Abstract
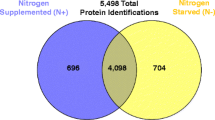
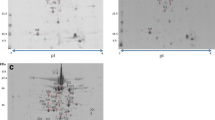
Caffeine is toxic to most microorganisms. However, some filamentous fungi, such as Aspergillus tamarii, are able to metabolize this alkaloid when fed caffeine as the sole nitrogen source. The aim of the present work was to identify intracellular A. tamarii proteins, regulated by caffeine, using fluorescence difference two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Specific proteins from two culture media of A. tamarii grown either on ammonium sulfate or caffeine as the sole nitrogen source were analysed by mass spectrometry. Thirteen out of a total of 85 differentially expressed spots were identified after database search. Identified up-regulated proteins include phosphoglycerate kinase, malate dehydrogenase, dyp-type peroxidase family protein, heat shock protein, Cu, Zn superoxidase dismutase and xanthine dehydrogenase. Some of the proteins identified in this study are involved in the caffeine degradation pathway as well as in stress response, suggesting that stress proteins could be involved in caffeine metabolism in filamentous fungi.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brand, D., Pandey, A., Roussos, S., & Soccol, C. R. (2000). Biological detoxification of coffee husk by filamentous fungi using a solid state fermentation system. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 27, 127–133.
Bressani, R. (1979). Antiphysiological factors in coffee pulp. In J. E. Braham & R. Bressani (Eds.), Chemical composition of coffee-berry by-products (pp. 83–95). Ottawa: INDRC.
Cabezas, M. T., Estrada, E., Murillo, B., Gonzalez, J. M., & Brezan, R. (1976). Coffee hulls and pulp. XII. Effect of storage of coffee pulp on its nutritive value for calves. Archivos Latinoamericanos de Nutricion, 26, 203–215.
Denis, S. (1996). Université de Montpellier, Montpellier, France.
Droge, W. (2002). Free radicals in the physiological control of cell function. Physiological Reviews, 82, 47–95.
Drori, N., Kramer-Haimovich, H., Rollins, J., Dinoor, A., Okon, Y., Pines, O., et al. (2003). External pH and nitrogen source affect secretion of pectate lyase by Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 69, 3258–3262.
Freitag, D. G., Ouimet, P. M., Girvitz, T. L., & Kapoor, M. (1997). Heat shock protein 80 of Neurospora crassa, a cytosolic molecular chaperone of the eukaryotic stress 90 family, interacts directly with heat shock protein 70. Biochemistry, 36, 10221–10229.
Gomez-Brenes, R. A., Bendana, G., Gonzalez, J. M., Braham, J. E., & Bressani, R. (1985). Relationship between the included levels of coffee pulp and the protein content in rations for monogastric animals. Archivos Latinoamericanos de Nutricion, 35, 422–437.
Gonzalez-Candelas, L., & Kolattukudy, P. E. (1992). Isolation and analysis of a novel inducible pectate lyase gene from the phytopathogenic fungus Fusarium solani f. sp. pisi (Nectria haematococca, mating population VI). Journal of Bacteriology, 174, 6343–6349.
Gutierrez-Sanchez, G. (2004). Université de Provence, Provence, France.
Gutierrez-Sanchez, G., Roussos, S., & Augur, C. (2004). Effect of the nitrogen source on caffeine degradation by Aspergillus tamarii. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 38, 50–55.
Hakil, M. (1999). Université de Franche-Comté, Franche-Comté, France.
Hakil, M., Denis, S., Viniegra-González, G., & Augur, C. (1998). Degradation and product analysis of caffeine and related dimethylxanthines by filamentous fungi. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 22, 355–359.
Hakil, M., Voisinet, F., Viniegra-González, G., & Augur, C. (1999). Caffeine degradation in solid state fermentation by Aspergillus tamarii: effects of additional nitrogen sources. Process Biochemistry, 35, 103–109.
Hernandez-Macedo, M. L., Ferraz, A., Rodriguez, J., Ottoboni, L. M. M., & De Mello, M. P. (2002). Iron-regulated proteins in Phanerochaete chrysosporium and Lentinula edodes: differential analysis by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis profiles. Electrophoresis, 23, 655–661.
Holdom, M. D., Hay, R. J., & Hamilton, A. J. (1996). The Cu, Zn superoxide dismutases of Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus terreus: purification and biochemical comparison with the Aspergillus fumigatus Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase. Infection and Immunity, 64, 3326–3332.
Hu, Y., Wang, G., Chen, G. Y. J., Fu, X., & Yao, S. Q. (2003). Proteome analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae under metal stress by two-dimensional differential gel electrophoresis. Electrophoresis, 24, 1458–1470.
Ina, K. (1971). Biochemical studies of caffeine—degradation of caffeine by mold. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 35, A32–A35.
Kernec, F., Ünlü, M., Labeikovsky, W., Minden, J. S., & Koretsky, A. P. (2001). Changes in the mitochondrial proteome from mouse hearts deficient in creatine kinase. Physiological Genomics, 6, 117–128.
Lawrence, J. C., Jr., & Salsgiver, W. J. (1984). Evidence that levels of malate dehydrogenase and fumarase are increased by cAMP in rat myotubes. American Journal of Physiology, 247, C33–C38.
