biosynthesis was knocked out or overexpressed to obtain the recombinant C. glutamicum SYPS-062 ΔpabAB and SYPS-062(pJC-tac-pabAB), respectively. The results indicated that decreased levels of cofactor folate supported l-serine accumulation, whereas increased levels of cofactor folate aided in cell growth of C. glutamicum SYPS-062. Thus, this study not only elucidated the role of folate in C. glutamicum SYPS-062 growth and l-serine accumulation, but also provided a novel and convenient approach to regulate folate biosynthesis in C. glutamicum.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker, J., Zelder, O., Hafner, S., Schroder, H., & Wittmann, C. (2011). From zero to hero-design-based systems metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for L-lysine production. Metabolic Engineering, 13, 159–168.
Chang, Z., Sun, Y., He, J., & Vining, L. C. (2001). p-Aminobenzoic acid and chloramphenicol biosynthesis in Streptomyces venezuelae: gene sets for a key enzyme, 4-amino-4-deoxychorismate synthase. Microbiology, 147, 2113–2126.
Eggeling, L. (2007). L-Serine and glycine (5th ed.). Berlin: Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
Hjortmo, S., Patring, J., & Andlid, T. (2008). Growth rate and medium composition strongly affect folate content in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 123, 93–100.
Holatko, J., Elisakova, V., Prouza, M., Sobotka, M., Nesvera, J., & Patek, M. (2009). Metabolic engineering of the L-valine biosynthesis pathway in Corynebacterium glutamicum using promoter activity modulation. Journal of Biotechnology, 139, 203–210.
Jiang, W., Xia, B., & Liu, Z. (2013). A serine hydroxymethyltransferase from marine bacterium Shewanella algae: isolation, purification, characterization and L-serine production. Microbiology Research, 168, 477–484.
Jin, X., Zhang, X., Dou, W., Xu, H., & Xu, Z. (2011). Activity analysis of L-serine dehydratase and effect of the gene knockout on L-serine accumulation in Corynebacterium glutamicum SYPS-062. China Biotechnology, 31, 29–34.
Kimura, E. (2003). Metabolic engineering of glutamate production. Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology, 79, 37–57.
Kubota, K. (1985). Improved production of L-serine by mutants of Corynebacterium glycinophilum with less serine dehydratase activity. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry 49.
Leuchtenberger, W., Huthmacher, K., & Drauz, K. (2005). Biotechnological production of amino acids and derivatives: current status and prospects. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 69, 1–8.
Li, Y., Chen, G. K., Tong, X. W., Zhang, H. T., Liu, X. G., Liu, Y. H., et al. (2012). Construction of Escherichia coli strains producing L-serine from glucose. Biotechnology Letters, 34, 1525–1530.
Lin, L., Dou, W., Zhang, X., Xu, H., Xu, Z., & Wang, Z. (2008). Analysis of glyA gene from Corynebacterium glutamicum SYPS-062 which can produce L-serine from sugar substances. Biotechnology Bulletin, 5, 176–180.
Netzer, R., Peters-Wendisch, P., Eggeling, L., & Sahm, H. (2004). Cometabolism of a nongrowth substrate: L-serine utilization by Corynebacterium glutamicum. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70, 7148–7155.
Omori, K., Kakimoto, T., & Chibata, I. (1983). L-serine production by a mutant of Sarcina albida defective in L-serine degradation. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 45, 1722–1726.
Park, S. D., Lee, J. Y., Sim, S. Y., Kim, Y., & Lee, H. S. (2007). Characteristics of methionine production by an engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum strain. Metabolic Engineering, 9, 327–336.
Peters-Wendisch, P., Netzer, R., Eggeling, L., & Sahm, H. (2002). 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase from Corynebacterium glutamicum: the C-terminal domain is not essential for activity but is required for inhibition by L-serine. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 60, 437–441.
Peters-Wendisch, P., Stolz, M., Etterich, H., Kennerknecht, N., Sahm, H., & Eggeling, L. (2005). Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for L-serine production. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71, 7139–7144.
Prabhu, V., Chatson, K. B., Abrams, G. D., & King, J. (1996). 13C nuclear magnetic resonance detection of interactions of serine hydroxymethyltransferase with C1-tetrahydrofolate synthase and glycine decarboxylase complex activities in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 112, 207–216.
Prabhu, V., Chatson, K. B., Lui, H., Abrams, G. D., & King, J. (1998). Effects of sulfanilamide and methotrexate on 13C fluxes through the glycine decarboxylase/serine hydroxymethyltransferase enzyme system in arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 116, 137–144.
Ren, J., Zhang, X., Dou, W., Xu, H., & Xu, Z. (2009). The activity study of aminodeoxychorismate synthase of different Corynebacterium glutamicum. China Biotechnology, 29, 57–61.
San, K. Y., Bennett, G. N., Berrios-Rivera, S. J., Vadali, R. V., Yang, Y. T., Horton, E., et al. (2002). Metabolic engineering through cofactor manipulation and its effects on metabolic flux redistribution in Escherichia coli. Metabolic Engineering, 4, 182–192.
Schafer, A., Tauch, A., Jager, W., Kalinowski, J., Thierbach, G., & Puhler, A. (1994). Small mobilizable multi-purpose cloning vectors derived from the Escherichia coli plasmids pK18 and pK19: selection of defined deletions in the chromosome of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Gene, 145, 69–73.
Simic, P., Willuhn, J., Sahm, H., & Eggeling, L. (2002). Identification of glyA (encoding serine hydroxymethyltransferase) and its use together with the exporter ThrE to increase L-threonine accumulation by Corynebacterium glutamicum. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 3321–3327.
Stolz, M., Peters-Wendisch, P., Etterich, H., Gerharz, T., Faurie, R., Sahm, H., et al. (2007). Reduced folate supply as a key to enhanced L-serine production by Corynebacterium glutamicum. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73, 750–755.
Tauch, A., Kirchner, O., Loffler, B., Gotker, S., Puhler, A., & Kalinowski, J. (2002). Efficient electrotransformation of Corynebacterium diphtheriae with a mini-replicon derived from the Corynebacterium glutamicum plasmid pGA1. Current Microbiology, 45, 362–367.
Wendisch, V. F., Bott, M., & Eikmanns, B. J. (2006). Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli and Corynebacterium glutamicum for biotechnological production of organic acids and amino acids. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 9, 268–274.
Zhang, X., Dou, W., Xu, H., & Xu, Z. (2009). Identification of L-serine producer SYPS-062 and the effect of different carbon source. Microbiology, 36, 789–793.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the High Tech Development Program of China (863 Project, No. 2012AA022102) and the production project of Ministry of Education of Guangdong province (No. 2012B091000083).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Xu, G., Li, H. et al. Effect of Cofactor Folate on the Growth of Corynebacterium glutamicum SYPS-062 and l-Serine Accumulation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 173, 1607–1617 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0945-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0945-8