Abstract
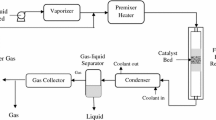
Steam reforming of bio-oil derived from the fast pyrolysis of biomass is an economic and renewable process for hydrogen production. The main objective of the present work has been to investigate the effects of the preparation method of Ni/Al2O3 catalysts on their performance in hydrogen production by bio-oil steam reforming. The Ni/Al2O3 catalysts were prepared by impregnation, co-precipitation, and sol–gel methods. XRD, XPS, H2-TPR, SEM, TEM, TG, and N2 physisorption measurements were performed to characterize the texture and structure of the catalysts obtained after calcination and after their subsequent use. Ethanol and bio-oil model compound were selected for steam reforming to evaluate the catalyst performance. The catalyst prepared by the co-precipitation method was found to display better performance than the other two. Under the optimized reaction conditions, an ethanol conversion of 99% and a H2 yield of 88% were obtained.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bridgwater, A. V., & Peacocke, G. V. C. (2000). Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 4, 1–73.
Huber, G. W., Iborra, S., & Corma, A. (2008). Chemical Reviews, 106, 4044–4098.
Czernik, S., & Bridgwater, A. V. (2004). Energy Fuels, 18, 590–598.
Xiong, W., Fu, Y., Lai, D., & Guo, Q. (2009). Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 30, 1754–1758.
Wang, D., Montané, D., & Chornet, E. (1996). Applied Catalysis. A, General, 143, 245–270.
Wang, D., Czernik, S., Montané, D., Mann, M., & Chornet, E. (1997). Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 36, 1507–1518.
Wang, D., Czernik, S., & Chornet, E. (1998). Energy and Fuels, 12, 19–24.
Garcia, L., French, R., Czernik, S., & Chornet, E. (2000). Applied Catalysis. A, General, 201, 225–239.
Czernik, S., Evans, R., & French, R. (2007). Catalysis Today, 129, 265–268.
Wu, C., Huang, Q., Sui, M., Yan, Y., & Wang, F. (2008). Fuel Processing Technology, 89, 1306–1316.
Yuan, L., Chen, Y., Song, C., Ye, T., Guo, Q., Zhu, Q., et al. (2008). Chemical Communications, 41, 5215–5217.
Rioche, C., Kulkarni, S., Meunier, F. C., Breen, J. P., & Burch, R. (2005). Applied Catalysis. B, Environmental, 61, 130–139.
Wen, G., Xu, Y., & Xu, Z. (2009). Catalysis Letters, 129, 250–257.
Akande, A. J., Idem, R. O., & Dalai, A. K. (2005). Applied Catalysis. A, General, 287, 159–175.
Fajardo, H. V., & Probst, L. F. D. (2006). Applied Catalysis A: General, 306, 134–141.
Zhang, L., Wang, X., Tan, B., & Ozkan, U. S. (2009). Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemistry, 297, 26–34.
Seo, J. G., Youn, M. H., Jung, J. C., & Song, I. K. (2009). International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 34, 5409–5416.
Fan, J., Boettcher, S. W., & Stucky, G. D. (2006). Chemistry of Materials, 18, 6391–6396.
Hoste, S., Van De Vondel, D., & Van Der Kelen, G. P. (1979). Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 16, 407–413.
Hou, Z., Yokota, O., Tanaka, T., & Yashima, T. (2003). Applied Catalysis. A, General, 253, 381–387.
Comas, J., Mariño, F., Laborde, M., & Amadeo, N. (2004). Chemical Engineering Journal, 98, 61–68.
Breen, J. P., Burch, R., & Coleman, H. M. (2002). Applied Catalysis. B, Environmental, 39, 65–74.
Goula, M. A., Kontou, S. K., & Tsiakaras, P. E. (2004). Applied Catalysis. B, Environmental, 49, 135–144.
Li, M., Wang, X., Li, S., Wang, S., & Ma, X. (2010). International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 35, 6699–6708.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for financial support from the Doctoral Foundation of the Ministry of Education of China (20090101110034), the International Science and Technology Cooperation Program (2009DFA61050), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (2009AA05Z407), and the National Basic Research Program of China (2007CB210200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Wang, S., Cai, Q. et al. Effects of Preparation Method on the Performance of Ni/Al2O3 Catalysts for Hydrogen Production by Bio-Oil Steam Reforming. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 168, 10–20 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9269-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9269-0