Abstract
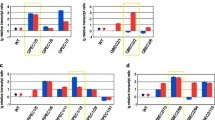
Xylitol, a naturally occurring five-carbon sugar alcohol derived from d-xylose, is currently in high demand by industries. Trichoderma reesei, a prolific industrial cellulase and hemicellulase producing fungus, is able to selectively use d-xylose from hemicelluloses for xylitol production. The xylitol production by T. reesei can be enhanced by genetic engineering of blocking further xylitol metabolism in the d-xylose pathway. We have used two different T. reesei strains which are impaired in the further metabolism of xylitol including a single mutant in which the xylitol dehydrogenase gene was deleted (∆xdh1) and a double mutant where additionally l-arabinitol-4-dehydrogenase, an enzyme which can partially compensate for xylitol dehydrogenase function, was deleted (∆lad1∆xdh1). Barely straw was first pretreated using NaOH and Organosolv pretreatment methods. The highest xylitol production of 6.1 and 13.22 g/L was obtained using medium supplemented with 2 % Organosolv-pretreated barley straw and 2 % d-xylose by the ∆xdh1 and ∆lad1∆xdh1 strains, respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ∆xdh1 :
-
Xylitol dehydrogenase gene deleted strain (T. reesei single mutant strain)
- ∆lad1∆xdh1 :
-
l-Arabinitol-4-dehydrogenase and xylitol dehydrogenase genes deleted strain (T. reesei double mutant strain)
- PPP:
-
Pentose phosphate pathway
- FTIR:
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic
- HPAE-PAD:
-
High-performance anion exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection
- DNS:
-
3,5-Dinitrosalicylic acid
- FPU:
-
Filter paper unit
- MCC:
-
Microcrystalline cellulose
- RS:
-
Reducing sugars
References
Dashtban, M., Schraft, H., & Qin, W. (2009). International Journal of Biological Sciences, 5, 578–595.
Yu, C., Cao, Y., Zou, H., & Xian, M. (2011). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 89, 573–583.
Nygard, Y., Toivari, M. H., Penttila, M., Ruohonen, L., & Wiebe, M. G. (2011). Metabolic Engineering, 13, 383–391.
Seiboth, B., & Metz, B. (2011). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 89, 1665–1673.
Taherzadeh, M. J., & Karimi, K. (2008). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 9, 1621–1651.
Dashtban, M., Schraft, H., Syed, T. A., & Qin, W. (2010). International Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 1, 36–50.
Seiboth, B., Hartl, L., Pail, M., & Kubicek, C. P. (2003). Eukaryotic Cell, 2, 867–875.
Seiboth, B., Gamauf, C., Pail, M., Hartl, L., & Kubicek, C. P. (2007). Molecular Microbiology, 66, 890–900.
Sato, H., Ide, Y., Nasu, M., & Numabe, Y. (2011). Odontology, 99, 28–33.
Prakasham, R., Rao, R., & Hobbs, P. (2009). Current Trends in Biotechnology and Pharmacy, 3, 8–36.
Santos, D. T., Sarrouh, B. F., Rivaldi, J. D., Converti, A., & Silva, S. S. (2008). Journal of Food Engineering, 86, 542–548.
Khankal, R., Chin, J. W., & Cirino, P. C. (2008). Journal of Biotechnology, 134, 246–252.
Ahmad, I., Shim, W. Y., Jeon, W. Y., Yoon, B. H., & Kim, J. H. (2012). Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 35, 199–204.
Akinterinwa, O., Khankal, R., & Cirino, P. C. (2008). Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 19, 461–467.
El-Batal, I. A., & Khalaf, S. A. (2004). International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 6, 1066–1073.
Rodrigues, R. C., Kenealy, W. R., & Jeffries, T. W. (2011). Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 38, 1649–1655.
Cheng, S., D’Cruz, I., Wang, M., Leitch, M., & Xu, M. (2010). Energy Fuels, 24, 4659–4667.
Deshpande, P., Nair, S., & Khedkar, S. (2009). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 158, 552–560.
Mandels, M. M., & Andreotti, R. E. (1978). Process Biochemistry, 13, 6–13.
Gamerith, G., Groicher, R., Zeilinger, S., Herzog, P., & Kubicek, C. P. (1992). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 38, 315–322.
Miller, G. L. (1959). Analytical Chemistry, 31, 426–428.
Dashtban, M., Buchkowski, R., & Qin, W. (2011). International Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2, 274–286.
Dashtban, M., Maki, M., Leung, K. T., Mao, C., & Qin, W. (2010). Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 30, 302–309.
Dashtban, M., & Qin, W. (2012). Microbial Cell Factories, 11, 63.
Vidal, B. C., Jr., Dien, B. S., Ting, K. C., & Singh, V. (2011). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 164, 1405–1421.
Pedersen, M., & Meyer, A. S. (2009). Biotechnology Progress, 25, 399–408.
da Silva, A. S., Inoue, H., Endo, T., Yano, S., & Bon, E. P. (2010). Bioresource Technology, 101, 7402–7409.
Hsu, T. C., Guo, G. L., Chen, W. H., & Hwang, W. S. (2010). Bioresource Technology, 101, 4907–4913.
Chundawat, S. P., Venkatesh, B., & Dale, B. E. (2007). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 96, 219–231.
Kumar, R., Mago, G., Balan, V., & Wyman, C. E. (2009). Bioresource Technology, 100, 3948–3962.
Wang, B., Wang, X., & Feng, H. (2010). Bioresource Technology, 101, 752–760.
Guo, G. L., Chen, W. H., Men, L. C., & Hwang, W. S. (2008). Bioresource Technology, 99, 6046–6053.
Prathumpai, W., McIntyre, M., & Nielsen, J. (2004). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 63, 748–753.
Prakash, G., Varma, A. J., Prabhune, A., Shouche, Y., & Rao, M. (2011). Bioresource Technology, 102, 3304–3308.
Pan, X., Gilkes, N., Kadla, J., Pye, K., Saka, S., Gregg, D., et al. (2006). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 94, 851–861.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Shuna Cheng and Dr. Chunbao (Charles) Xu for their great help with the Organosolv pretreatment. The authors would also like to thank Dr. Matthew Leitch for allowing us to use Wiley mill machine. This work was supported by a scholarship from Ontario Graduate Scholarship to M.D. and NSERC-RCD and Ontario Research Chair funding to W.Q.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dashtban, M., Kepka, G., Seiboth, B. et al. Xylitol Production by Genetically Engineered Trichoderma reesei Strains Using Barley Straw as Feedstock. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 169, 554–569 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-0008-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-0008-y