Abstract
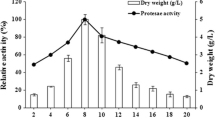
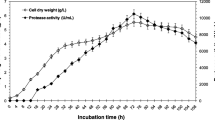
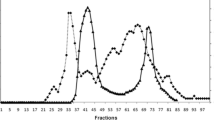
The purpose of this work was to purify a protease from Penicillium waksmanii and to determine its biochemical characteristics and specificity. The extracellular protease isolated that was produced by P. waksmanii is a serine protease that is essential for the reproduction and growth of the fungus. The protease isolated showed 32 kDa, and has optimal activity at pH 8.0 and 35 °C towards the substrate Abz-KLRSSKQ-EDDnp. The protease is active in the presence of CaCl2, KCl, and BaCl, and partially inhibited by CuCl2, CoCl2 and totally inhibited by AlCl3 and LiCl. In the presence of 1 M urea, the protease remains 50 % active. The activity of the protease increases 60 % when it is exposed to 0.4 % nonionic surfactant-Triton X-100 and loses 10 % activity in the presence of 0.4 % Tween-80. Using fluorescence resonance energy transfer analysis, the protease showed the most specificity for the peptide Abz-KIRSSKQ-EDDnp with k cat/K m of 10,666 mM−1 s−1, followed by the peptide Abz-GLRSSKQ-EDDnp with a k cat/K m of 7,500 mM−1 s−1. Basic and acidic side chain-containing amino acids performed best at subsite S1. Subsites S2, S3, S′ 2, and S′ 1, S′ 3 showed a preference for binding for amino acids with hydrophobic and basic amino acid side chain, respectively. High values of k cat/K m were observed for the subsites S2, S3, and S′ 2. The sequence of the N-terminus (ANVVQSNVPSWGLARLSSKKTGTTDYTYD) showed high similarity to the fungi Penicillium citrinum and Penicillium chrysogenum, with 89 % of identity at the amino acid level.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rao, M. B., Tanksale, A. M., Ghatge, M. S., & Deshpande, V. V. (1998). Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 62, 597–635.
Diamond, S. L. (2007). Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 11, 46–51.
Kumar, C. G., & Takagi, H. (1999). Biotechnology Advances, 17, 561–594.
Gupta, R., Beg, Q. K., & Lorenz, P. (2002). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 59, 15–32.
Joo, H. S., Chang, C. S., & Kumar, C. G. (2003). Journal of Applied Microbiology, 95, 267–272.
Wang, S. L., Yang, C. H., Liang, T. W., & Yen, Y. H. (2008). Bioresource Technology, 99, 3700–3707.
Djamel, C., Ali, T., & Nelly, C. (2009). European Journal of Scientific Research, 25, 469–477.
Doughari, J. H. (2011). African Journal of Biotechnology, 10, 9657–9660.
Schechter, I., & Berger, A. (1967). Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 27, 157–162.
Alves, A. C. V., Rogana, E., Barbosa, C. F., & Ferreira-Alves, D. L. (2007). Journal of Biochemical and Biophysical Methods, 70, 471–479.
Tran, L. H., & Nagano, H. (2002). Journal of Food Science, 67, 1184–1187.
Sarath, G., De La Motte, R. S., & Wagner, F. W. (1989). In R. J. Beynon & J. S. Bond (Eds.), Proteolytic enzymes: a practical approach, vol.1.; Peptidase assay methods (pp. 25–55). New York: IRL Press, Oxford University Press.
Meyers, S. P., & Ahearn, D. G. (1977). Mycologia, 69, 646–651.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Nature, 227, 680–685.
See, Y. S., & Jackowski, G. (1989). In T. E. Creigton (Ed.), Protein structure: a practical approach, vol.1: Estimating molecular weights of polypeptides by SDS gel electrophoresis (pp. 1–21). New York: IRL Press, Oxford University.
Hirata, I. Y., Cezari, M. H. S., Nakaie, C. R., Boschcov, P., Ito, A. S., Juliano, M. A., & Juliano, L. (1994). Letters in Peptide Science, 1, 299–308.
Bersanetti, P. A., Park, H. Y., Bae, K. S., Son, K. H., Shin, D. H., Hirata, I. Y., Juliano, M. A., Carmona, A. K., & Juliano, L. (2005). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 37, 574–581.
