Abstract
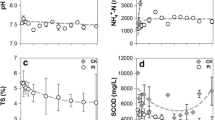
Digested slurry samples from twenty-one large-scale anaerobic digestion plants together with intensive pig and dairy farms in Jiangsu Province of China were collected and analyzed for total and dissolved concentrations of Zn, Cu and As, as well as chemical characteristics. The results showed that total concentrations of Zn, Cu and As in digested pig slurries were concentrated to <10, <5 and 0.02–0.1 mg/l, respectively; while <2 and 10–30, <1, and 0.02–0.1 mg/l, respectively, in digested dairy slurries. Lowering the dietary supply of these elements to pig and dairy would be the most effective way to control heavy metal contents in digested manure slurries. Dissolved fractions of Zn, Cu and As accounted for 1–74%, 1–33% and 2–53% of the total concentrations, respectively, in digested pig slurries; and 18–65%, 12–58% and 3–68% in digested dairy slurries. The chemical fractions of heavy metals in digested slurries were not only dependent on the total concentrations of heavy metals in raw manures but also on conditions of digestion and storage. Oxidation pond systems could significantly cripple the total contents of heavy metals in digested slurries, and the removal effect was better in multi-oxidation-pond systems than that in primary-oxidation-pond systems. However, the chemical fractions of heavy metals in digested slurries changed in a complicated manner when stored in oxidation ponds, due to the suspended solid deposition, elements reduction, as well as variations of pH values and oxidation-reduction potential.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yan, L., Li, J. M., & Ren, Y. X. (2006). Symbiosis effect of rural biogas project. Transactions CSAE, 22(S1), 89–92.
Lu, J. B., Zhu, L., Hu, G. L., & Wu, J. G. (2010). Integrating animal manure-based bioenergy production with invasive species control: a case study at Tongren Pig Farm in China. Biomass and Bioenergy, 34(6), 821–827.
Gebrezgabher, S. A., Meuwissen, M. P. M., Prins, B. A. M., & Oude Lansink, A. G. J. M. (2010). Economic analysis of anaerobic digestion—a case of green power biogas plant in the Netherlands. NJAS–Wageningen Journal of Life Sciences, 57(2), 109–115.
Börjesson, P., & Berglund, M. (2006). Environmental systems analysis of biogas systems: part I. Fuel-cycle emissions. Biomass and Bioenergy, 30(5), 469–485.
Murphy, J. D., & Power, N. (2009). Technical and economic analysis of biogas production in Ireland utilizing three different crop rotations. Applied Energy, 86(1), 25–36.
Amon, T., Amon, B., Kryvoruchko, V., Machmüller, A., Hopfner-Sixt, K., Bodiroza, V., et al. (2007). Methane production through anaerobic digestion of various energy crops grown in sustainable crop rotations. Bioresource Technology, 98(17), 3204–3212.
Weiland, P. (2006). Biomass digestion in agriculture: a successful pathway for the energy production and waste treatment in Germany. Engineering in Life Science, 6(3), 302–309.
Chen, Y., Yang, G. H., Sweeney, S., & Feng, Y. Z. (2010). Household biogas use in rural China: a study of opportunities and constraints. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 14(1), 545–549.
Gómez, X., Cuetos, M. J., García, A. I., & Morán, A. (2005). Evaluation of digestates stability from anaerobic process by thermogravimetric analysis. Thermochimica Acta, 426(1–2), 179–184.
Marcato, C. E., Pinelli, E., Pouech, P., Winterton, P., & Guiresse, M. (2008). Particle size and metal distributions in anaerobically digested pig slurry. Bioresource Technology, 99(7), 2340–2348.
Jondreville, C., Revy, P. S., & Dourmad, J. Y. (2003). Dietary means to better control the environmental impact of copper and zinc by pigs from weaning to slaughter. Livestock Production Science, 84(2), 147–156.
Silbergeld, E. K., & Nachman, K. (2008). The environmental and public health risks associated with arsenical use in animal feeds. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1140, 346–357.
Cang, L., Wang, Y. J., Zhou, D. M., & Dong, Y. H. (2004). Heavy metals pollution in poultry and livestock feeds and manures under intensive farming in Jiangsu Province, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 16(3), 371–374.
Dong, Z. R., Chen, Y. D., Lin, X. Y., Zhang, Y. S., & Ni, D. H. (2008). Investigation on the contents and fraction of heavy metals in swine manures from intensive livestock farms in the suburb of Hangzhou. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 20(1), 35–39.
Suo, C., Li, Y. X., Zhang, Z. Q., Han, W., Xiong, X., Li, W., et al. (2009). Residual character of Zn in feeds and their feces from intensive livestock and poultry farms in Beijing. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 28(10), 2173–2179.
Nicholson, F. A., Chambers, B. J., Williams, J. R., & Unwin, R. J. (1999). Heavy metal contents of livestock feeds and animal manures in England and Wales. Bioresource Technology, 70(1), 23–31.
Garbarino, J. R., Bednar, A. J., Rutherford, D. W., Beyer, R. S., & Wershaw, R. L. (2003). Environmental fate of roxarsone in poultry litter: I. Degradation of roxarsone during composting. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(8), 1509–1514.
Su, D. C., & Wong, J. W. C. (2004). Chemical speciation and phytoavailability of Zn, Cu, Ni and Cd in soil amended with fly ash-stabilized sewage sludge. Environment International, 29(7), 895–900.
