Abstract
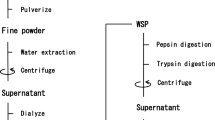
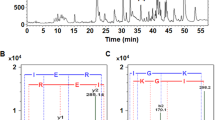
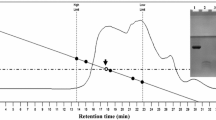
Ammonium sulphate cut protein extracts, and their pepsin hydrolysates, from the rhizomes of 15 plants in the Zingiberaceae family were screened for their in vitro angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory (ACEI) activity. The protein extract from Zingiber ottensii had the highest ACEI activity (IC50 of 7.30 × 10−7 mg protein/mL) and was enriched for by SP Sepharose chromatography with five NaCl step gradients 0, 0.25, 0.50, 0.75 and 1 M NaCl collecting the corresponding five fractions. The highest ACEI activity was found in the F75 fraction, which appeared to contain a single 20.7-kDa protein, suggesting enrichment to or near to homogeneity. The ACEI activity of the F75 fraction was moderately thermostable (−20–60 °C), showed >80% activity across a broad pH range of 4–12 (optimal at pH 4–5) and appeared as a competitive inhibitor of ACE (K i of 9.1 × 10−5 mg protein/mL). For the pepsin hydrolysates, that from Zingiber cassumunar revealed the highest ACEI activity (IC50 of 0.38 ± 0.012 mg/mL), was enriched to a single active hexapeptide by RP-HPLC with a strong ACEI activity (IC50 of 0.011 ± 0.012 mg/mL) and acted as a competitive inhibitor of ACE (K i of 1.25 × 10−6 mg protein/mL).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guyton, A. C., & Hall, J. E. (2006). Textbook of medical physiology (11th ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders.
Egan, B. M., Basile, J. N., & Lackland, D. T. (2004). Hypertension: Hot topics. Philadelphia: Hanley & Belfus, Inc.
Ganten, D., Unger, T., & Lang, R. E. (1984). Arzneimittel-Forschung, 34, 1391–1398.
Kostis, J. B., & DeFelice, E. A. (1987). Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. New York: Alan R. Liss., Inc.
Brown, N. J., & Vaughan, D. E. (1998). Circulation, 97, 1411–1420.
Pihlanto, A., & Korhonen, H. (2003). Advances in Food and Nutrition Research, 47, 175–276.
Kitts, D. D., & Weiler, K. (2003). Current Pharmaceutical Design, 9, 1309–1323.
Möller, N. P., Scholz-Ahrens, K. E., Roos, N., & Schrezenmeir, J. (2008). European Journal of Nutrition, 47, 171–182.
Larsen, K. (1980). Natural History Bulletin of the Siam Society, 151–169.
Je, J. Y., Park, P. J., Kim, E. K., & Ahn, C. B. (2009). Food Chemistry, 113, 932–935.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Nature, 227, 680–685.
Tiptara, P., Petsom, A., Roengsumran, S., & Sangvanich, P. (2008). Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 88, 1025–1034.
Mortz, E., Vorm, O., Mann, M., & Roepstorff, P. (1994). Biological Mass Spectrometry, 23, 249–261.
Arihara, K., Nakashima, T., Mukai, T., Ishikawa, S., & Itoh, M. (2001). Meat Science, 57, 319–324.
Demir, Y., Güngör, A. A., Duran, E. D., & Demir, N. (2008). Food Technology and Biotechnology, 46, 286–291.
Rameshwaram, N. R., & Nadimpalli, S. K. (2008). Journal of Chromatography B, 861, 209–217.
Wang, S., Ng, T., Chen, T., Lin, D., Wu, J., Rao, P., et al. (2005). Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 327, 820–827.
Ye, X. Y., & Ng, T. B. (2001). Journal of Protein Chemistry, 20, 353–359.
Tiengburanatam, N., Boonmee, A., Sangvanich, P., & Karnchanatat, A. (2010). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 162, 1938–1951.
Emmermann, M., Clericus, M., Braun, H. P., Mozo, T., Heins, L., Kruft, V., et al. (1994). Plant Molecular Biology, 25, 271–281.
Mallikarjun, G. K. G., Gowda, L. R., Rao, A. G., & Prakash, V. (2006). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 54, 4568–4573.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the 90th Anniversary of Chulalongkorn University fund, the National Research University Project of CHE, the Ratchadaphiseksomphot Endowment Fund (AG001B, AM1019A and AS613A), the Thai Government Stimulus Package 2 (TKK2555) and the Thailand Research Fund through the TRF-CHE Research Grant for Mid-Career University Faculty (RMU5380036), for financial support of this research, as well as the Institute of Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering for support and facilities. We also thank Dr. Robert Butcher (Publication Counseling Unit, Chulalongkorn University) for his constructive comments in preparing this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yodjun, M., Karnchanatat, A. & Sangvanich, P. Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Proteins and Peptides from the Rhizomes of Zingiberaceae Plants. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 166, 2037–2050 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9630-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9630-y