Abstract
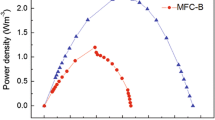
Two microbial fuel cells (MFCs) inoculated with activated sludge of a wastewater treatment plant were constructed. Oxygen was provided by mechanical aeration in the cathodic chamber of one MFC, whereas it was obtained by the photosynthesis of algae in the other. Electrogenic capabilities of both MFCs were compared under the same operational conditions. Results showed that the MFC with mechanical aeration in the cathodic chamber displayed higher power output than the one with photosynthesis of algae. Good linear relationship between power density and chemical oxygen demand (COD) loading rate was obtained only on the MFC with mechanical aeration. Furthermore, the relationships between power density and effluent COD and between Coulombic efficiency and COD loading rate can only be expressed as binary quadratic equations for the MFC with mechanical aeration and not for the one with photosynthesis of algae.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Logan, B. E., & Regan, J. M. (2006). Electricity-producing bacterial communities in microbial fuel cells. Trends in Microbiology, 14, 512–518.
You, S. J., Zhao, Q. L., Jiang, J. Q., & Zhang, J. N. (2006). Treatment of domestic wastewater with simultaneous electricity generation in microbial fuel cell under continuous operation. Chemical and Biochemical Engineering Quarterly, 20, 407–412.
Kim, H. J., Park, H. S., Hyun, M. S., Chang, I. S., Kim, M., & Kim, B. H. (2002). A mediator-less microbial fuel cell using a metal reducing bacterium, Shewanella putrefacians. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 30, 145–152.
Rabaey, K., & Verstraete, W. (2005). Microbial fuel cells: Novel biotechnology for energy generation. Trends in Biotechnology, 23, 291–298.
Oh, S., & Logan, B. (2006). Proton exchange membrane and electrode surface areas as factors that affect power generation in microbial fuel cells. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 70, 162–169.
Ieropoulos, I., Winfield, J., & Greenman, J. (2010). Effects of flow-rate, inoculum and time on the internal resistance of microbial fuel cells. Bioresource Technology, 101, 3520–3525.
Gil, G. C., Chang, L. S., Kim, B. H., Kim, M., Jang, J. K., Park, H. S., et al. (2003). Operational parameters affecting the performance of a mediator-less microbial fuel cell. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 18, 327–334.
Kang, K. H., Jang, J. K., Pham, T. H., Moon, H., Chang, I. S., & Kim, B. H. (2003). A microbial fuel cell with improved cathode reaction as a low biochemical oxygen demand sensor. Biotechnology Letters, 25, 1357–1361.
Pham, T. H., Jang, J. K., Chang, I. S., & Kim, B. H. (2004). Improvement of cathode reaction of a mediatorless microbial fuel cell. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 14, 324–329.
Rodrigo, M. A., Cañizares, P., & Lobato, J. (2010). Effect of the electron-acceptors on the performance of a MFC. Bioresource Technology, 101, 7014–7018.
Rosenbaum, M., He, Z., & Angenent, L. T. (2010). Light energy to bioelectricity: Photosynthetic microbial fuel cells. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 21, 259–264.
Strik, D. P. B. T. B., Terlouw, H., Hamelers, H. V. M., & Buisman, C. J. N. (2008). Renewable sustainable biocatalyzed electricity production in a photosynthetic algal microbial fuel cell (PAMFC). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 81, 659–668.
Schamphelaire, L. D., & Verstraete, W. (2009). Revival of the biological sunlight-to-biogas energy conversion system. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 103, 296–304.
Wang, X., Feng, Y., Liu, J., Lee, H., Li, C., Li, N., et al. (2010). Sequestration of CO2 discharged from anode by algal cathode in microbial carbon capture cells (MCCs). Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 25, 2639–2643.
Rodrigo, M. A., Cañizares, P., Lobato, R., Paz, R., Sáez, C., & Linares, J. J. (2007). Production of electricity from the treatment of urban waste water using a microbial fuel cell. Journal of Power Sources, 169, 198–204.
Mohan, S. V., Mohanakrishna, G., & Sarma, P. N. (2010). Composite vegetable waste as renewable resource for bioelectricity generation through non-catalyzed open-air cathode microbial fuel cell. Bioresource Technology, 101, 970–976.
Min, B., & Logan, B. E. (2004). Continuous electricity generation from domestic wastewater and organic substrates in a flat plate microbial fuel cell. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 5809–5814.
Wang, X., Feng, Y., & Lee, J. H. (2008). Electricity production from beer brewery wastewater using single chamber microbial fuel cell. Water Science and Technology, 57, 1117–1121.
Juang, D. F., Yang, P. C., & Kuo, T. H. (2012). Effects of flow rate and COD removal characteristics on power generation performance of microbial fuel cells. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 9, 267–280.
Clesceri, L. S., Greenberg, A. E., & Eaton, A. D. (2001). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association (APHA), American Water Works Association (AWWA) and Water Environment Federation (WEF).
Behera, M., & Ghangrekar, M. M. (2009). Performance of microbial fuel cell in response to change in sludge loading rate at different anodic feed pH. Bioresource Technology, 100, 5114–5121.
Rodrigo, M. A., Cañizares, P., García, H., Linares, J. J., & Lobato, J. (2009). Study of the acclimation stage and of the effect of the biodegradability on the performance of a microbial fuel cell. Bioresource Technology, 100, 4704–4710.
Sun, J., Hu, Y., Bi, Z., & Cao, Y. (2009). Improved performance of air-cathode single-chamber microbial fuel cell for wastewater treatment using microfiltration membranes and multiple sludge inoculation. Journal of Power Sources, 187, 471–479.
Jiang, J., Zhaom, Q., Zhang, J., Zhang, G., & Lee, D. (2009). Electricity generation from bio-treatment of sewage sludge with microbial fuel cell. Bioresource Technology, 100, 5808–5812.
Ghangrekar, M. M., & Shinde, V. B. (2007). Performance of membrane-less microbial fuel cell treating wastewater and effect of electrode distance and area on electricity production. Bioresource Technology, 98, 2879–2885.
Teneva, I., Dzhambazov, B., Koleva, L., Mladenov, R., & Schirmer, K. (2005). Toxic potential of five freshwater Phormidium species (Cyanoprokaryota). Toxicon, 45, 711–725.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to express their gratitude and appreciation to the National Science Council (NSC) of Taiwan for the financial support of this research under contract no. NSC-99-2221-E-276-004-.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Juang, DF., Lee, CH., Hsueh, SC. et al. Power Generation Capabilities of Microbial Fuel Cells with Different Oxygen Supplies in the Cathodic Chamber. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 167, 714–731 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9708-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9708-6