Abstract
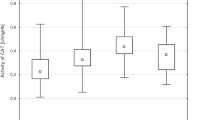
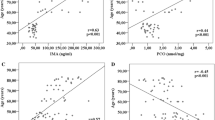
Aging is a biological process characterized by a progressive functional impairment which is associated with increased susceptibility to a variety of diseases. The main purpose of this study is to understand the gender-based relationship between human aging and activities of two erythrocyte membranes bound enzymes, Ca++-ATPase and Na+/K+-ATPase. Ca++-ATPase and Na+/K+-ATPase activities were determined as per the previous reports. Statistical differences were analyzed with Student’s t test. Our results show a significant (p < 0.0001) decrease in the Ca++-ATPase and Na+/K+-ATPase activities in males and females as a function of age. We also correlate the activities of ATPases with total antioxidant capacity of the plasma in term of ferric reducing ability of plasma values. The Ca++-ATPase and Na+/K+-ATPase activities positively correlated with ferric reducing ability of plasma value. No significant differences in the ATPase activity between males and females were observed. Decreased activity of Ca++-ATPase and Na+/K+-ATPase during human aging may be due to increased free radical generation which leads to oxidative stress and alter the erythrocyte membrane transport function and other activities. Our results emphasize the need to establish age-dependent reference values for membrane bound enzymes in studies involving its role in different disease conditions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harman, D. (2006). Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1067, 1–12.
Gil, L., Siems, W., Mazurek, B., et al. (2006). Free Radical Research, 40, 495–505.
Pandey, K. B., Mehdi, M. M., Maurya, P. K., & Rizvi, S. I. (2010). Disease Markers, 29(1), 31–36.
Rizvi, S. I., & Maurya, P. K. (2007). Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1100, 373–382.
Rizvi, S. I., Pandey, K. B., Jha, R., & Maurya, P. K. (2009). Rejuvenation Research, 12, 3–6.
Carafoli, E. (1987). Annual Review of Biochemistry, 56, 395–433.
Weed, R. I., LaCelle, P. L., & Merrill, E. W. (1969). The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 48(5), 795–809.
Dunn, M. J. (1974). Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 352(1), 97–116.
Palek, J., Stewart, G., & Lionetti, F. J. (1974). Blood, 44(4), 583–97.
Romero, P. J., & Romero, E. A. (1999). Blood Cells Molecular Disease, 25(1), 9–19.
Chandra, R., Joshi, P. C., Bajpai, V. K., & Gupta, C. M. (1987). Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 902(2), 253–262.
Zaidi, A. (2010). World J. Biol. Chem., 1(9), 271–280.
Sweadner, K. J., & Goldin, S. M. (1980). The New England Journal of Medicine, 302, 777–783.
Bor-Kucukatay, M., Wenby, R. B., Meiselman, H. J., & Baskurt, O. K. (2003). Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol, 284(5), H1577–84.
Jaitovich, A., & Bertorello, A. M. (2010). Life Sciences, 86, 73–78.
Maurya, P. K., & Prakash, S. (2011). Phytotherapy Research, 25(6), 944–946.
Rizvi, S. I., & Maurya, P. K. (2007). Molecular Biotechnology, 27, 58–61.
Rizvi, S. I., Jha, R., & Maurya, P. K. (2006). Rejuvenation Research, 9, 490–474.
Marchesi, V. T., & Palade, G. E. (1967). The Journal of Cell Biology, 35, 385–404.
Rizvi, S. I., & Luqman, S. (2003). Cellular and Molecular Biology Letters, 8, 919–925.
Fiske, C., & Subbarow, Y. (1925). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 66, 375–400.
Suhail, M., & Rizvi, S. I. (1987). Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 146, 179–186.
Benzie, I. F. F., & Strain, J. J. (1996). Analytical Biochemistry, 239, 70–76.
Lowry, O. H., Rosenbrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., & Randall, R. J. (1951). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 193, 265–275.
Dhermy, D., Simeon, J., Wautier, M. P., Boivin, P., & Wautier, J. L. (1987). Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 904(2), 201–206.
Romero, P. J. (1976). Journal of Membrane Biology, 29(4), 329–343.
Skekhoren, M. A., & Bonting, S. L. (1981). Physiological Reviews, 61, 1–76.
Rizvi, S. I., Kumar, N., Kant, R., & Maurya, P. K. (2012). Phytotherapy Research, 26(11), 1644–1647.
Friederichs, E., & Wurz, A. (1990). Biochemical Medicine and Metabolic Biology, 43, 39–44.
Kawamoto, E. M., Munhoz, C. D., Glezer, I., et al. (2005). Neurobiology of Aging, 26(6), 857–64.
Rizvi, S. I., & Zaid, M. A. (2005). Clinica Chimica Acta, 354, 59–67.
Freikman, I., Ringel, I., & Fibach, E. (2011). Journal of Membrane Biology, 240(2), 73–82.
Jain, K. S., & Sohet, S. B. (1981). Lipids, 642, 46–54.
Jorgensen, P. L., Hakansson, K. O., & Karlish, S. J. (2003). Annual Review of Physiology, 65, 817–49.
Conflicts of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maurya, P.K., Prakash, S. Decreased Activity of Ca++-ATPase and Na+/K+-ATPase during Aging in Humans. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 170, 131–137 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0172-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0172-8