Abstract
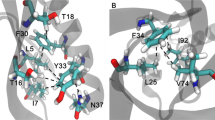
C–H….π interactions are known to be important contributors to protein stability. In this study, we have analyzed the influence of C–H….π interactions in single chain “all-alpha” proteins. In the data set, a total of 181 C–H….π interactions were observed. The most prominent representatives are the interactions between aromatic C–H donor groups and aromatic π acceptors. Eighty-one percent of the C–H….π interactions between side chain to side chain and remaining19% of the C–H….π interactions were observed between side-chain to side-chain five-member aromatic ring. The donor atom contribution to C–H….π interactions was mainly from Phe, Tyr, and Trp residues. The acceptor atom contribution to C–H….π interactions was mainly from Phe, Tyr, Trp, and His. The highest percentage of C–H….π interactions were observed form Phe residue. The secondary structure preference analysis of all C–H….π interacting residues showed that Phe, Tyr, Trp, and His preferred to be in helix. Long-range C–H….π interactions are the predominant type of interactions in single chain all-alpha proteins data set. All the C–H….π interactions forming residues in the data set preferred to be in the buried region. Seventy-three percent of the donor residues and 65% of the acceptor residues are highly conserved.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tamres, M. (1952). Journal of the American Chemical Society, 74, 3375–3378. doi:10.1021/ja01133a047.
Reeves, L. W., & Schneider, W. G. (1957). Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 35, 251–261. doi:10.1139/v57-036.
Nishio, M., Hirota, M., & Umezawa, Y. (Eds.) (1998). New York: Wiley.
Matsui, I., Matsui, E., Sakai, Y., Kikuchi, H., Kawarabayasi, Y., Ura, H., et al. (2000). The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275, 4871–4879. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.7.4871.
Chakrabarti, P., & Samanta, U. (1995). Journal of Molecular Biology, 251, 9–14. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1995.0411.
Umezawa, Y., & Nishio, M. (1998). Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 6, 493–504. doi:10.1016/S0968-0896(98)00002-9.
Muraki, M., Harata, K., Sugita, N., & Sato, K. I. (2000). Biochemistry, 39, 292–299. doi:10.1021/bi991402q.
Umezawa, Y., & Nishio, M. (1998). Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 6, 2507–2515. doi:10.1016/S0968-0896(98)80024-2.
Jabs, A., Weiss, M. S., & Hilgenfeld, R. (1999). Journal of Molecular Biology, 286, 291–304. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1998.2459.
Shimohigashi, Y., Maeda, I., Nose, T., Ikesue, K., Sakamoto, H., Ogawa, Y., et al. (1996). Journal of the Chemical Society, 1, 2479–2485.
Shimohigashi, Y., Nose, T., Yamauchi, Y., & Maeda, I. (1999). Biopolymers, 51, 9–17. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0282(1999)51:1<9::AID-BIP3>3.0.CO;2-5.
Steiner, T. (2002). Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English, 41, 48–76. doi:10.1002/1521-3773(20020104)41:1<48::AID-ANIE48>3.0.CO;2-U.
Steiner, T., & Koellner, G. J. (2001). Journal of Molecular Biology, 305, 535–557. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2000.4301.
Meyer, E. A., Castellano, R. K., & Diederich, F. (2003). Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English, 42, 1210–1250. doi:10.1002/anie.200390319.
Martis, R. L., Singh, S. K., Michael Gromiha, M., & Santhosh, C. (2008). Journal of Theoretical Biology, 250, 655–662. doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2007.10.024.
Berman, H. M., Westbrook, J. Z., Feng, G., Gillilandm, T. N., Bhat, H., Weissig, I. N., et al. (2000). Nucleic Acids Research, 28, 235–242. doi:10.1093/nar/28.1.235.
Conte, L. L., Ailey, B., Hubbard, T. J. P., Brenner, S. E., Murzin, A. G., & Chothia, C. (2000). Nucleic Acids Research, 28, 257–259. doi:10.1093/nar/28.1.257.
Tiwari, A., & Panigrahi, S. K. (2007). In Silico Biology, 7, 0057.
Babu, M. M. (2003). Nucleic Acids Research, 31, 3345–3348. doi:10.1093/nar/gkg528.
Kabsch, W., & Sander, C. (1983). Biopolymers, 22, 2577–2637. doi:10.1002/bip. 360221211.
Gilis, D., & Rooman, M. (1996). Journal of Molecular Biology, 257, 1112–1126. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1996.0226.
Gilis, D., & Rooman, M. (1997). Journal of Molecular Biology, 272, 276–290. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1997.1237.
Gromiha, M. M., & Selvaraj, S. (1997). Journal of Biological Physics, 23, 151–162. doi:10.1023/A:1004981409616.
Gromiha, M. M., Santhosh, C., & Ahmed, S. (2004). International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 34, 203–211. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2004.04.003.
Selvaraj, S., & Gromiha, M. M. (2003). Biophysical Journal, 84, 1919–1925. doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(03)75000-0.
Gromiha, M. M., & Selvaraj, S. (2004). Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology, 86, 235–277. doi:10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2003.09.003.
Glaser, F., Pupko, T., Paz, I., Bell, R. E., Bechor, D., Martz, E., et al. (2003). Bioinformatics (Oxford, England), 19, 163–164. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/19.1.163.
Boeckman, B., Bairoch, A., Apweiler, R., Blatter, M. C., Estreicher, A., Gasteiger, E., et al. (2003). Nucleic Acids Research, 31, 365–370. doi:10.1093/nar/gkg095.
Brandl, M., Weiss, M. S., Jabs, A., Sühnel, J., & Hilgenfeld, R. (2001). Journal of Molecular Biology, 307, 357–377. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2000.4473.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the management of Vellore Institute of Technology for providing the facilities to carry out this work. The authors also thank the reviewers for their suggestions in the improvement of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shanthi, V., Ramanathan, K. & Sethumadhavan, R. Exploring the Role of C–H….π Interactions on the Structural Stability of Single Chain “All-Alpha” Proteins. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160, 1473–1483 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-009-8584-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-009-8584-1