Abstract
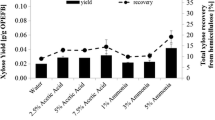
Oil palm empty fruit bunch (EFB) is abundantly available in Malaysia and it is a potential source of xylose for the production of high-value added products. This study aimed to optimize the hydrolysis of EFB using dilute sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and phosphoric acid (H3PO4) via response surface methodology for maximum xylose recovery. Hydrolysis was carried out in an autoclave. An optimum xylose yield of 91.2 % was obtained at 116 °C using 2.0 % (v/v) H2SO4, a solid/liquid ratio of 1:5 and a hydrolysis time of 20 min. A lower optimum xylose yield of 24.0 % was observed for dilute H3PO4 hydrolysis at 116 °C using 2.4 % (v/v) H3PO4, a solid/liquid ratio of 1:5 and a hydrolysis time of 20 min. The optimized hydrolysis conditions suggested that EFB hydrolysis by H2SO4 resulted in a higher xylose yield at a lower acid concentration as compared to H3PO4.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh, R. P., Ibrahim, M. H., Esa, N., & Iliyana, M. S. (2010). Reviews in Environmental Science and Biotechnology, 9, 331–344.
Sreekala, M. S., Kumaran, M. G., & Thomas, S. J. (1997). Applied Polymer Science, 66, 821–835.
Abdul Khalil, H. P. S., Siti Aiwani, M., & Ridzuan, R. (2008). Polymer-Plastic Technology, 47, 273–280.
Mohamad, N. L., Mustapa Kamal, S. M., & Liew, A. G. J. (2009). Applied Sciences, 9, 3192–3195.
Zhang, D., Ong, L. Y., Li, Z., & Wu, J. C. (2010). Chemical Engineering Journal, 181, 636–642.
Arruda, P. V., Rodrigues, R. C., Silva, D. D., & Felipe, M. G. (2011). Biodegradation, 22, 815–822.
Mani, S., Tabil, L. G., & Sokhansanj, S. (2004). Biomass and Bioenergy, 27, 339–352.
Hendriks, A. T. W. M., & Zeeman, G. (2009). Bioresource Technology, 100, 10–18.
Gray, K. A., Zhao, L., & Emptage, M. (2006). Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 10, 141–146.
Pienkos, P. T., & Zhang, M. (2009). Cellulose, 16, 743–762.
Chandel, A. K., Kapoor, R. K., Singh, A., & Kuhad, R. C. (2007). Bioresource Technology, 98, 1947–1950.
Gamez, S., Cabriales, J. J. G., Ramirez, J. A., Garrote, G., & Vazquez, M. J. (2006). Food Engineering, 74, 78–88.
Vazquez, M., Oliva, M., Tellez-Luis, S. J., & Ramirez, J. A. (2007). Bioresource Technology, 98, 3053–3060.
Moutta, R. O., Chandel, A. K., Rodrigues, R. C. L. B., Silva, M. B., Rocha, G. J. M., & Silva, S. S. (2012). Sugar Technology, 14, 53–60.
Vancov, T., & McIntosh, S. (2012). Applied Energy, 92, 421–428.
Carvalho, W., Batista, M. A., Canilha, L., Santos, J. C., Converti, A., & Silva, S. S. J. (2004). Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 79, 1308–1312.
Boonmanumsin, P., Treeboobpha, S., Jeamjumnunja, K., Luengnaruemitchai, A., Chaisuwan, T., & Wongkasemjit, S. (2012). Bioresource Technology, 103, 425–431.
Overend, R. P., & Cornet, E. (1987). Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 321, 523–536.
Rahman, S. H. A., Choudhury, J. P., Ahmad, A. L., & Kamaruddin, A. H. (2007). Bioresource Technology, 98, 554–559.
Choi, C. H., & Oh, K. K. (2012). Bioresource Technology, 110, 349–354.
Laopaiboon, P., Thani, A., Leelavatcharamas, V., & Laopaiboon, L. (2010). Bioresource Technology, 101, 1036–1043.
Chirat, C., Lachenal, D., & Sanglard, M. (2012). Process Biochemistry, 47, 381–385.
Shen, J. C., & Wyman, C. E. (2011). Bioresource Technology, 102, 9111–9120.
Rahman, S. H. A., Choudhury, J. P., & Ahmad, A. L. (2006). Biochemical Engineering Journal, 30, 97–103.
Wu, T. Y., Mohammad, A. W., Jahim, J. M., & Anuar, N. J. (2009). Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 84, 1390–1396.
Luterbacher, J. S., Tester, J. W., & Walker, L. P. (2010). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 107, 451–460.
Won, K. Y., Um, B. H., Kim, S. W., & Oh, K. K. (2011). Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 10, 1–7.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to School of Science, Monash University Sunway Campus for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, H.T., Dykes, G.A., Wu, T.Y. et al. Enhanced Xylose Recovery from Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunch by Efficient Acid Hydrolysis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 170, 1602–1613 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0298-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0298-8