Abstract
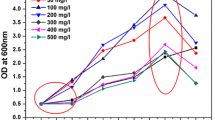
The present study reports the kinetics of p-nitrophenol (PNP) biodegradation by Arthrobacter chlorophenolicus A6 in batch shake flasks for initial PNP concentrations in the range of 25–225 mg l−1. Results of batch growth kinetics of A. chlorophenolicus A6 at various initial PNP concentrations revealed that the culture followed substrate inhibition kinetics with estimated decay coefficient value of 0.0132 h−1. Biokinetic constants involved in the process were estimated by fitting the experimental data to several substrate inhibition kinetics models available from the literature. Among the models tested, Webb model fitted the experimental data best with the least root mean square error value, and the estimated model constants values were μ = 0.161 h−1, K i = 128 mg l−1, K s = 60.15 mg l−1, and K = 100 mg l−1. In addition, observed and theoretical yield coefficients, maintenance energy, and specific growth rate of the culture at various initial PNP concentrations were also investigated in the study.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Uberoi, V., & Bhattacharya, S. K. (1997). Toxicity and degradability of nitrophenols in anaerobic systems. Water Environment Research, 69, 146–154.
Haghighi-Podeh, M. R., Bhattacharya, S. K., & Mingbo, Q. (1995). Effects of nitrophenols on acetate utilizing methanogenic systems. Water Research, 29, 391–399.
Environmental Protection Agency. (1988). Effluent guidelines and standards, organic chemicals, plastics, and synthetic fibers. 40 CFR part 414, Washington, DC.
Dolon, B. A., Razo-Flares, E., Lettiga, G., & Field, J. A. (1996). Continous detoxification, trans-formation and degradation of nitrophenol in upflow anerobic sludge blacket (UASB) reactors. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 51, 439–449.
Tomei, M. C., Annesini, M. C., Lubertia, R., Cento, G., & Senia, A. (2003). Kinetics of 4-nitrophenol biodegradation in a sequencing batch reactor. Water Research, 37, 3803–3814.
Environmental Protection Agency. (1980). Ambient water quality for nitrophenols. 440/5 80-063 Washington, DC.
Trapido, M., & Kallas, J. (2000). Advanced oxidation processes for the degradation and the detoxification of 4-nitrophenol. Environmental Technology, 21, 799–808.
Chen, D., & Ray, A. K. (1998). Photodegradation kinetics of 4-nitrophenol in TiO2, suspension. Water Research, 32, 3223–3234.
Wei, Q., Liu, H., Zhang, J. J., Wang, S. H., Xiao, Y., & Zhou, N. Y. (2010). Characterization of a para-nitrophenol catabolic cluster in Pseudomonas sp. strain NyZ402 and construction of an engineered strain capable of simultaneously mineralizing both para- and ortho-nitrophenols. Biodegradation. doi:10.1007/s10532-009-9325-4.
Bhushan, B., Chauhan, A., Samanta, S. K., & Jain, R. K. (2000). Kinetics of biodegradation of p-nitrophenol by different bacteria. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 274, 626–630.
Zaidi, B. R., & Mehta, N. K. (1995). Effects of organic compounds on the degradation of p-nitrophenol in lake and industrial wastewater by inoculated bacteria. Biodegradation, 6, 275–281.
Lima, S. A. C., Castro, P. M. L., & Morais, R. (2003). Biodegradation of p-nitrophenol by microalgae. Journal of Applied Phycology, 15, 137–142.
Westerberg, K., Elvang, A. M., Stackebrandtm, E., & Jansson, J. K. (2000). Arthrobacter chlorophenolicus sp. nov., a new species capable of degrading high concentrations of 4-chlorophenol. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 50, 2083–2092.
Sahoo, N. K., Pakshirajan, K., & Ghosh, P. K. (2010). Enhancing the biodegradation of 4-chlorophenol by Arthrobacter chlorophenolicus A6 via medium development. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 64, 474–480.
Hao, O. J., Kim, M. H., Seagren, E. A., & Kim, H. (2002). Kinetics of phenol and chlorophenol utilization by Acinetobacterspecies. Chemosphere, 46, 797–807.
Cho, Y. G., Rhee, S. K., & Lee, S. T. (2000). Influence of phenol on biodegradation of p-nitrophenol by freely suspended and immobilized Nocardioides sp. NSP41. Biodegradation, 11, 21–28.
Kumar, A., & Kumar, S. (2005). Biodegradation kinetics of phenol and catechol using Pseudomonas putida MTCC 1194. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 22, 151–159.
