Abstract
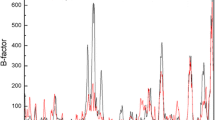
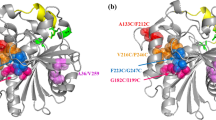
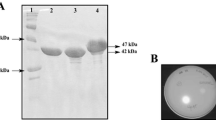
A novel lipase lipB from Serratia marcescens ECU1010 is highly stable in the presence of organic solvents. By sequence and structure comparison with homologous lipase lipA, three amino acid residues were found to be different between them. To identify the residues which increase the organic solvent stability of lipB, residues that potentially provide this stability were mutated to the ones of lipA at equivalent positions. The replacement of Gly at position 33 by Asp obviously decreased its stability in organic solvents. Molecular modeling and structural analysis also suggested that the Gly33 residue is important for the organic solvent stability of lipB.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reetz, M. T. (2002). Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 6, 145–150.
Jaeger, K. E., & Eggert, T. (2002). Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 13, 390–397.
Bornscheuer, U. T., & Kazlauskas, R. J. (1999). Hydrolases in organic synthesis: regio- and stereoselective biotransformations. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH.
Lee, M. Y., & Dordick, J. S. (2002). Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 13, 376–384.
Meie, R., Drepper, T., Svensson, V., Jaeger, K. E., & Baumann, U. (2007). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 282, 31477–31483.
Hyun-Ju, K., Amada, K., Haruki, M., Morikawa, M., & Kanaya, S. (2000). FEBS Letters, 483, 139–142.
Zhao, L. L., Xu, J. H., Zhao, J., Pan, J., & Wang, Z. L. (2008). Process Biochemistry, 43, 626–633.
Ogino, H., Uchiho, T., Doukyu, N., Yasuda, M., Ishimi, K., & Ishikawa, H. (2007). Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 358, 1028–1033.
Cygler, M., Schrag, J. D., Sussman, J. L., Harel, M., & Silman, I. (1993). Protein Science, 2, 366–382.
Lotti, M., Tramontano, A., Longhi, S., Fusetti, F., & Brocca, S. (1994). Protein Engineering, 7, 531–535.
Kazlauskas, R. J. (2000). Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 4, 81–88.
Long, Z. D., Xu, J. H., Zhao, L. L., & Pan, J. (2007). Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 47, 105–110.
Akatsuka, H., Kawai, E., Omori, K., Komatsubara, S., Shibatani, T., & Tosa, T. (1994). Journal of Bacteriology, 176, 1949–1956.
Amada, K., Haruki, M., Imanaka, T., Morikawa, M., & Kanaya, S. (2000). Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1478, 201–210.
Hazarika, S., Goswami, P., Dutta, N. N., & Hazarika, A. K. (2002). Chemical Engineering Journal, 85, 61–68.
Tanford, C. (1961). Physical chemistry of macromolecules. New York: Wiley.
Singer, S. J. (1962). Advances in Protein Chemistry, 17, 1–68.
Careri, G. (1998). Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology, 70, 223–249.
Serdakowski, A. L., & Dordick, J. S. (2008). Trends in Biotechnology, 26, 48–54.
Klibanov, A. M. (1997). Trends in Biotechnology, 15, 97–101.
Lima, V. M. G., Krieger, N., Mitchell, D. A., & Fontana, J. D. (2004). Biochemical Engineering Journal, 18, 65–71.
Martinez, P., Van Dam, M. E., Robinson, A. C., Chen, K., & Arnold, F. H. (1992). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 39, 141–147.
Arnold, F. H. (1988). Protein Engineering, 2, 21–25.
Arnold, F. H. (1990). Trends in Biotechnology, 8, 244–249.
Pleiss, J., Fischer, M., & Schmid, R. D. (1998). Chemistry and Physics of Lipids, 93, 67–70.
Luque, I., & Freire, E. (2000). Proteins, Suppl. 4, 63–71.
Higuchi, R. (1992). Using PCR to engineer DNA in PCR technology: principles and applications for DNA amplification (pp. 61–70). New York: Stockton.
Matsumae, H., Furui, M., Shibatani, T., & Tosa, T. (1994). Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering, 78, 59–63.
Long, Z. D., Xu, J. H., Zhao, L. L., & Pan, J. (2007). Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 28, 175–179.
Gao, L., Xu, J. H., & Li, X. J. (2004). Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 31, 525–530.
Chin, J. H., Rahman, R. N. Z. A., Salleh, A. B., & Basri, M. (2003). Biochemical Engineering Journal, 15, 147–151.
Jinwal, U. K., Roy, U., Chowdhury, A. R., Bhaduri, A. P., & Roy, P. K. (2003). Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry, 11, 1041–1046.
Arnold, K., Bordoli, L., Kopp, J., & Schwede, T. (2006). Bioinformatics, 22, 195–201.
Kiefer, F., Arnold, K., Kunzli, M., Bordoli, L., & Schwede, T. (2009). Nucleic Acids Research, 37, 387–392.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National High-tech R&D (863) Program (No. 2007AA02Z225) and the National Special Fund for State Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering (no. 2060204), People’s Republic of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 301 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, SX., Ma, Q., Lin, K. et al. Essential Role of Gly33 in a Novel Organic Solvent-Tolerant Lipase from Serratia marcescens ECU1010 as Determined by Site-Directed Mutagenesis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172, 2945–2954 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0690-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0690-4