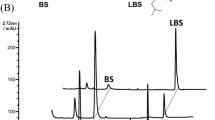
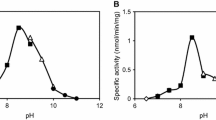
Abstract
β-Aminopeptidases exhibit both hydrolytic and aminolytic (peptide bond formation) activities and have only been reported in bacteria. We identified a gene encoding the β-aminopeptidase homolog from a genome database of the filamentous fungus Aspergillus oryzae. The gene was overexpressed in A. oryzae, and the resulting recombinant enzyme was purified. Apart from bacterial homologs [β-Ala-para-nitroanilide (pNA)], the enzyme preferred d-Leu-pNA and d-Phe-pNA as substrates. Therefore, we designated this gene as d-stereoselective aminopeptidase A (damA). The purified recombinant DamA was estimated to be a hexamer and was composed of two subunits with molecular masses of 29.5 and 11.5 kDa, respectively. Optimal hydrolytic activity of DamA toward d-Leu-pNA was observed at 50 °C and pH 8.0. The enzyme was stable up to 60 °C and from pH 4.0–11.0. DamA also exhibited aminolytic activity, producing d-Leu-d-Leu-NH2 from d-Leu-NH2 as a substrate. In the presence of 3.0 M NaCl, the amount of pNA liberated from d-Leu-pNA by DamA was 3.1-fold higher than that in the absence of NaCl. Thus, DamA is a halophilic enzyme. The enzyme was utilized to synthesize several hetero-dipeptides containing a d-amino acid at the N-terminus as well as physiologically active peptides.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gill, I., López-Fandiño, R., Jorba, X., & Vulfson, E. N. (1996). Biologically active peptides and enzymatic approaches to their production. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 18, 163–183.
Kumar, D., & Bhalla, T. C. (2005). Microbial proteases in peptide synthesis: approaches and applications. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 68, 726–736. Review.
Montalbetti, C. A. G. N., & Falque, V. (2005). Amide bond formation and peptide coupling. Tetrahedron, 61, 10827–10852.
Lombard, C., Saulnier, J., & Wallach, J. M. (2005). Recent trends in protease-catalyzed peptide synthesis. Protein and Peptide Letters, 12, 621–629. Review.
Guzman, F., Barberis, S., & Illanes, A. (2007). Peptide synthesis: chemical or enzymatic. Electronic Journal of Biotechnology, 10, 279–314.
Yagasaki, M., & Hashimoto, S. (2008). Synthesis and application of dipeptides; current status and perspectives. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 81, 13–22. Review.
Trusek-Holownia, A. (2003). Synthesis of ZAlaPheOMe, the precursor of bitter dipeptide in the two-phase ethyl acetate-water system catalysed by thermolysin. Journal of Biotechnology, 102, 153–163.
Yokozeki, K., & Hara, S. (2005). A novel and efficient enzymatic method for the production of peptides from unprotected starting materials. Journal of Biotechnology, 115, 211–220.
Arima, J., Uesugi, Y., Uraji, M., Iwabuchi, M., & Hatanaka, T. (2006). Dipeptide synthesis by aminopeptidase from Streptomyces septatus TH-2 and its application to synthesis of biologically active peptides. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72, 4225–4231.
Arima, J., Morimoto, M., Usuki, H., Mori, N., & Hatanaka, T. (2010). Beta-alanyl peptide synthesis by Streptomyces S9 aminopeptidase. Journal of Biotechnology, 147, 52–58.
Arima, J., Chiba, M., Ichiyanagi, T., Yabuta, Y., Mori, N., & Aimi, T. (2010). Eryngase: a Pleurotus eryngii aminopeptidase exhibiting peptide bond formation activity. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 87, 1791–1801.
Hatanaka, T., Yamasato, A., Arima, J., Usuki, H., Yamamoto, Y., & Kumagai, Y. (2011). Extracellular production and characterization of Streptomyces X-prolyl dipeptidyl aminopeptidase. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 164, 475–486.
Arima, J., Ito, H., Hatanaka, T., & Mori, N. (2011). Aminolytic reaction catalyzed by d-stereospecific amidohydrolases from Streptomyces spp. Biochimie, 93, 1460–1469.
Usuki, H., Yamamoto, Y., Arima, J., Iwabuchi, M., Miyoshi, S., Nitoda, T., et al. (2011). Peptide bond formation by aminolysin-A catalysis: a simple approach to enzymatic synthesis of diverse short oligopeptides and biologically active puromycins. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 9, 2327–2335.
