Abstract
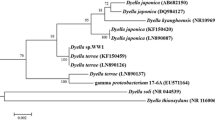
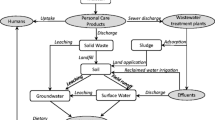
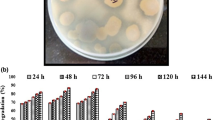
Triclosan (2, 4, 4′-trichloro-2′-hydroxyl diphenyl ether) is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent present in a number of house hold consumables. Aerobic and anaerobic enrichment cultures tolerating triclosan were developed and 77 bacterial strains tolerating triclosan at different levels were isolated from different inoculum sources. Biodegradation of triclosan under aerobic, anoxic (denitrifying and sulphate reducing conditions), and anaerobic conditions was studied in batch cultures with isolated pure strains and enrichment consortium developed. Under aerobic conditions, the isolated strains tolerated triclosan up to 1 g/L and degraded the compound in inorganic-mineral-broth and agar media. At 10 mg/L level triclosan, 95 ± 1.2% was degraded in 5 days, producing phenol, catechol and 2, 4-dichlorophenol as the degradation products. The strains were able to metabolize triclosan and its degradation products in the presence of monooxygenase inhibitor 1-pentyne. Under anoxic/anaerobic conditions highest degradation (87%) was observed in methanogenic system with acetate as co-substrate and phenol, catechol, and 2, 4-dichlorophenol were among the products. Three of the isolated strains tolerating 1 g/L triclosan were identified as Pseudomonas sp. (BDC 1, 2, and 3).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singer, H., Muller, S., Tixier, C., & Pillonel, L. (2002). Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 4998–5004.
US Environmental Protection Agency (2003) Region/ORD workshop on emerging pollutants-Summary report available from: http://www.epa.gov/osp/regions/emerpoll_rep.pdf.
Mezcua, M., Gomez, M. J., Ferrer, I., Aguera, A., Hernando, M. D., & Fernandez-Alba, A. R. (2004). Analytica Chimica Acta, 524, 241–247.
Sanford, J. C., Aminov, R. I., Krapac, I. J., Jeanjean, N. G., & Mackie, R. I. (2001). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67, 1494–1502.
Orvos, D. R., Versteeg, D. J., Inauen, J., Capdevielle, M., Rothenstein, A., & Unningham, V. C. (2002). Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 21, 1338–1349.
Balmer, M. E., Droz, T. P., Romanin, C. K., Bergqvist, P. A., Muller, M. D., & Buser, H. R. (2004). Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 390–395.
Liu, F., Ying, G. G., Yang, L. H., & Zhou, Q. X. (2009). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 72, 86–92.
Bester, K. (2003). Water Research, 16, 3891–3896.
Stasinakis, A. S., Gatidou, G., Mamais, D., Thomaidis, N. S., & Lekkas, T. D. (2008). Water Research, 42, 1796.
Heidler, J., & Halden, R. U. (2007). Chemosphere, 66, 362–369.
Winkler, G., Thompson, A., Fischer, R., Krebs, P., Griffin, P., & Cartmell, E. (2007). Engineering Life Science, 7, 42–51.
Wu, C., Spongberg, A. L., & Witter, J. D. (2009). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 57, 4900.
Ying, G. G., Yu, X. Y., & Kookana, R. S. (2007). Environmental Pollution, 150, 300–305.
Meade, M. J., Waddell, R. L., & Callahan, T. M. (2001). FEMS Microbiology Letters, 204, 45–48.
Roh, H., Subramanya, N., Zhao, F., Yu, C. P., Sandt, J., & Chu, K. H. (2009). Chemosphere, 77(8), 1084–1089.
Hundt, K., Martin, D., Hammer, E., Jonas, U., Kindermann, M. K., & Schauer, F. (2000). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66, 4157–4160.
Hay, A. G., Dees, P. M., & Sayler, G. S. (2001). FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 36, 105–112.
Carr, D. L., Morse, A. N., Zak, J. C., & Anderson, T. A. (2011). Water Air and Soil Pollution, 216, 633–642.
Siegmund, I., & Wagner, F. (1991). Biotechnology Techniques, 5, 265–268.
Wilson, K., Ausubel, F. M., Brent, R., Kingston, R. E., Moore, D. D., Seidman, J. G., et al. (1987). Current Protocols in Mol. Biol (pp. 2.4.1–2.4.5). New York: Wiley.
Liaw, H. J., & Srinivasan, V. R. (1990). Journal of Industrial Microbiology, 6, 235–242.
Schmidt, S., Wittich, R. M., Erdmann, D., Wilkes, H., Francke, W., & Fortnagel, P. (1992). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 58, 2744–2750.
Kim, Y. J., & Nicell, J. A. (2006). Bioresource Technology, 97, 1431–1442.
Kim, Y. M., Nam, I. H., Murugesan, K., Schmidt, S., Crowley, D. E., & Chang, Y. S. (2007). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 77, 187–194.
Canosa, P., Rodriguez, I., Rubí, E., & Cela, R. (2005). Journal of Chromatography. A, 1072, 107–115.
Barkay, T., Navon-Venezia, S., Ron, E. Z., & Rosenberg, E. (1999). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 65, 2697–2702.
Kim, Y. M., Murugesan, K., Schmidt, S., Bokare, V., Jeon, J. K., Kim, E. J., et al. (2011). Bioresource Technology, 102, 2206–2212.
Yen, K. M., Karl, M. R., Blatt, L. M., Simon, M. J., Winter, R. B., Fausset, P. R., et al. (1991). Journal of Bacteriology, 173, 5315–5327.
Yeager, C. M., Bottomley, P. J., Arp, D. J., & Hyman, M. R. (1999). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 65, 632–639.
Zhao, F. (2006). Zachry Department of Civil Engineering, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas (http://hdl.handle.net/1969.1/5966).
Ying, G. G., Kookana, R. S., & Dillon, P. (2003). Water Research, 37, 3785–3791.
Acknowledgements
Financial assistance from International Foundation for Science (IFS), Sweden (Ref. no. W/4218-1) and infrastructural facilities from CSIR-India for conducting the present study is greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gangadharan Puthiya Veetil, P., Vijaya Nadaraja, A., Bhasi, A. et al. Degradation of Triclosan under Aerobic, Anoxic, and Anaerobic Conditions. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 167, 1603–1612 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9573-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9573-3