Ko, H. J., Kim, K. Y., Kim, H. T., Kim, C. N., & Umeda, M. (2008). Evaluation of maturity parameters and heavy metal contents in composts made from animal manure. Waste Management, 28(5), 813–820.
He, M. M., Li, W. H., Liang, X. Q., Wu, D. L., & Tian, G. M. (2009). Effect of composting process on phytotoxicity and speciation of copper, zinc and lead in sewage sludge and swine manure. Waste Management, 29(2), 590–597.
Nachman, K. E., Graham, J. P., Price, L. B., & Silbergeld, E. K. (2005). Arsenic: a roadblock to potential animal waste management solutions. Environmental Health Perspectives, 113(9), 1123–1124.
Zhang, X. Z., Zhang, F. S., Li, Y. X., Han, W., & Yang, M. (2009). The effects of manure composing on distribution of Cu and Zn speciations in soils. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 28(9), 1975–1979.
Wang, W. S., Shen, X. Q., Wen, B., & Zhang, S. Z. (2003). Relationship between the extractable metals from soils and metals taken up by Maize roots and shoots. Chemosphere, 53(5), 523–530.
Tripathi, R. D., Srivastava, S., Mishra, S., Singh, N., Tuli, R., Gupta, D. K., et al. (2007). Arsenic hazards: strategies for tolerance and remediation by plant. Trends in Biotechnology, 25(4), 158–165.
Khan, S., Cao, Q., Zheng, Y. M., Huang, Y. Z., & Zhu, Y. G. (2008). Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing, China. Environmental Pollution, 152(3), 686–692.
Huang, M. L., Zhou, S. L., Sun, B., & Zhao, Q. G. (2008). Heavy metals in wheat grain: assessment of potential health risk for inhabitants in Kunshan, China. The Science of the Total Environment, 405(1–3), 54–61.
Gan, S. W., Xu, Z. B., & Huang, W. (2008). Key technology for ecological application of large-scale biogas project. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 16(5), 1293–1297.
Fuentes, A., Lloréns, M., Sáez, J., Soler, A., Aguilar, M. I., Orthño, J. F., et al. (2004). Simple and sequential extractions of heavy metals from different sewage sludges. Chemosphere, 54(8), 1039–1047.
Houghton, J. I., Burgess, J. E., & Stephenson, T. (2002). Off-line particle size analysis of digested sludge. Water Research, 36(18), 4643–4647.
Zhong, P., Li, Z. B., Li, Q. R., & Wang, Z. Y. (2007). Contents of selected nutrients and heavy metals in biogas slurry. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 26(S), 165–171.
Alonso, E., Villar, P., Santos, A., & Aparicio, I. (2006). Fraction of heavy metals in sludge from anaerobic wastewater stabilization ponds in southern Spain. Waste Management, 26(11), 1270–1276.
Li, X. L., He, W. L., & Dong, S. L. (2006). Contamination by heavy metals in feed and measures of prevention and control. Feed Industry, 27(17), 48–51.
MAFF (1991). Code of Good Agricultural Practice for the Protection of Water. MAFF publications, London (PB0587).
Ye, C., Xu, Q. J., Kong, H. N., Shen, Z. M., & Yan, C. Z. (2007). Eutrophication conditions and ecological status in typical bays of Lake Taihu in China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 135(1–3), 217–225.
Zhao, Y. F., Shi, X. Z., Huang, B., Yu, D. S., Wang, H. J., Sun, W. X., et al. (2007). Spatial distribution of heavy metals in agricultural soils of an industry-based peri-urban area in Wuxi, China. Pedosphere, 17(1), 44–51.
Wan, H. Y., Zhou, S. L., & Zhao, Q. G. (2005). Spatial variation of content of soil heavy metals in region with high economy development of south Jiangsu province. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 25(3), 329–334.
Temminghoff, E. J. M., Van der Zee, S. E. A. T. M., & de Haan, F. A. M. (1997). Copper mobility in a copper-contaminated sandy soil as affected by pH and solid and dissolved organic matter. Environmental Science & Technology, 31(4), 1109–1115.
Oremland, R. S., & Stolz, J. F. (2003). The ecology of arsenic. Science, 300(5621), 939–944.
Bolan, N. S., Khan, M. A., Donaldson, J., Adriano, D. C., & Matthew, C. (2003). Distribution and bioavailability of copper in farm effluent. The Science of the Total Environment, 309(1–3), 225–236.
Zobrist, J., Dowdle, P. R., Davis, J. A., & Oremland, R. S. (2000). Mobilization of arsenite by dissimilatory reduction of adsorbed arsenate. Environmental Science & Technology, 34(22), 4747–4753.
Smedley, P. L., & Kinniburgh, D. G. (2002). A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Applied Geochemistry, 17(5), 517–568.
Acknowledgements
This work was finally supported by the Ministry of Agriculture (No. 200903011-01) and Jiangsu International Cooperation Project (No. BZ2009101). The authors thank Dr. Xiaomei Ye, Dr. Yan Ma and Ms. Jin Zhu for data sharing, and Ms. Zhi Xu and the staff in various farms for logistic assistance and help with sampling. We thank He Chang for help with translating clearly. The constructive comments by two anonymous reviewers have helped to improver this paper over an earlier version.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, H., Chang, Z. Distribution of Heavy Metal Contents and Chemical Fractions in Anaerobically Digested Manure Slurry. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 164, 268–282 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-010-9133-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-010-9133-7