Machida, M., Asai, K., Sano, M., Tanaka, T., Kumagai, T., Terai, G., et al. (2005). Genome sequencing and analysis of Aspergillus oryzae. Nature, 438, 1157–1161.
Vongsangnak, W., Olsen, P., Hansen, K., Krogsgaard, S., & Nielsen, J. (2008). Improved annotation through genome-scale metabolic modeling of Aspergillus oryzae. BMC Genomics, 9, 245.
Kobayashi, T., Abe, K., Asai, K., Gomi, K., Juvvadi, P. R., Kato, M., et al. (2007). Genomics of Aspergillus oryzae. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 71, 646–670. Review.
Kusumoto, K. I., Matsushita-Morita, M., Furukawa, I., Suzuki, S., Yamagata, Y., Koide, Y., et al. (2008). Efficient production and partial characterization of aspartyl aminopeptidase from Aspergillus oryzae. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 105, 1711–1719.
Matsushita-Morita, M., Furukawa, I., Suzuki, S., Yamagata, Y., Koide, Y., Ishida, H., et al. (2010). Characterization of recombinant prolyl aminopeptidase from Aspergillus oryzae. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 109, 156–165.
Matsushita-Morita, M., Tada, S., Suzuki, S., Hattori, R., Marui, J., Furukawa, I., et al. (2010). Overexpression and characterization of an extracellular leucine aminopeptidase from Aspergillus oryzae. Current Microbiology, 62, 557–564.
Marui, J., Matsushita-Morita, M., Tada, S., Hattori, R., Suzuki, S., Amano, H., Ishida, H., Yamagata, Y., Takeuchi, M., & Kusumoto, K. (2012). Enzymatic properties of the glycine-d-alanine aminopeptidase of Aspergillus oryzae and its activity profiles in liquid-cultured mycelia and solid-state rice culture (rice koji). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 93, 655–669. erratum 901.
Marui, J., Matsushita-Morita, M., Tada, S., Hattori, R., Suzuki, S., Amano, H., et al. (2012). Comparison of expression and enzymatic properties of Aspergillus oryzae lysine aminopeptidases ApsA and ApsB. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 28, 2643–2650.
Rawlings, N. D., Barrett, A. J., & Bateman, A. (2012). MEROPS: the database of proteolytic enzymes, their substrates and inhibitors. Nucleic Acids Research, 40, D343–D350.
Heck, T., Geueke, B., & Kohler, H. P. (2012). Bacterial β-aminopeptidases: structural insights and applications for biocatalysis. Chemistry & Biodiversity, 9, 2388–2409.
Geueke, B., Namoto, K., Seebach, D., & Kohler, H. P. (2005). A novel beta-peptidyl aminopeptidase (BapA) from strain 3-2W4 cleaves peptide bonds of synthetic beta-tri- and beta-dipeptides. Journal of Bacteriology, 187, 5910–5917.
Geueke, B., Heck, T., Limbach, M., Nesatyy, V., Seebach, D., & Kohler, H. P. (2006). Bacterial beta-peptidyl aminopeptidases with unique substrate specificities for beta-oligopeptides and mixed beta, alpha-oligopeptides. FEBS Journal, 273, 5261–5272.
Geueke, B., & Kohler, H. P. (2007). Bacterial beta-peptidyl aminopeptidases: on the hydrolytic degradation of beta-peptides. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnolog, 74, 1197–1204.
Heck, T., Kohler, H. P., Limbach, M., Flögel, O., Seebach, D., & Geueke, B. (2007). Enzyme-catalyzed formation of beta-peptides: beta-peptidyl aminopeptidases BapA and DmpA acting as beta-peptide-synthesizing enzymes. Chemistry & Biodiversity, 4, 2016–2030.
Heck, T., Reimer, A., Seebach, D., Gardiner, J., Deniau, G., Lukaszuk, A., et al. (2010). Beta-aminopeptidase-catalyzed biotransformations of beta(2)-dipeptides: kinetic resolution and enzymatic coupling. Chembiochem, 11, 1129–1136.
Heyland, J., Antweiler, N., Lutz, J., Heck, T., Geueke, B., Kohler, H. P., et al. (2010). Simple enzymatic procedure for l-carnosine synthesis: whole-cell biocatalysis and efficient biocatalyst recycling. Microbial Biotechnology, 3, 74–83.
Quinn, P., Boldyrev, A., & Formazuyk, V. (1992). Carnosine: its properties, functions and potential therapeutic applications. Molecular Aspects of Medicine, 13, 379–444.
