Abstract
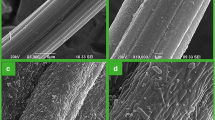
In order to assess the effects of the surface hydrophilicity of supports on the biofilm formation and evaluate the performance of completely autotrophic nitrogen removal over nitrite (CANON) process in a sequencing batch biofilm reactor (SBBR), unmodified activity carbon fibers (ACFs) and ACFs hydrophilic modified by heat treatment were used as supports. CANON process was initiated in a SBBR from conventional activated sludge. An operation temperature of 32 ± 2 °C, dissolved oxygen (DO) level at 1.5 mg L−1 and free ammonia (FA) concentration with 3.98–15.93 mg L−1 were maintained in the SBBR. Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectra and Boehm’s neutralizing titration exhibited that modified ACFs had more oxygen-containing groups than unmodified ACFs. Larger biofilm growth on the modified surfaces examined by scanning electron microscopy and biofilm’s total dry weight, and the biofilm on the modified surfaces were more active, compared with those on the unmodified surfaces. This study demonstrates the hydrophilic-modified ACFs have better biological affinity than unmodified ACFs. Maximal total nitrogen removal rate of 0.088 k g N m−3 day−1 was achieved for the CANON process on day 80, indicating the CANON process was successfully started up. Apart from supports, the strategies of DO supplying and controlling FA concentration were also keys in starting up the CANON process within a shorter period.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sliekers, A. O., Derwort, N., Gomez, J. L. C., Strous, M., Kuenen, J. G., & Jetten, M. S. M. (2002). Water Research, 36, 2475–2482.
Ahn, Y. H. (2006). Process Biochemistry, 41, 1709–1721.
Jetten, M. S. M., Wagner, M., Fuerst, J., Van Loosdrecht, M., Kuenen, G., & Strous, M. (2001). Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 12, 283–288.
Prosser, J. I. (1989). Advances in Microbial Physiology, 30, 125–181.
Zhang, Z. J., Chen, S. H., Wu, P., Lin, C. F., & Luo, H. Y. (2010). Bioresource Technology, 101, 6309–6314.
Zhang, Z. Y., Zhou, J. T., Wang, J., Guo, H. Y., & Tong, J. (2006). Process Biochemistry, 41, 599–608.
Gieseke, A., Arnz, P., Amann, R., & Schramm, A. (2002). Water Research, 36, 501–509.
Strous, M., Heijnen, J. J., Kuenen, J. G., & Jetten, M. S. M. (1998). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 50, 589–596.
Wilderer, P. A., & Mcswain, B. S. (2004). Water Science and Technology, 50, 1–10.
Fernández, I., Vázquez-Padín, J. R., Mosquera-Corral, A., Campos, J. L., & Méndez, R. (2008). Biochemical Engineering Journal, 42, 308–313.
Liu, Y. (1995). Colloid Surface B, 5, 213–219.
Lackner, S., Holmberg, M., Terada, A., Kingshott, P., & Smets, B. F. (2009). Water Research, 43, 3469–3479.
Khan, M. M. T., Ista, L. K., Lopez, G. P., & Schuler, A. J. (2011). Environmental Science and Technology, 45, 1055–1060.
Sousa, M., Azeredo, J., Feijo, J., & Oliveira, R. (1997). Biotechnology Techniques, 11, 751–754.
Fernándeza, M. R., Casabonaa, M. G., Anupamab, V. N., Krishnakumarb, B., Curutchetc, G. A., & Bernika, D. L. (2010). Colloid Surface B, 81, 289–296.
Chavant, P., Martinie, B., Meylheuc, T., Bellon-Fontaine, M. N., & Hebraud, M. (2002). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 728–737.
Ryu, Z. Y., Rong, H. Q., Zheng, J. T., Wang, M. Z., & Zhang, B. J. (2002). Carbon, 40, 1144–1147.
Vlaeminck, S. E., Terada, A., Smets, B. F., Van Der Linden, D., Boon, N., Verstraete, W., et al. (2009). Environmental Science and Technology, 43, 5035–5041.
Boehm, H. P. (1994). Carbon, 32, 759–769.
Boehm, H. P. (2002). Carbon, 40, 145–149.
Lazarova, V., Pierzo, V., Fontvielle, D., & Manem, J. (1994). Water Science and Technology, 29, 345–354.
Chinese NEPA. (2002). Water and wastewater monitoring methods (4th ed.). Beijing: Chinese Environmental Science Press.
Yamamoto, T., Takaki, K., Koyama, T., & Furukawa, K. (2008). Bioresource Technology, 99, 6419–6425.
Third, K. A., Olav Sliekers, A., Kuenen, J. G., & Jetten, M. S. M. (2001). Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 24, 588–596.
Lai, J. N., Sunderland, B., Xue, J. M., Yan, S., Zhao, W. J., Folkard, M., et al. (2006). Applied Surface Science, 252, 3375–3379.
Chen, Y., Zhao, Z. Q., & Liu, Y. M. (2008). Applied Surface Science, 254, 5497–5500.
Kim, Y. H., Cho, J. H., Lee, Y. W., & Lee, W. K. (1997). Biotechnology Techniques, 11, 773–776.
Xu, Z. Y., Zeng, G. M., Yang, Z. H., Xiao, Y., Cao, M., Sun, H. S., et al. (2010). Bioresource Technology, 101, 79–86.
Joss, A., Salzgeber, D., Eugster, J., Konig, R., Rottermann, K., Burger, S., et al. (2009). Environmental Science and Technology, 43, 5301–5306.
Li, X. M., Xiao, Y., & Liao, D. X. (2011). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 163, 1053–1065.
Wang, L., Zhu, J., & Curtis, M. (2011). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 163, 362–372.
Wiesmann, U. (1994). Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology, 51, 113–154.
Anthonisen, A. C., Loehr, R. C., Prakasam, T. B., & Srinath, E. G. (1976). Journal of the Water Pollution Control Federation, 48, 835–852.
Strous, M., van Gerven, E., Kuenen, J. G., & Jetten, M. (1997). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 63, 2446–2448.
Third, K. A., Paxman, J., Schmid, M., Strous, M., Jetten, M. S. M., & Cord-Ruwisch, R. (2005). Microbiology Ecology, 49, 236–244.
Acknowledgment
We would like to thank the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (CDJZR10210001) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, YP., Li, S., Ning, YF. et al. Start-up of Completely Autotrophic Nitrogen Removal Over Nitrite Enhanced by Hydrophilic-Modified Carbon Fiber. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 166, 866–877 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9476-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9476-8