Abstract
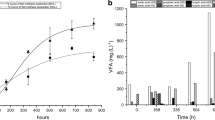
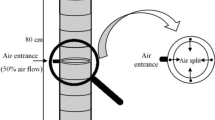
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of the support material used for biomass attachment and bed porosity on the potential generation of hydrogen gas in an anaerobic bioreactor treating low-strength wastewater. For this purpose, an upflow anaerobic packed-bed (UAPB) reactor fed with sucrose-based synthetic wastewater was used. Three reactors with various support materials (expanded clay, vegetal coal, and low-density polyethylene) were operated for hydraulic retention time (HRT) of 0.5 and 2 h. Based on the results obtained, three further reactors were operated with low-density polyethylene as a material support using various bed porosities (91, 75, and 50 %) for an HRT of 0.5 h. The UAPB reactor was found to be a feasible technology for hydrogen production, reaching a maximum substrate-based hydrogen yield of 7 mol H2 mol−1 sucrose for an HRT of 0.5 h. The type of support material used did not affect hydrogen production or the microbial population inside the reactor. Increasing the bed porosity to 91 % provided a continuous and cyclic production of hydrogen, whereas the lower bed porosities resulted in a reduced time of hydrogen production due to biomass accumulation, which resulted in a decreasing working volume.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hammed, A., & Gondal, M. A. (2005). Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 233, 35–41.
Junbo, Z., Kuisheng, W., Huitang, S., & Shaobo, W. (2004). International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 29, 1393–1396.
Wang, J. L., & Wan, W. (2009). International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 34, 799–811.
Wang, Y.-Y., Ai, P., Hu, C.-X., & Zhang, Y.-L. (2011). International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 36, 390–396.
Fan, Y., Li, C., Lay, J. J., Hou, H., & Zahng, G. (2004). Bioresource Technology, 91, 189–193.
Kim, D. H., Han, S. K., Kim, S. H., & Shin, H. S. (2006). International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 31, 2158–2169.
Mu, Y., Yu, H. Q., & Wang, G. (2007). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 40, 947–953.
Maintinguer, S. I., Fernandes, B. S., Duarte, I. C. S., Saavedra, N. K., Adorno, M. A. T., & Varesche, M. B. (2008). International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 33, 4309–4317.
Zhu, H., & Béland, M. (2006). International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 31, 1980–1988.
Leite, J. A. C., Fernandes, B. S., Pozzi, E., Barboza, M., & Zaiat, M. (2008). International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 33, 579–586.
Fernandes, B. S., Peixoto, G., Albrecht, F. R., Saavedra del Aguila, N. K., & Zaiat, M. (2010). Energy for Sustainable Development, 14, 143–148.
Wu, S. Y., Lin, C. N., Chang, J. S., Lee, K. S., & Lin, P. J. (2002). Biotechnology Progress, 18, 921–926.
Lee, K. S., Lo, Y. S., Lo, Y. C., Lin, P. J., & Chang, J. S. (2003). Biotechnology Letters, 25, 133–138.
Kawagoshi, K., Hino, N., Fujimoto, A., Nakao, M., Fujita, Y., Sugimura, S., & Furukawa, K. (2005). Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 100, 524–530.
Steven, W., van Ginkel, V., & Logan, B. (2005). Water Research, 39, 3819–3826.
Chang, F., & Lin, C. (2004). International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 29, 33–39.
Amorim, E. L. C., Barros, A. R., Damianovic, M. H. R. Z., & Silva, E. L. (2009). International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 34, 783–790.
Ren, N.Q., Ding, J., Wang, A.J., Ding, L., Wu, Y.N. (2005). In Proceedings of the 10th World Congress of Anaerobic Digestion, Montreal, Canada, 773–778.
Silva, A. J., Hirasawa, J. S., Varesche, M. B., Foresti, E., & Zaiat, M. (2005). Anaerobe, 12, 93–98.
Del Nery, V. (1987). M.Sc. Dissertation. Engineering School of São Carlos, University of São Paulo, Brazil. (in Portuguese).
Stenerson, K. (2004). Analysis of permanent gases. The Reporter, 3(1), 3.
Moraes, E.M., Adorno, M.A.T., Zaiat, M., Foresti, E. (2000). Report of the Latin-American Workshop and Seminar of Anaerobic Digestion, Recife, Brazil, p. 146–149. (in Portuguese).
Dubois, M., Gillees, K. A., Hamilton, J. K., Rebers, P. A., & Smith, F. (1956). Analytical Chemistry, 28, 350–356.
Griffiths, R. I., Whiteley, A. S., O’Donnell, A. G., & Bailey, M. J. (2000). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66, 5488–5491.
Nielsen, T. A., Liu, W. T., Filipe, C., Grady, L., Molin, S., & Stahl, D. A. (1999). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 65, 1251–1258.