Hanahan, D. (1983). Studies on the transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. Journal of Molecular Biology, 166, 557–580.
Gomi, K., Iimura, Y., & Hara, S. (1987). Integrative transformation of Aspergillus oryzae with a plasmid containing the Aspergillus nidulans argB gene. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 51, 2549–2555.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for detecting microgram amounts of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227, 680–685.
Exterkate, F. A. (1984). Location of peptidases outside and inside the membrane of Streptococcus cremoris. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 47, 177–183.
Fanuel, L., Thamm, I., Kostanjevecki, V., Samyn, B., Joris, B., Goffin, C., et al. (1999). Two new aminopeptidases from Ochrobactrum anthropi active on d-alanyl-p-nitroanilide. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 55, 812–818.
Fanuel, L., Goffin, C., Cheggour, A., Devreese, B., Van Driessche, G., Joris, B., et al. (1999). The DmpA aminopeptidase from Ochrobactrum anthropi LMG7991 is the prototype of a new terminal nucleophile hydrolase family. Biochemical Journal, 341, 147–155.
Komeda, H., & Asano, Y. (2005). A DmpA-homologous protein from Pseudomonas sp. is a dipeptidase specific for beta-alanyl dipeptides. FEBS Journal, 272, 3075–3084.
Fuchs, V., Jaeger, K.-E., Wilhelm, S., & Rosenau, F. (2011). The BapF protein from Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a β-peptidyl aminopeptidase. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 27, 713–718.
Bompard-Gilles, C., Villeret, V., Davies, G. J., Fanuel, L., Joris, B., Frère, J. M., et al. (2000). A new variant of the Ntn hydrolase fold revealed by the crystal structure of l-aminopeptidase d-ala-esterase/amidase from Ochrobactrum anthropi. Structure, 8, 153–162.
Miyoshi, S., Ishikawa, H., Kaneko, T., Fukui, F., Tanaka, H., & Maruyama, S. (1991). Structures and activity of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in an alpha-zein hydrolysate. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 55, 1313–1318.
Kwon, O. S., Park, S. H., Yun, B. S., Pyun, Y. R., & Kim, C. J. (2001). Cyclo(d-Pro-l-Val), a specific beta-glucosidase inhibitor produced by Aspergillus sp. F70609. Journal of Antibiotics, 54, 179–181.
Briza, P., Ellinger, A., Winkler, G., & Breitenbach, M. (1990). Characterization of a DL-dityrosine-containing macromolecule from yeast ascospore walls. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 265, 15118–15123.
Kim, K. W., Sugawara, F., Yoshida, S., Murofushi, N., Takahashi, N., & Curtis, R. W. (1993). Structure of malformin B, a phytotoxic metabolite produced by Aspergillus niger. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 57, 787–791.
Bompard-Gilles, C., Villeret, V., Fanuel, L., Joris, B., Frère, J. M., & Van Beeumen, J. (1999). Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of a new l-aminopeptidase-d-amidase/d-esterase activated by a Gly-Ser peptide bond hydrolysis. Acta Crystallographica Section D: Biological Crystallography, 55, 699–701.
Merz, T., Heck, T., Geueke, B., Mittl, P. R., Briand, C., Seebach, D., et al. (2012). Autoproteolytic and catalytic mechanisms for the beta-aminopeptidase BapA - a member of the Ntn hydrolase family. Structure, 20, 1850–1860.
Uraji, M., Arima, J., Uesugi, Y., Iwabuchi, M., & Hatanaka, T. (2007). Effect of salt on the activity of Streptomyces prolyl aminopeptidase. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1774, 1462–1469.
Bock, M. G., & Longmore, J. (2000). Bradykinin antagonists: new opportunities. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 4, 401–406.
Cucchi, P., Meini, S., Quartara, L., Giolitti, A., Zappitelli, S., Rotondaro, L., et al. (2002). Interaction of linear and cyclic peptide antagonists at the human B(2) kinin receptor. Peptides, 23, 1457–1463.
Takagi, H., Shiomi, H., Ueda, H., & Amano, H. (1979). Morphine-like analgesia by a new dipeptide, l-tyrosyl-l-arginine (Kyotorphin) and its analogue. European Journal of Pharmacology, 55, 109–111.
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by the Program for Promotion of Basic Research Activities for Innovative Biosciences (PROBRAIN).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 105 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsushita-Morita, M., Nakagawa, H., Tada, S. et al. Characterization of a d-Stereoselective Aminopeptidase (DamA) Exhibiting Aminolytic Activity and Halophilicity from Aspergillus oryzae . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 171, 145–164 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0330-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0330-z