Abstract
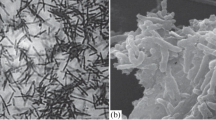
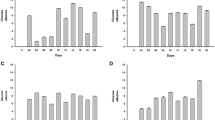
A unique thermophilic microbial community developed initially from swine waste was investigated in this study. Cellulase activities were observed when this community was inoculated to media containing either cellulose or carboxymethylcellulose at 57 °C. Through constructing a clone library for the 16S ribosomal DNA, it was revealed that this community was mainly composed of three genera: Thermobacillus, Brevibacillus, and Anoxybacillus. New findings regarding the thermo- and pH stability of crude cellulases secreted by Brevibacillus sp. JXL were presented. Recent study on the growth characteristics of Anoxybacillus sp. 527 was discussed.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Demain, A. L., Newcomb, M., & Wu, J. H. D. (2005). Cellulase, clostridia, and ethanol. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 69, 124–154.
Perlack, R. D., Wright, L. L., Turhollow, A. F., Graham, R. L., & Stokes B. J. (2005). Biomass as feedstock for a bioenergy and bioproducts industry: The technical feasibility of a billion-ton annual supply. In Oak Ridge National Research Laboratory Report TM-2005, under contract DOE/GO-1022005-2135, Oak Ridge, TN.
Wyman, C. E. (1999). Biomass ethanol: Technical progress, opportunities, and commercial challenges. Annual Review of Energy and the Environment, 24, 189–226.
Wyman, C. E., Dale, B. E., Elander, R. T., Holtzapple, M., Ladisch, M. R., & Lee, Y. Y. (2005). Coordinated development of leading biomass pretreatment technologies. Bioresource Technology, 96, 1959–1966.
Zhang, Y. H. P., Himmel, M. E., & Mielenz, J. R. (2006). Outlook for cellulase improvement: Screening and selection strategies. Biotechnology Advance, 24, 452–481.
Irwin, D., Leathers, T. D., Greene, R. V., & Wilson, D. B. (2003). Corn fiber hydrolysis by Thermobifida fusca extracellular enzymes. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 61, 352–358.
Suchardová, O., Krumphanzl, V., & Panos, J. (1981). Physiology of growth of a mixed culture of thermophilic bacteria on cellulose under microaerophilic conditions. Biotechnology Letters, 3, 47–550.
Blackburn, J. W., Liang, Y., & Das, D. (2009). Biohydrogen from complex carbohydrate wastes as feedstocks- cellulose degraders from a unique series enrichment. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 34(17), 7428–7434. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.04.014.
Liang, Y., Yesuf, J., Schmitt, S., Bender, K., & Bozzola, J. (2009). Study of cellulases from a newly-isolated thermophilic and cellulolytic Brevibacillus sp. strain JXL. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 36, 961–970.
Liang, Y., Feng, Z., & Yesuf, J. (2009). Optimization of growth medium and enzyme assay conditions for crude cellulases produced by a novel thermophilic and cellulolytic bacterium, Anoxybacillus sp. 527. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, doi:10.1007/s12010-009-8677-x.
Atlas, R. M. (2004). Handbook of microbiological media (3rd ed.). Boca Raton: CRC.
Ghose, T. K. (1987). Measurement of cellulase activities. Pure & Applied Chemistry, 59, 257–268.
Watanabe, K., Nagao, N., Yamamoto, S., Toda, T., & Kurosawa, N. (2007). Thermobacillus composti sp. nov., a moderately thermophilic bacterium isolated from a composting reactor. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 57, 1473–1477.
Touzel, J. P., O’Donohue, M., Debeire, P., Samain, E., & Breton, C. (2000). Thermobacillus xylanilyticus gen. nov., sp. nov., a new aerobic thermophilic xylan-degrading bacterium isolated from farm soil. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 50, 315–320.
Johnson, E. A., Sakajoh, M., Halliwell, G., Madia, A., & Demain, A. L. (1982). Saccharification of complex cellulosic substrates by the cellulase system from Clostridium thermocellum. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 43, 1125–1132.
Pikuta, E., Lysenko, A., Chuvilskaya, N., Mendrock, U., Hippe, H., Suzina, N., et al. (2000). Anoxybacillus pushchinensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel anaerobic, alkaliphilic, moderately thermophilic bacterium from manure, and description of Anoxybacillus flavitherms comb. nov. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 50, 2109–2117.
Pikuta, E., Cleland, D., & Tang, J. (2003). Aerobic growth of Anoxybacillus pushchinoensis K1(T): Emended descriptions of A. pushchinoensis and the genus Anoxybacillus. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 53, 1561–1562.
Gul-Guven, R., Guven, K., Poli, A., & Nicolaus, B. (2008). Anoxybacillus kamchatkensis subsp. asaccharedens subsp. nov., a thermophilic bacterium isolated from a hot spring in Batman. Journal of General Applied Microbiology, 54, 327–334.
Atanassova, M., Derekova, A., Mandeva, R., Sjoholm, C., & Kambourova, M. (2008). Anoxybacillus bogrovensis sp. nov., a novel thermophilic bacterium isolated from a hot spring in Dolni Bogrov, Bulgaria. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 58, 2359–2362.
Kevbrin, V. V., Zengler, K., Lysenko, A. M., & Wiegel, J. (2005). Anoxybacillus kamchatkensis sp. nov., a novel thermophilic facultative aerobic bacterium with a broad pH optimum from the Geyser valley, Kamchatka. Extremophiles, 9, 391–398.
De Clerck, E., Rodriguez-Diaz, M., Vanhoutte, T., Heyrman, J., Logan, N. A., & De Vos, P. (2004). Anoxybacillus contaminans sp. nov. and Bacillus gelatini sp. nov., isolated from contaminated gelatin batches. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 54, 941–946.
Poli, A., Esposito, E., Lama, L., Orlando, P., Nicolaus, G., de Appolonia, F., et al. (2006). Anoxybacillus amylolyticus sp. nov., a thermophilic amylase producing bacterium isolated from Mount Rittmann (Antarctica). Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 29, 300–307.
Derekova, A., Sjoholm, C., Mandeva, R., & Kambourova, M. (2007). Anoxybacillus rupiensis sp. nov., a novel thermophilic bacterium isolated from Rupi basin (Bulgaria). Extremophiles, 11, 577–583.
Dulger, S., Demirbag, Z., & Belduz, A. O. (2004). Anoxybacillus ayderensis sp. nov. and Anoxybacillus kestanbolensis sp. nov. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 54, 1499–1503.
Schäffer, C., Franck, W. L., Scheberl, A., Kosma, P., McDermott, T. R., & Messner, P. (2004). Classification of isolates from locations in Austria and Yellowstone National Park as Geobacillus tepidamans sp. nov. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 54, 2361–2368.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. James Blackburn for providing the bacterial source sample for this work. This research is supported by SIUC’s new faculty startup funds. Financial support from Material Technology Center at SIUC is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, Y., Yesuf, J. & Feng, Z. Toward Plant Cell Wall Degradation Under Thermophilic Condition: A Unique Microbial Community Developed Originally from Swine Waste. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 161, 147–156 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-009-8780-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-009-8780-z