Leatherbarrow, R. J. (1992) Grafit version 5.0. Staines: Erithacus Software Ltd.
Klemencic, I., Carmona, A. K., Cezari, M. H., Juliano, M. A., Juliano, L., Guncar, G., Turk, D., Krizaj, I., Turk, V., & Turk, B. (2000). European Journal of Biochemistry, 267, 5404–5412.
Dunn, B. M. (1989). In R. J. Beynon & J. S. Bond (Eds.), Proteolytic enzymes, vol.1: A practical approach: determination of protease mechanism (pp. 57–81). New York: IRL Press, Oxford University Press.
Edman, P. A. (1949). Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 22, 475.
Fretweel, J. F., Ismail, S. M. K., Cummings, J. M., & Selby, T. L. (2008). Molecular BioSystems, 4, 862–870.
Reichard, U., Büttner, S., Eiffert, H., Staib, F., & Rüchel, R. (1990). Journal of Medical Microbiology, 33, 243–251.
Monod, M., Togni, G., Rahalison, L., & Frenk, E. (1991). Journal of Medical Microbiology, 35, 23–28.
Larcher, G., Bouchara, J. P., Annaix, V., Symoens, F., Chabasse, D., & Tronchin, G. (1992). FEBS Letters, 308, 65–69.
Tunga, R., Shrivastava, B., & Banerjee, R. (2003). Process Biochemistry, 38, 1553–1558.
Tremacoldi, C. R., Monti, R., Selistre-De-Araújo, H. S., & Carmona, E. C. (2007). World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 23, 295–299.
Hajji, M., Kanoun, S., Nasri, M., & Gharsallah, N. (2007). Process Biochemistry, 42, 791–797.
Peña-Montes, C., González, A., Castro-Ochoa, D., & Farrés, A. (2008). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 78, 603–612.
Rocco, A. G., Mollica, L., Ricchiuto, P., Baptista, A. M., Gianazza, E., & Eberini, I. (2008). Biophysical Journal, 94, 2241–2251.
Merheb-Dini, C., Cabral, H., Leite, R. S. R., Zanphorlin, L. M., Okamoto, D. N., Rodriguez, G. O. B., Juliano, L., Arantes, E. C., Gomes, E., & Da Silva, R. (2009). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 57, 9210–9217.
Haddar, A., Agrebi, R., Bougatef, A., Hmidet, N., Sellami-Kamoun, A., & Nasri, M. (2009). Bioresource Technology, 100, 3366–3373.
Sampaio e Silva, T. A., Knob, A., Tremacoldi, C. R., Brochetto-Braga, M. R., & Carmona, E. C. (2011). World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 27, 2491–2497.
Zanphorlin, L. M., Cabral, H., Arantes, E., Assis, D., Juliano, L., Juliano, M. A., Da-Silva, R., Gomes, E., & Bonilla-Rodriguez, G. O. (2011). Process Biochemistry, 46, 2137–2143.
Honorata, C., & Jacek, O. (1999). European Journal of Biochemistry, 260, 571–595.
Yamamoto, N., Matsumoto, K., Yamagata, Y., Hirano, K., & Ichishima, E. (1999). Phytochemistry, 32, 1393–1397.
van den Berg, M. A., Albang, R., Albermann, K., Badger, J. H., Daran, J. M., Driessen, A. J., Garcia-Estrada, C., Fedorova, N. D., Harris, D. M., Heijne, W. H., Joardar, V., Kiel, J. A., Kovalchuk, A., Martin, J. F., Nierman, W. C., Nijland, J. G., Pronk, J. T., Roubos, J. A., van der Klei, I. J., van Peij, N. N., Veenhuis, M., von Dohren, H., Wagner, C., Wortman, J., & Bovenberg, R. A. (2008). Nature Biotechnology, 26, 1161–1168.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from Brazilian National Council for Research and Development (CNPq) and Sao Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) Sao Paulo, Brazil. All authors have agreed to submit this manuscript to the “Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Graminho, E.R., da Silva, R.R., de Freitas Cabral, T.P. et al. Purification, Characterization, and Specificity Determination of a New Serine Protease Secreted by Penicillium waksmanii . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 169, 201–214 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9974-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9974-3