Abstract
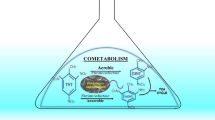
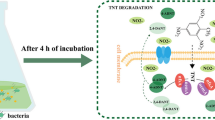
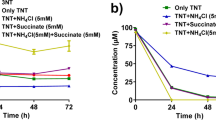
2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene (TNT), an extensively used and versatile explosive, is harmful in soil and water. In the present study, four bacterial strains capable of degrading TNT have been isolated from contaminated sites and named as Thu-A, Thu-B, Thu-C, and Thu-Z. Thu-Z, which gave the highest degradation efficiency compared to the others, was assigned to the genus Pantoea according to its 16S rRNA gene. Similarities in both biochemical properties and morphology suggested that Thu-Z was a Pantoea sp. strain. Thu-Z was proved to be capable of using TNT as a sole nitrogen source by cleaving NO2 from the nitroaromatic ring by direct aromatic ring reduction. Under nitrogen-limited conditions, 96.6 % N of TNT was consumed by Thu-Z for growth, which was determined in terms of NaNO2. Trace nitro reduction metabolites such as 2,4-diamino-6-nitrotoluene (24Dam) and 2,6-diamino-4-nitrotoluene (26Dam) were identified in the presence of (NH4)2SO4. On the other hand, 4,4′,6,6′-tetranitro-2,2′-azoxytoluene (22Azo) and 2,2′,6,6′-tetranitro-4,4′-azoxytoluene (44Azo) were detected in the absence of (NH4)2SO4. These indicated the existence of a dual pathway for Thu-Z, while the direct aromatic ring reduction was predominant. Addition of a nitrogen source ((NH4)2SO4) after inoculation stimulated the growth of Thu-Z and accelerated TNT degradation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lewis, T. A., Newcombe, D. A., & Crawford, R. L. (2004). Journal of Environmental Management, 70, 291–307.
Zou, H. F., Zhou, S. F., Hu, X., Zhang, Y. K., Lu, P. C. (1994). JPC-J. Planar Chromatogr.-Mod. TLC 7, 461-463.
Schrader, P. S., & Hess, T. F. (2004). Journal of Environmental Quality, 33(4), 1202–1209.
Ibeanusi, V., Jeilani, Y., Houston, S., Doss, D., & Coley, B. (2009). Biotechnology Letters, 31, 65–69.
Zarlpov, S. A., Naumov, A. V., Abdrakhmanova, J. F., Garusov, A. V., & Naumma, R. P. (2002). FEMS Microbiology Letters, 217, 213–217.
Hawari, J., Beaudet, S., Halasz, A., Thiboutot, S., & Ampleman, G. (2000). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 54, 605–618.
Jain, M. R., Zinjarde, S. S., Deobagkar, D. D., & Deobagkar, D. N. (2004). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 49, 783–788.
Held, T., Draude, G., Schmidt, F. R. J., Brokamp, A., & Reis, K. H. (1997). Environmental Technology, 18, 479–487.
Schmelling, D. C., & Gray, K. A. (1995). Water Research, 29, 2651–2662.
Hundal, L. S., Singh, J., Bier, E. L., Shea, P. J., Comfort, S. D., & Powers, W. L. (1997). Environmental Pollution, 97, 55–64.
Arienzo, M. (2000). Chemosphere, 40, 441–448.
Park, J., Comfort, S. D., Shea, P. J., & Machacek, T. A. (2004). Journal of Environmental Quality, 33, 1305–1313.
Singh, J., Comfort, S. D., & Shea, P. J. (1999). Environmental Science and Technology, 33, 1488–1494.
Hwang, S., Batchelor, C. J., Davis, J. L., & MacMillan, D. K. (2005). Journal Environment Science Health Part A: Toxic/Hazard Substance Environment Engineering, 40, 581–592.
Saupe, A., Garvens, H. J., & Heinze, L. (1998). Chemosphere, 36, 1725–1744.