Muyzer, G., Waal, E. C., & Uitterlinden, A. G. (1993). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 59, 695–700.
Vanio, E. J., & Hantula, J. (2000). Mycological Research, 104, 927–936.
Gomes, N. C. O., Fagbola, R., Costa, N. G., Rumjanek, A., Buchner, L., Mendonca-Hagler, & Smalla, K. (2003). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 69, 3758–3766.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F., & Maniatis, T. (1989). Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual (2nd ed.). Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Khanal, S. K., Chen, W. H., Li, L., & Sung, S. (2004). International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 29, 1123–1131.
Stronach, S. M., Rudd, T., & Lester, J. N. (1986). Anaerobic digestion processes in industrial wastewater treatment. Berlin, Germany: Springer.
Mohan, V. S., Bhaskar, V. Y., & Sarm, P. N. (2007). International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 32, 2286–2295.
Liu, X., Zhu, Y., & Yang, S. T. (2005). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 38, 521–528.
Tamburini, E., León, A. G., Perito, B., & Mastromei, G. (2003). Environmental Microbiology, 5, 730–736.
Dworkin, M., Falkow, S., Rosenberg, E., Schleifer, K.H., Stackebrandt, E. (2006). The Prokaryotes. In: S. Brisse, F. Grimont, P.A.D. Grimont. The Genus Klebsiella. v. 6, chapter 3.3.8 (p. 159–196). New York.
Rainey, F.A., Hollen, B.J., Small, A. (2007). In: Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology—vol. 3—The Firmicutes, 2nd edn. Springer, New York. pp. 738–828.
Hung, C. H., Lee, K. S., Cheng, L. H., Huang, Y. H., Lin, P. J., & Chang, J. S. (2007). Journal of Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 75, 693–701.
Holt, J.G., Krieg, N.R., Sneath, P.H.A., Staley, J.T., Williams, S.T. (1994). In: Bergey’ s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, 3th edn. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore.
Yokoi, H., Aratake, T., Hirose, J., Hayashi, S., & Takasaki, Y. (2001). World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 17, 609–613.
Fang, H. H. P., Li, C., & Zhang, T. (2006). International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 31, 683–692.
Bowman, K. S., Moe, W. M., Rash, B. A., Bae, H. S., & Rainey, F. A. (2006). FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 58, 120–133.
Zhang, Z. P., Adav, S. S., Show, K. Y., Tay, J. H., Liang, D. T., Lee, D. J., & Su, A. (2008). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 101, 926–936.
Minamisawa, K., Nishioka, K., Miyaki, T., Ye, B., Miyamoto, T., & You, M. (2004). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70, 3096–3102.
Wang, A., Ren, N., Shi, Y., & Lee, D. J. (2008). International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 33, 912–917.
Hata, J., Miyata, N., Kim, E. S., Takamiza, K., & Iwahori, K. (2004). Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 97, 196–201.
Lueders, T., Pommerenke, B., & Friedrich, M. (2004). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70, 5778–5786.
Sugita, T., & Nakase, T. (1999). Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 22, 79–86.
Suh, S. O., McHugh, J. V., Pollock, D. D., & Blackwell, M. (2005). Mycological Research, 109, 261–265.
Kurtzman, C. P., & Robnett, C. J. (2003). FEMS Yeast Research, 3, 417–432.
Cai, J., Roberts, I. N., & Collins, M. D. (1996). International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology, 46, 542–549.
Ueda-Nishimura, K., & Mikata, K. (2000). Microbiology, 146, 1045–1051.
Arnold, J. L., Knapp, J. S., & Johnson, C. L. (2000). Water Research, 34, 3699–3708.
Wyder, M. T., Bachmann, H. P., & Puhan, Z. (1999). Lebensmittel-Wissenschaft & Technologie, 32, 333–343.
Boxma, B., de Graaf, R. M., van der Staay, G. W. M., van Alen, T. A., Ricard, G., Gabaldon, T., van Hoek, A. H. A. M., Moon-van der Staay, S. Y., Koopman, W. J. H., van Hellemond, J. J., Tielens, A. G. M., Friedrich, T., Veenhuis, M., Huynen, M. A., & Hackstein, J. H. P. (2005). Nature, 434, 74–79.
Cheng, Q., Sanglard, D., Vanhanen, S., Liu, H. T., Bombelli, P., Smith, A., & Slabas, A. R. (2005). Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1735, 192–203.
Hackstein, J.H.P. (2004). Eukaryotic Fe-hydrogenases—old eukaryotic heritage or adaptive acquisitions? International Hydrogenases Conference.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) and the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernandes, B.S., Saavedra, N.K., Maintinguer, S.I. et al. The Effect of Biomass Immobilization Support Material and Bed Porosity on Hydrogen Production in an Upflow Anaerobic Packed-Bed Bioreactor. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 170, 1348–1366 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0262-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0262-7