Abstract
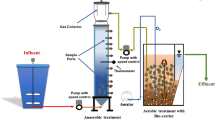
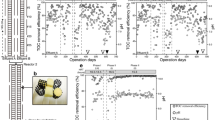
The performance of a novel sponge-submerged membrane bioreactor (SSMBR) was evaluated to treat primary treated sewage effluent at three different activated sludge concentrations. Polyurethane sponge cubes with size of 1 × 1 × 1 cm were used as attached growth media in the bioreactor. The results indicated the successful removal of organic carbon and phosphorous with the efficiency higher than 98% at all conditions. Acclimatised sponge MBR showed about 5% better ammonia nitrogen removal at 5 and 10 g/L sludge concentration as compared to the new sponge system. The respiration test revealed that the specific oxygen uptake rate was around 1.0–3.5 mgO2/gVSS.h and likely more stable at 10 g/L sludge concentration. The sludge volume index of less than 100 mL/g during the operation indicated the good settling property of the sludge. The low mixed liquor suspended solid increase indicated that SSMBR could control the sludge production. This SSMBR was also successful in reducing membrane fouling with significant lower transmembrane pressure (e.g. only 0.5 kPa/day) compared to the conventional MBR system. Further study will be conducted to optimise other operating conditions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang, W., Cicek, N., & Ilg, J. (2006). Journal of Membrane Science, 270, 201–211.
Kocadagistan, B., Kocadagistan, E., Topcu, N., & Demircioglu, N. (2005). Process Biochemistry, 40, 177–182.
Ren, X. H., Shon, H. K., Jang, N. J., Lee, Y. G., Bae, M. S., Lee, J. H., et al. (2010). Water Research, 44, 751–760.
Rahimi, Y., Torabian, A., Mehrdadi, N., Habibi-Rezaie, M., Pezeshk, H., & Bidhendi, G. R. N. (2011). Journal of Hazardous Material, 86, 1097–1102.
Sombatsompop, K., Visvanathan, C., & Ben Aim, R. (2006). Desalination, 201, 138–149.
Lee, J. M., Ahn, W. Y., & Lee, C. H. (2001). Water Research, 35, 2435–2445.
Lee, W., Kang, S., & Shin, H. (2003). Journal of Membrane Science, 216, 217–227.
APHA., AWWA., WEF. (1998). Standard Methods for the examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th edition, American Public Health Association.
Khan, S. J., Ilyas, S., Javid, S., Visvanathan, C., & Jegatheesan, V. (2011). Bioresource Technology, 102, 5331–5336.
Ngo, H. H., Guo, W. S., & Xing, W. (2008). Bioresource Technology, 99, 2429–2435.
Guo, W. S., Ngo, H. H., Palmer, C. G., Xing, W., Hu, A. Y. J., & Listowski, A. (2009). Desalination, 249, 672–676.
Lobos, J., Wisniewski, C., Heran, M., & Grasmick, A. (2008). Journal of Membrane Science, 317, 71–77.
Ye, F., Ye, Y., & Li, Y. (2011). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 188, 37–43.
Jin, B., Wilén, B. M., & Lant, P. (2003). Chemical Engineering Journal, 95, 221–234.
Guo, J. H., Peng, Y. Z., Peng, C. Y., Wang, S. Y., Chen, Y., Huang, H. J., et al. (2010). Bioresource Technology, 101, 1120–1126.
Her, N., Amy, G., Park, H. R., & Song, M. (2004). Water Research, 38, 1427–1438.
Nataraj, S., Schomäcker, R., Kraume, M., Mishra, I. M., & Drews, A. (2008). Journal of Membrane Science, 308, 152–161.
Liu, F., Xu, Y. Y., Zhu, B. K., Zhang, F., & Zhu, L. P. (2009). Journal of Membrane Science, 345, 331–339.
James, K. E., William, C. B., & Kevin, L. W. (1985). Journal of American Water Works Association, 77, 122.
Kalbitz, K. S., Geyer, S. B., & Geyer, W. (2000). Chemosphere, 40, 1305.
Nguyen, T. T., Guo, W. S., Ngo, H. H., & Vigneswaran, S. (2010). Separation and Purification Technology, 75, 204–209.
Yang, S., Yang, F., Fu, Z., & Lei, R. (2009). Bioresource Technology, 100, 6655–6657.
Le-Clech, P., Chen, V., & Fane, T. (2006). Journal of Membrane Science, 284, 17–53.
Kim, M., & Nakhla, G. (2009). Journal of Membrane Science, 331, 91–99.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the Australian Research Council (ARC) Industry Linkage Grant (LP0882089). The authors are also grateful for the support of UTS Chancellor’s Postdoctoral Research Fellowship and UTS Early Career Researcher Grants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, T.T., Ngo, H.H., Guo, W. et al. Effects of Sludge Concentrations and Different Sponge Configurations on the Performance of a Sponge-Submerged Membrane Bioreactor. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 167, 1678–1687 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9579-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9579-x