Ma, B., Zhang, K., Hendrie, C., Liang, C., Li, M., Doherty-Kirby, A., et al. (2003). PEAKS: powerful software for peptide de novo sequencing by tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 17, 2337–2342.
Mukhopadhyay, S., Mondal, A., & Poddar, M. K. (2003). Chronic administration of caffeine: effect on the activities of hepatic antioxidant enzymes of Ehrlich ascites tumor-bearing mice. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology, 41, 283–289.
O'Farrell, P. H. (1975). High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 250, 4007–4021.
Oberegger, H., Zadra, I., Schoeser, M., & Haas, H. (2000). Iron starvation leads to increased expression of Cu/Zn—superoxide dismutase in Aspergillus. FEBS Letters, 485, 113–116.
Park, S. G., Cha, M. K., Jeong, W., & Kim, I. H. (2000). Distinct physiological functions of thiol peroxidase isoenzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275, 5723–5732.
Piper, P. W., Curran, B., Davies, M. W., Hirst, K., Lockheart, A., & Seward, K. (1988). Catabolite control of the elevation of PGK mRNA levels by heat shock in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Molecular Microbiology, 2, 353–361.
Plesofsky-Vig, N., & Brambl, R. (1990). Gene sequence and analysis of hsp30, a small heat shock protein of Neurospora crassa which associates with mitochondria. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 265, 15432–15440.
Roussos, S., Aquiahuatl, M. D., Trejo Hernandez, M. D., Perraud, I. G., Favela, E., Ramakrishna, M., et al. (1995). Biotechnological management of coffee pulp—isolation, screening characterization, selection of caffeine degrading fungi and natural microflora present in coffee pulp and husk. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 42, 756–762.
Roussos, S., Hannibal, L., Aquiahuatl, M. A., Hernandez, M. R. T., & Marakis, S. (1994). Caffeine degradation by Penicillium verrucosum in solid-state fermentation of coffee pulp—critical effect of additional inorganic and organic nitrogen sources. Journal of Food Science and Technology Mys, 31, 316–319.
Sakai, J., Ishikawa, H., Kojima, S., Satoh, H., Yamamoto, S., & Kanaoka, M. (2003). Proteomic analysis of rat heart in ischemia and ischemia reperfusion using fluorescence two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis. Proteomics, 3, 1318–1324.
Schwimmer, S., Kurtzman, J. R. H., & Heftmann, E. (1971). Caffeine metabolism by Penicillium roqueforti. Arch Biochem Biophys, 147, 109–113.
Skynner, H. A., Rosahl, T. W., Knowles, M. R., Salim, K., Reid, L., Cothliff, R., et al. (2002). Alterations of stress related proteins in genetically altered mice revealed by two-dimensional differential in-gel electrophoresis analysis. Proteomics, 2, 1018–1025.
Tagliari, C. V., Sanson, R. K., Zanette, A., Franco, T. T., & Soccol, C. R. (2003). Caffeine degradation by Rhizopus delemar in packed bed column bioreactor using coffee husk as substrate. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 34, 102–104.
Tonge, R., Shaw, J., Middleton, B., Rowlinson, R., Rayner, S., Young, J., et al. (2001). Validation and development of fluorescence two-dimensional differential gel electrophoresis proteomics technology. Proteomics, 1, 377–396.
Tortora, P., Burlini, N., Hanozet, G. M., & Guerritore, A. (1982). Effect of caffeine on glucose-indused inactivation of gluconeogenetic enzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. A possible role of cyclic AMP. European Journal of Biochemistry, 126, 617–622.
Ünlü, M., Morgan, M. E., & Minden, J. S. (1997). Difference gel electrophoresis: a single gel method for detecting changes in proteinextracts. Electrophoresis, 18, 2071–2077.
Van den Bergh, G., Clerens, S., & Arckens, L. (2003). Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography prefractionation prior to two-dimensional difference gel eletrophoresis and mass spectrometry identifies new differentially expressed proteins between striate cortex of kitten and adult cat. Electrophoresis, 24, 1471–1481.
Van den Bergh, G., Clerens, S., Cnops, L., Vandesande, F., & Arckens, L. (2003). Fluorescent two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry identify age- related protein expression differences for the primary visual cortex of kitten and adult cat. Journal of Neurochemistry, 85, 193–205.
Yan, J. X., Devenish, R., Wait, R., Stone, T., Lewis, S., & Fowler, S. (2002). Fluorescence two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry based proteomic analysis of Escherichia coli. Proteomics, 2, 1682–1698.
Zhou, G., Li, H. M., DeCamp, D., Chen, S., Shu, H. J., Gong, Y., et al. (2002). 2D differential in-gel electrophoresis for the identification of esophageal scans cell cancer—specific protein markers. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 1, 117–124.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge Dr. Tracy Andacht and Dr. Maria E. for the technical advice. Present work was supported by the Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD-France). G. Gutiérrez-Sánchez was awarded a Ph.D. scholarship by the National Council of Science and Technology (CONACyT, Mexico), Grant No. 130250.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper is dedicated to the memory of Christopher Augur, esteemed colleague and friend.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gutiérrez-Sánchez, G., Atwood, J., Kolli, V.S.K. et al. Initial Proteome Analysis of Caffeine-Induced Proteins in Aspergillus tamarii Using Two-Dimensional Fluorescence Difference Gel Electrophoresis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 166, 2064–2077 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9634-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9634-7