Kappeler, J., & Gujer, W. (1992). Estimation of kinetic parameters of heterotrophic biomass under aerobic conditions and characterization of wastewater for activated sludge modelling. Water Science and Technology, 25, 125–139.
Henze, M., Harremoës, P., Jansen, J., & Arvin, E. (2002). Waste water treatment. Biological and chemical processes. Berlin: Springer.
Kovari, K. K., & Elgim, T. (1998). Growth kinetics of suspended microbial cells: from single substrate controlled growth to mixed substrate kinetics. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 62, 646–666.
Yan, J., Jianping, W., Jing, B., Daoquan, W., & Zongding, H. (2006). Phenol biodegradation by the yeast Candida tropicalis in the presence of m-cresol. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 29, 227–234.
Bai, J., Wen, J. P., Li, H. M., & Jiang, Y. (2007). Kinetic modeling of growth and biodegradation of phenol and m-cresol using Alcaligenes faecalis. Process Biochemistry, 42, 510–517.
Edwards, V. H. (1970). The influence of high substrate concentrations on microbial kinetics. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 12, 679–712.
Aiba, S., Shoda, M., & Nagalani, M. (1968). Kinetics of product inhibition in alcohol fermentation. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 10, 845–864.
Yano, T., Nakahara, T., Kamiyama, S., & Yamada, K. (1996). Kinetic studies on microbial activities in concentrated solutions and effect of excess sugars on oxygen uptake rate of a cell-free respiratory system. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 30, 42–48.
Andrews, J. F. (1968). A mathematical model for the continuous culture of microorganisms utilizing inhibitory substrates. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 10, 707–723.
Haldane, J. B. S. (1965). Enzymes (p. 84). Cambridge: MIT.
Webb, J. L. (1963). Enzyme and metabolic inhibitors. Boston: Academic.
Wang, S. J., & Loh, K. C. (1999). Modeling the role of metabolic intermediates in kinetics of phenol biodegradation. Enzyme and Microbiol Technology, 25, 177–184.
Salehi, Z., Sohrabi, M., Vahabzadeh, F., Fatemi, S., & Kawase, Y. (2010). Modeling of p-nitrophenol biodegradation by Ralstonia eutropha via application of the substrate inhibition concept. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 177, 582–585.
Goswami, M., Shivaraman, N., & Singh, R. P. (2002). Kinetics of chlorophenol degradation by benzoate-induced culture of Rhodococcus erythropolis M1. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 18, 779–783.
Juang, R., & Tsai, S. (2006). Growth kinetics of Pseudomonas putida in the biodegradation of single and mixed phenol and sodium salicylate. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 31, 133–140.
Tomei, M. C., & Annesini, M. C. (2008). Biodegradation of phenolic mixtures in a sequencing batch reactor a kinetic study. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 15, 188–195.
Kumaran, P., & Paruchuri, Y. L. (1997). Kinetics of phenol biotransformation. Water Research, 31, 11–22.
Bhatti, Z. I., Toda, H., & Furukawa, K. (2002). p-Nitrophenol degradation by activatedsludge attached on nonwovens. Water Research, 36, 1135–1142.
Ray, P., Oubelli, A. M., & Loser, C. (1999). Aerobic 4-nitrophenol degradation by microorganisms fixed in a continuously working aerated solid-bed reactor. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 51, 284–290.
Golovleva, L. A., Zaborina, O., Pertsova, R., Baskunov, B., Schurukhin, Y., & Kuzmin, S. (1992). Degradation of polychlorinated phenols by Streptomyces rochei 303. Biodegradation, 2, 201–208.
Chen, F., & Johns, M. R. (1996). Relationship between substrate inhibition and maintenance energy of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in heterotrophic culture. Journal of Applied Phycology, 8, 15–19.
Onysko, K. A., Budman, H. M., & Robinson, C. W. (2000). Effect of temperature on the inhibition kinetics of phenol biodegradation by Pseudomonas putida Q5. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 70, 291–299.
Shuler, M. L., & Kargi, F. (1992). Bioprocess engineering (pp. 154–61). New Jersey: Prentice- Hall.
Rangaswami, G., & Bagyaraj, D. J. (2001). Agricultural microbiology (Secondth ed., p. 112). New Delhi: Prentice-Hall of India, Private Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahoo, N.K., Pakshirajan, K. & Ghosh, P.K. Batch Biodegradation of Para-Nitrophenol Using Arthrobacter chlorophenolicus A6. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 165, 1587–1596 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9379-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9379-8