Abstract
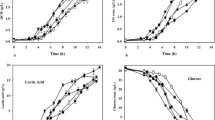
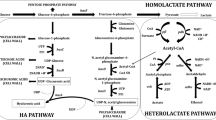
The effect of phosphatidylcholine on the molecular weight properties of hyaluronic acid (HA) was studied in batch culture of Streptococcus zooepidemicus by adding phosphatidylcholine at the early stage of exponential phase. With the addition of 80 mg/L of phosphatidylcholine, maximum HA yield (2.47 g/L) and weight-average molecular weight (902.60 KDa) were achieved, increased by 17.4% and 67.1%, respectively, as compared to the control. Metabolic flux analysis was employed to study the mechanism of phosphatidylcholine on the molecular weight of HA. The normalized flux distribution maps based on fermentation data at phosphatidylcholine addition indicated that phosphatidylcholine resulted in higher flux flowing to the HA pathway and lower flux flowing to the glycolysis and biomass synthesis pathway, coupling with higher level of UDPNAG generation and extra regeneration of ATP. The GC-MS analysis of fatty acids in the plasma membrane showed that the addition of phosphatidylcholine could promote the mobility and permeability of the cell membrane, making the HA chain pass through the membrane more easily, thus decreasing the energy consumption. All these results led to higher molecular weight of hyaluronic acid.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Radaeva, I. F., Kostina, G. A., & Zmievskii, A. V. (1997). Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology, 33, 111–115.
Swann, DA., and Kuo, JW. (1991) Stockton Press, New York, pp. 286–305
Chong, F. B., & Nielsen, L. K. (2003). Biochemical Engineering Journal, 16(2), 153–162.
Kang, S. W., Cho, E. R., & Kim, B. S. (2005). Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 15, 510–518.
Kogan, G., Šoltés, L., Stern, R., & Gemeiner, P. (2007). Biotechnology Letters, 29, 17–25.
Chong, F. B., Blank, L. M., Mclaughlin, R., & Nielsen, L. K. (2005). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 66, 341–351.
Gao, H. J., Du, G. C., & Chen, J. (2006). World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 22(4), 399–408.
Armstrong, D. C., & Johns, M. R. (1997). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 63, 2759–2764.
Jagannath, S., & Ramachandran, K. B. (2010). Biochemical Engineering Journal, 48, 148–158.
Chen, W. Y., Marcellin, E., Hung, J., & Nielsen, L. K. (2009). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 284, 18007–18014.
Duan, X. J., Niu, H. X., Tan, W. S., & Zhang, X. (2009). Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 19, 299–306.
Bai, D. M., Zhao, X. M., Li, X. G., & Xu, S. M. (2004). Biochemical Engineering Journal, 18, 41–48.
Kim, T. Y., & Lee, S. Y. (2006). Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 16, 1139–1143.
Liu, H. J., Li, Q., Liu, D. H., & Zhong, J. J. (2006). Biochemical Engineering Journal, 28, 92–98.
Bitter, T., & Muir, H. M. (1962). Analytical Biochemistry, 4, 330–333.
Laurent, T. C., Ryan, M., & Pietruszkiewicz, A. (1960). Biochem Biophys Acta, 42, 476–485.
Folch, J., Lees, M., & Sloane Stanley, G. H. (1957). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 226, 497–509.
Liu, L., Wang, M., & Du, G. C. (2008). Letters in Applied Microbiology, 46, 383–388.
Widner, B., Behr, R. V., Dollen, S., Tang, M., Heu, T., & Sloma, A. (2005). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71, 3747–3752.
Acknowledgments
The support obtained from the National “973” Project (numbers 2007CB714304 and 2007CB707804), 863 High-Tech Project (numbers 2009AA02Z207, 2009AA033001, and 2009AA033002) is highly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix. 1
Appendix. 2
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, J., Wang, M., Chen, Y. et al. Understanding the Influence of Phosphatidylcholine on the Molecular Weight of Hyaluronic Acid Synthesized by Streptococcus zooepidemicus . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 168, 47–57 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9320-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9320-1