Abstract
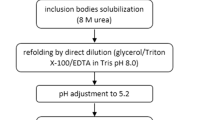
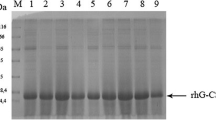
The toxicity of the recombinant protein towards the expression host remains a significant deterrent for bioprocess development. In this study, the expression of human granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor (hGM-CSF), which is known to be toxic to its host, was enhanced many folds using a combination of genetic and bioprocess strategies in Escherichia coli. The N terminus attachment of endoxylanase and asparaginase signal sequences from Bacillus subtilis and E. coli, respectively, in combination with and without His-tag, considerably improved expression levels. Induction and media optimization studies in shake flask cultures resulted in a maximal hGM-CSF concentration of 365 mg/L in the form of inclusion bodies (IBs) with a specific product yield (Y P/X) of 120 mg/g dry cell weight in case of the asparaginase signal. Culturing the cells in nutrient rich Terrific broth maintained the specific product yields (Y P/X) while a 6.6-fold higher volumetric concentration of both product and biomass was obtained. The purification and refolding steps were optimized resulting in a 95% pure protein with a fairly high refolding yield of 45%. The biological activity of the refolded protein was confirmed by a cell proliferation assay on hGM-CSF dependent human erythroleukemia TF-1 cells. This study demonstrated that this indeed is a viable route for the efficient production of hGM-CSF.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wacker, M., Linton, D., Hitchen, P. G., Nita-Lazar, M., Haslam, S. M., North, S. J., et al. (2002). Science, 298, 1790–1793.
Zhang, Z., Gildersleeve, J., Yang, Y. Y., Xu, R., Loo, J. A., Uryu, S., et al. (2004). Science, 303, 371–373.
Zoonens, M., & Miroux, B. (2010). Method Molecular Biology, 601, 49–66.
Makrides, S. C. (1996). Microbiological Reviews, 60, 512–538.
Hannig, G., & Makrides, S. C. (1998). Trends in Biotechnology, 16, 54–60.
Bhattacharya, P., Pandey, G., Srivastava, P., & Mukherjee, K. J. (2005). Molecular Biotechnology, 30, 103–116.
Bachmair, A., Finley, D., & Varshavsky, A. (1986). In vivo half-life of a protein is a function of its amino terminal residue. Science, 234, 179–186.
Nygren, P. A., Stahl, S., & Uhlen, M. (1994). Engineering proteins to facilitate bioprocessing. Trends in Biotechnology, 12, 184–188.
Ni, Y., & Chen, R. (2009). Biotechnological Letters, 31, 1661–1670.
Yoon, S. H., Kim, S. K., & Kim, J. F. (2010). Recent Patents on Biotechnology, 4, 23–29.
Gaofu, Q., Jie, L., Rongyue, C., Xin, Y., Dan, M., Jie, W., et al. (2005). Journal of Immunological Methods, 299, 9–19.
Khushoo, A., Pal, Y., & Mukherjee, K. J. (2005). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 68, 189–197.
Choi, J. H., Jeong, K. J., Kim, S. C., & Lee, S. Y. (2000). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 53, 640–645.
Jeong, K. J., & Lee, S. Y. (2000). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 67, 398–407.
Jeong, K. J., & Lee, S. Y. (2001). Protein Expression and Purification, 23, 311–318.
Metcalf, D. (1985). Science, 229, 16–22.
Armitage, J. O. (1998). Blood, 92, 4491–4508.
Ling, M., Zou, M., Xu, M., Wang, J., & Ma, X. (1995). Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 11, 157–62.
Schwanke, R. C., Renard, G., Chies, J. M., Campos, M. M., Junior, E. L., Santos, D. S., et al. (2009). International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 45, 97–102.
Berges, H., Joseph-Liauzun, E., & Fayet, O. (1996). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 62, 55–60.
Srinivasa, B. K., Muthukumaran, T., Antony, A., Singh, P., Samuel, S. D., Balamurali, M., et al. (2009). Biotechnological Letters, 31, 659–664.
Lee, J. H., Kim, N. S., Kwon, T. H., Jang, Y. S., & Yang, M. S. (2002). Journal of Biotechnology, 96, 205–211.
Ryoo, Z. Y., Kim, M. O., Kim, K. E., Bahk, Y. Y., Lee, J. W., Park, S. H., et al. (2001). Transgenic Research, 10, 193–200.
Au, L. C., Liu, T. J., Shen, H. D., Choo, K. B., & Wang, S. Y. (1996). Journal of Biotechnology, 51, 107–113.
Tapryal, S., Khasa, Y. P., & Mukherjee, K. J. (2010). Biotechnology Journal, 5, 1078–1089.
Srivastava, P., & Mukherjee, K. J. (2001). Preparative Biochemistry & Biotechnology, 31, 389–400.
Kitamura, T., Tange, T., Terasawa, T., Chiba, S., Kuwaki, T., Miyagawa, K., et al. (1989). Journal of Cellular Physiology, 140, 323–334.
Khushoo, A., Pal, Y., Singh, B. N., & Mukherjee, K. J. (2004). Protein Expression and Purification, 38, 29–36.
Hua, Z., Jie, L., & Zhu, D. (1994). Biochemistry and Molecular Biology International, 34, 621–626.
Gnoth, S., Jenzsch, M., Simutis, R., & Lübbert, A. (2008). Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 31, 41–46.
Saida, F., Uzan, M., Odaert, B., & Bontems, F. (2006). Current Protein & Peptide Science, 7, 47–56.
Panda, A. K. (2005). Method Molecular Biology, 308, 155–161.
Baneyx, F., & Mujacic, M. (2004). Nature Biotechnology, 22, 1399–1408.
Jungbauer, A., & Kaar, W. (2007). Journal of Biotechnology, 128, 587–596.
Belew, M., Zhou, Y., Wang, S., Nystrom, L. E., & Janson, J. C. (1994). Journal of Chromatography A, 679, 67–83.
Yazdani, S. S., & Mukherjee, K. J. (2002). Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 24, 341–346.
Kayser, A., Weber, J., Hecht, V., & Rinas, U. (2005). Microbiology, 151, 693–706.
Kopetzki, E., Schumacher, G., & Buckel, P. (1989). Molecular & General Genetics, 216, 149–155.
Sorensen, S. J., Bailey, M., Hansen, L. H., Kroer, N., & Wuertz, S. (2005). Nature Reviews. Microbiology, 3, 700–710.
Vethanayagam, J. G., & Flower, A. M. (2005). Microbial Cell Factories, 4, 3.
Shiloach, J., & Fass, R. (2005). Biotechnology Advances, 23, 345–357.
Acknowledgment
The authors are thankful to Prof. R. C. Kuhad, Department of Microbiology, University of Delhi South Campus, for his advice during the preparation of manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khasa, Y.P., Khushoo, A., Tapryal, S. et al. Optimization of Human Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (hGM-CSF) Expression Using Asparaginase and Xylanase Gene’s Signal Sequences in Escherichia coli . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 165, 523–537 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9272-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9272-5