Abstract
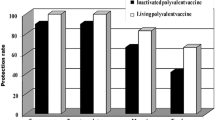
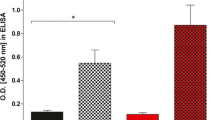
The present study aimed to detect and characterize antigenic proteins and to assess their activity as preventive vaccines against dermatobiosis. Polyclonal antibodies were produced against three larval instars (L1, L2, L3), and their antigenic proteins were assessed for reactivity. Polyclonal antibodies produced in animals immunized with extracts were analyzed, and L3-derived antibodies showed proteins with better antigenic responses. The study of reactivity using immunodetection showed that the 50-kDa protein had the highest antigenicity. This protein was purified and subjected to mass spectrometry, and the sequences obtained were compared with those in the databases available. No similarities were found with existing sequences. Subsequently, large quantities of purified protein were used to immunize cattle. Vaccine effectiveness was evaluated by comparing the number of cutaneous nodules formed in the control group and immunized animals. The antigen produced proved a promising candidate for vaccine production, with 90.67 % efficacy. Immunohistochemistry of antigen–antibody reaction in larval sections showed epitopes all over larval tissues.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pereira, M. C. T., Leite, V. H. R., & Leite, A. C. R. (2001). Medical and Veterinary Entomology, 15, 1–6.
Hall, M., & Wall, R. (1995). Advances in Parasitology, 35, 257–333.
Muniz, R. A., Cerqueira-Leite, R., Coronado, A., Soraci, O., Umehara, O., Moreno, J., & Errecalde, J. (1995). Veterinary Parasitology, 60, 265–271.
Stevens, J. R., Wallman, J. F., Otranto, D., Wall, R., Pape, T., & 4. (2006). Trends in Parasitology, 22, 181–188.
Barriga, O. O. (2002). Veterinary Parasitology, 55(1), 29–55.
Chabaudie, N., & Boulard, C. (1992). Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology, 31, 167–177.
Johnson, M., Labes, R. E., Taylor, M. J., & Mackintosh, C. G. (2003). Veterinary Parasitology, 117, 131–137.
Brant, M. P. R., Guimarães, S., Souza-Neto, J. A., Ribolla, P. E. M., & Oliveira-Sequeira, T. C. G. (2010). Veterinary Parasitology, 168(3–4), 304–311.
Sandeman, R. M., Feehan, J. P., Chandler, R. A., & Bowles, V. M. (1990). International Journal for Parasitology, 20, 1019–1023.
Pruett, J. H. (1993). Journal of Parasitology, 79, 829–833.
Muharsini, S., Sukarsih, R. G., Partoutomo, S., Hamilton, S., Willadesen, P., & Wijffels, G. (2000). International Journal for Parasitology, 30, 705–714.
Taubouret, G., Prevot, F., Bergeaud, J. P., Dorchies, P. H., & Jacquiet, P. (2001). Veterinary Parasitology, 101, 53–66.
Taubouret, G., Bret-Bennis, J., Dorchies, P., & Jacquiet, P. H. (2003). Veterinary Parasitology, 114, 305–314.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). Analytical Biochemistry, 72(1), 248–254.
Gingrich, R. E. (1982). Veterinary Parasitology, 9, 233–242.
Baron, R. W., & Weintraub, J. (1987). Veterinary Parasitology, 24, 285–296.
Tellam, R. L., Eismann, C. H., & Pearson, R. D. (1994). International Journal for Parasitology, 24, 757–764.
Innocenti, L., Masetti, M., Machhioni, F., & Giorgi, F. (1995). Veterinary Parasitology, 60, 273–282.
Smith, W. D., & Zarlenga, D. S. (2006). Veterinary Parasitology, 139, 347–359.
Crampton, A., & Vanniasinkam, T. (2007). Infection, Genetics and Evolution, 7(5), 664–673.
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported by National Council for Scientific and Technological Development, Brazil (CNPq) and was part of a doctoral thesis submitted to the PhD Program on Bioprocess Engineering and Biotechnology at Federal University of Paraná, Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernandes, N.L.M., Zanata, S.M., Rönnau, M. et al. Production of Potential Vaccine Against Dermatobia hominis for Cattle. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 167, 412–424 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9683-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9683-y