Vasilyeva, G. K., Kreslavski, V. D., Oh, B. T., & Shea, P. J. (2001). Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 20, 965–971.
Vasilyeva, G. K., Kreslavski, V. D., & Shea, P. J. (2002). Chemosphere, 47, 311–317.
Rodgers, J. D., & Bunce, N. J. (2001). Environmental Science and Technology, 35, 406–410.
Kulkarni, M., & Chaudhari, A. (2007). Journal of Environmental Management, 85, 496–512.
Harrison, I., & Vane, C. H. (2010). Water Science and Technology, 61, 2531–2538.
Parrish, F. W. (1977). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 34, 232–233.
Bayman, P., & Radkar, G. V. (1997). International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 39, 45–53.
Weber, R. W. S., Ridderbusch, D. C., & Anke, H. (2002). Mycological Research, 106, 336–344.
Oh, K. H., & Kim, Y. J. (1998). Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 61, 702–708.
French, C. E., Nicklin, S., & Bruce, N. C. (1998). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 64, 2864–2868.
De, L. M., & Craig, M. (2009). Current Microbiology, 58, 81–86.
Kim, H. Y., & Song, H. G. (2000). Current Microbiology, 41, 317–320.
Adrian, N. R., & Arnett, C. M. (2004). Current Microbiology, 48, 332–340.
Esteve-Nunez, A., Caballero, A., & Ramos, J. L. (2001). Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 65, 335–352.
Ziganshin, A. M., Naumov, A. V., Suvorova, E. S., Naumenko, E. A., & Naumova, R. P. (2007). Microbiology, 76, 676–682.
Ziganshin, A. M., Gerlach, R., Borch, T., Naumov, A. V., & Naumova, R. P. (2007). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73, 7898–7905.
Duque, E., Haidour, A., Godoy, F., & Ramos, J. L. (1993). Journal of Bacteriology, 175, 2278–2283.
Zaripov, S. A., Naumov, A. V., Nikitina, E. V., & Naumova, R. P. (2002). Microbiology, 71, 558–562.
Zaripov, S. A., Naumov, A. V., Suvorova, E. S., Garusov, A. V., & Naumova, R. P. (2004). Microbiology, 73, 398–403.
Borch, T., & Gerlach, R. (2004). Journal of Chromatography. A, 1022, 83–94.
Nyanhongo, G. S., Erlacher, A., Schroeder, M., & Gubitz, G. A. (2006). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 39, 1197–1204.
Cai, B., Han, Y., Liu, B., Ren, Y., & Jiang, S. (2003). Letters in Applied Microbiology, 36, 272–276.
Iimura, K., & Hosono, A. (1996). International Journal of Food Microbiology, 30, 243–253.
Cambria, M. T., Minniti, Z., Librando, V., & Cambria, A. (2008). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 149, 1–8.
Suja, E., Nancharaiah, Y. V., & Venugopalan, V. P. (2012). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology. doi:10.1007/s12010-012-9594-y.
Haidour, A., & Ramos, J. L. (1996). Environmental Science and Technology, 30, 2365–2370.
Hua, X. F., Wang, J., Wu, Z. J., Zhang, H. X., Li, H. P., Xing, X. H., & Liu, Z. (2010). Biochemical Engineering Journal, 49, 201–206.
Medrano, E. G., & Bell, A. A. (2007). Journal of Applied Microbiology, 102, 134–143.
Yeung, K. F., Lee, K. M., & Woodard, R. W. (1998). Journal of Natural Products, 61, 207–211.
Acknowledgment
Financial supports of this work by the Doctoral Fund of Ministry of Education of China (grant no. 20100002110023) and by the Ministry of Science and Technology through 973 Project under grant no. 2009CB724702 are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, L., Lu, D. & Liu, Z. Pathways for Degrading TNT by Thu-Z: a Pantoea sp. Strain. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 168, 1976–1988 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9911-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9911-5