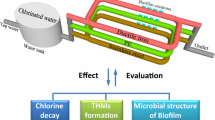
Abstract
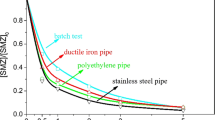
Drinking water distribution systems are composed of various pipe materials and may harbor biofilms even in the continuous presence of disinfectants. Biofilms formation on five pipe materials (copper (Cu), polyethylene (PE), stainless steel (STS), cast iron (CI), and concrete-coated polycarbonate (CP)) within drinking water containing 1.20 mg/L free chlorine, was investigated by flow cytometry, heterotrophic plate counts, and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis. Results showed that the biofilms formation varied in pipe materials. The biofilm formed on CP initially emerged the highest biomass in 12 days, but CI presented the significantly highest biomass after 28 days, and Cu showed the lowest bacterial numbers before 120 days, while STS expressed the lowest bacterial numbers after 159 days. In the biofilm community structure, Moraxella osloensis and Sphingomonas sp. were observed in all the pipe materials while Bacillus sp. was detected except in the CP pipe and Stenotrophomonas maltophila was found from three pipe materials (Cu, PE, and STS). Other bacteria were only found from one or two pipe materials. It is noteworthy that there are 11 opportunistic pathogens in the 17 classified bacterial strains. This research has afforded crucial information regarding the influence of pipe materials on chlorine-resistant biofilm formation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Simoes, L. C., & Simoes, M. (2013). RSC Advances, 3, 2520–2533.
Berry, D., Xi, C. W., & Raskin, L. (2006). Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 17, 297–302.
Lin, W., Yu, Z., Chen, X., Liu, R., & Zhang, H. (2013). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 97, 8393–8401.
Wang, H., Masters, S., Hong, Y. J., Stallings, J., Falkinham, J. O., Edwards, M. A., et al. (2012). Environmental Science & Technology, 46, 11566–11574.
Lehtola, M. J., Miettinen, I. T., Lampola, T., Hirvonen, A., Vartiainen, T., & Martikainen, P. J. (2005). Water Research, 39, 1962–1971.
Chu, C. W., Lu, C. Y., Lee, C. M., & Tsai, C. (2003). Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part A: Toxic/Hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering, 38, 1377–1388.
Bachmann, R., & Edyvean, R. (2005). Biofilms, 2, 197–227.
Jang, H. J., Choi, Y. J., & Ka, J. O. (2011). Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 21, 115–123.
Chowdhury, S. (2012). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 6087–6137.
Chen, L., Jia, R. B., & Li, L. (2013). Environmental Science, Processes & Impacts, 15, 1332–1340.
Simoes, L. C., Simoes, M., Oliveira, R., & Vieira, M. J. (2007). Journal of Basic Microbiology, 47, 174–183.
Zhang, M. L., Liu, W. J., Nie, X. B., Li, C. P., Gu, J. N., & Zhang, C. (2012). Microbes and Environments, 27, 443–448.
Kwon, S., Moon, E., Kim, T. S., Hong, S., & Park, H. D. (2011). Microbes and Environments, 26, 149–155.
Hong, P. Y., Hwang, C. C., Ling, F. Q., Andersen, G. L., LeChevallier, M. W., & Liu, W. T. (2010). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 76, 5631–5635.
Szabo, J. G., Impellitteri, C. A., Govindaswamy, S., & Hall, J. S. (2009). Water Research, 43, 5004–5014.
APHA. (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (21st ed.). Washington: American Public Health Association Inc.
Lehtola, M. J., Miettinen, K. T., Keinanen, M. M., Kekki, T. K., Laine, O., Hirvonen, A., et al. (2004). Water Research, 38, 3769–3779.
Lautenschlager, K., Boon, N., Wang, Y. Y., Egli, T., & Hammes, F. (2010). Water Research, 44, 4868–4877.
Bassam, B. J., Caetanoanolles, G., & Gresshoff, P. M. (1991). Analytical Biochemistry, 196, 80–83.
Zhang, W. D., & DiGiano, F. A. (2002). Water Research, 36, 1469–1482.
Norton, C. D., & LeChevallier, M. W. (2000). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66, 268–276.
