Abstract
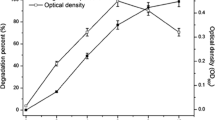
A multistep conversion system of para-substituted phenols by recombinant phenol hydroxylase (PHIND) and 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl 1,2-dioxygenase (BphCLA-4) was constructed in this study. Docking studies with different para-substituted phenols and corresponding catechols inside of the active site of PHIND and BphCLA-4 predicted that all the substrates should be transformed. High-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis showed that the products of multistep conversion were the corresponding para-substituted catechols and semialdehydes. For the first-step conversion, the formation rate of 4-fluorocatechol (0.39 μM/min/mg dry weight) by strain PHIND hydroxylation was 1.15, 6.50, 3.00, and 1.18-fold higher than the formation of 4-chlorocatechol, 4-bromocatechol, 4-nitrocatechol, and 4-methylcatechol, respectively. For the second-step conversion, the formation rates of semialdehydes by strain BphCLA-4 were as follows: 5-fluoro-HODA > 5-chloro-HODA > 2-hydroxy-5-nitro-ODA > 5-bromo-HODA > 2-hydroxy-5-methyl-ODA. The present study suggested that the multistep conversion by both ring hydroxylase and cleavage dioxygenase should be potential in the synthesis of industrial precursors and provide a novel avenue in the wastewater recycling treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Böttcher, D., & Bornscheuer, U. T. (2010). Current Opinion in Microbiology, 13, 274–282.
Schoemaker, H. E., Mink, D., & Wubbolts, M. G. (2003). Science, 299, 1694–1697.
Schmid, A., Dordick, J. S., Hauer, B., Kiener, A., Wubbolts, M., & Witholt, B. (2001). Nature, 409, 258–268.
Van Beilen, J. B., Duetz, W. A., Schmid, A., & Witholt, B. (2003). Trends in Biotechnology, 21, 170–177.
Tao, Y., Bentley, W. E., & Wood, T. K. (2005). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 68, 614–621.
Li, Z., van Beilen, J. B., Duetz, W. A., Schmid, A., de Raadt, A., Griengl, H., et al. (2002). Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 6, 136–144.
Urlacher, V. B., & Schmid, R. D. (2006). Recent advances in oxygenase-catalyzed biotransformations. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 10, 156–161.
Garikipati, S. V., McIver, A. M., & Peeples, T. L. (2009). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75, 6545–6552.
Coulombel, L., Nolan, L. C., Nikodinovic, J., Doyle, E. M., & O’Connor, K. E. (2011). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 89, 1867–1875.
Roberts, S. J., Morris, J. C., Dobson, R. C. J., & Gerrard, J. A. (2003). Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2, 265–267.
Gough, S. P., Kannangara, C. G., & Bock, K. (1989). Carlsberg Research Communications, 54, 99–108.
Grimm, B., Bull, A., & Breu, V. (1991). Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 225, 1–10.
Ferreira, M. I., Iida, T., Hasan, S. A., Nakamura, K., Fraaije, M. W., Janssen, D. B., et al. (2009). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75, 7767–7773.
Kitagawa, W., Kimura, N., & Kamagata, Y. (2004). Journal of Bacteriology, 186, 4894–4902.
Powlowski, J., & Shingler, V. (1994). Biodegradation, 5, 219–236.
Kirchner, U., Westphal, A. H., Müller, R., & van Berkel, W. J. (2003). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 284, 47545–47553.
Schlömann, M. (1994). Biodegradation, 5, 301–321.
Parales, R. E., Bruce, N. C., Schmid, A., & Wackett, L. P. (2001). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 4699–4709.
Marshall, C. T., & Woodley, J. M. (1995). Nature Biotechnology, 13, 1072–1078.
Bühler, B., Schmid, A., Hauer, B., & Witholt, B. (2000). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275, 10085–10092.
May, S. W., & Katopodis, A. G. (1986). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 8, 17–21.
Bell-Parikh, L. C., & Guengerich, F. P. (1999). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 274, 23833–23840.
Keener, W. K., & Arp, D. J. (1994). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 60, 1914–1920.
Li, A., Qu, Y. Y., Zhou, J. T., & Ma, F. (2009). FEMS Microbiology Letters, 292, 231–239.
Tan, D. H., Qu, Y. Y., Ma, F., Zhou, J. T., & Yuan, X. D. (2010). Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 42, 1977–1980.
Qu, Y. Y., Zhou, H., Li, A., Ma, F., & Zhou, J. T. (2011). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 89, 655–663.
Wu, Z. L., Podust, L. M., & Guengerich, F. P. (2005). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 41090–41100.
Furukawa, K., & Arimura, N. (1987). Journal of Bacteriology, 169, 924–927.
Eltis, L. D., Hofmann, B., Hecht, H. J., Lünsdorf, H., & Timmis, K. N. (1993). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 268, 2727–2732.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 21176040 and 51078054).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, Y., Shi, S., Ma, Q. et al. Multistep Conversion of para-Substituted Phenols by Phenol Hydroxylase and 2,3-Dihydroxybiphenyl 1,2-Dioxygenase. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 169, 2064–2075 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0112-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0112-7