Tsai, Y. P., Pai, T. Y., & Yang, Q. Z. (2008). Environmental Engineering Science, 25, 929–939.
Codony, F., Morató, J., & Mas, J. (2005). Water Research, 39, 1896–1906.
Maul, A., Vogost, D., & Block, J.-C. (1991). Microbiological analysis in water distribution networks: sampling strategies, methods and computer programs. New York: Ellis Horwood Publishers.
Holden, B., Greetham, M., Croll, B. T., & Scutt, J. (1995). Water Science and Technology, 32, 213–220.
Vaz-Moreira, I., Egas, C., Nunes, O. C., & Manaia, C. M. (2013). Fems Microbiology Ecology, 83, 361–374.
Xue, Z., Sendamangalam, V. R., Gruden, C. L., & Seo, Y. (2012). Environmental Science & Technology, 46, 13212–13219.
Percival, S. L., Knapp, J. S., Edyvean, R., & Wales, D. S. (1998). Water Research, 32, 243–253.
Appenzeller, B. M. R., Yanez, C., Jorand, F., & Block, J. C. (2005). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71, 5621–5623.
Chang, L., & Craik, S. (2012). Ozone: Science & Engineering, 34, 243–251.
Douterelo, I., Sharpe, R. L., & Boxall, J. B. (2013). Water Research, 47, 503–516.
McCoy, S. T., & VanBriesen, J. M. (2012). Journal of Environmental Engineering, ASCE, 138, 786–795.
Poitelon, J.-B., Joyeux, M., Welte, B., Duguet, J.-P., Prestel, E., & DuBow, M. S. (2010). Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 37, 117–128.
Lee, D. G., Lee, J. H., & Kim, S. J. (2005). World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 21, 155–162.
Mathieu, L., Bouteleux, C., Fass, S., Angel, E., & Block, J. C. (2009). Water Research, 43, 3375–3386.
Pelayo, J. S., Carnio, J., Ito, F. A. N., Kotaka, C. R., Fuganti, M. R., & Garcia, L. B. (2012). Revista Sul-Brasileira de Odontologia, 9, 245–253.
Weber, K. A., Achenbach, L. A., & Coates, J. D. (2006). Nature Reviews Microbiology, 4, 752–764.
Shane, W. T., Szabo, J. G., & Bishop, P. L. (2011). Environmental Technology, 32, 847–855.
Elhariry, H. M. (2011). Food Microbiology, 28, 1266–1274.
Luo, J., Liang, H., Yan, L., Ma, J., Yang, Y., & Li, G. (2013). Bioresource Technology, 148, 189–195.
Pavissich, J. P., Vargas, I. T., Gonzalez, B., Pasten, P. A., & Pizarro, G. E. (2010). Journal of Applied Microbiology, 109, 771–782.
Kjellerup, B. B., Kjeldsen, K. U., Lopes, F., Abildgaard, L., Ingvorsen, K., Frølund, B., et al. (2009). Biofouling, 25, 727–737.
Wang, Y., Zhang, X. J., Feng, S., Niu, Z. B., & Chen, C. (2009). Annals of Microbiology, 59, 353–358.
Tauch, A., Kaiser, O., Hain, T., Goesmann, A., Weisshaar, B., Albersmeier, A., et al. (2005). Journal of Bacteriology, 187, 4671–4682.
Hilbi, H., & Haas, A. (2012). Traffic, 13, 1187–1197.
Spilker, T., Uluer, A. Z., Marty, F. M., Yeh, W. W., Levison, J. H., Vandamme, P., et al. (2008). Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 46, 2774–2777.
Lu, P. P., Chen, C., Wang, Q. F., Wang, Z., Zhang, X. J., & Xie, S. G. (2013). Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 18, 119–124.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation for Youth of China (51108123) and State Key Laboratory of Urban Water Resource and Environment (Harbin Institute of Technology) (2014TS08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 64.5 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Z., Wu, C., Zhong, D. et al. Effects of Pipe Materials on Chlorine-resistant Biofilm Formation Under Long-term High Chlorine Level. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 173, 1564–1578 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0935-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0935-x