Abstract
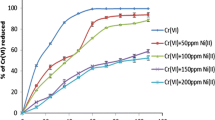
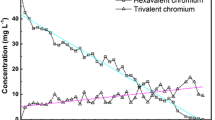
In the present study, hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) reduction potential of chromium reductase associated with the cell-free extracts (CFE) of Arthrobacter rhombi-RE species was evaluated. Arthrobacter rhombi-RE, an efficient Cr(VI) reducing bacterium, was enriched and isolated from a chromium-contaminated site. Chromium reductase activity of Arthrobacter rhombi-RE strain was associated with the cell-free extract and the contribution of extracellular enzymes to Cr(VI) reduction was negligible. NADH enhanced the chromium reductase activity. The enzyme activity was optimal at a pH of 5.5 and a temperature of 30 °C. Among the ten electron donors screened, sodium pyruvate was the most effective one followed by NADH and propionic acid. Michaelis–Menten constant, K m, and maximum reaction rate, V max, obtained from the Lineweaver–Burk plot were 48 μM and 4.09 nM/mg protein/min, respectively, in presence of NADH as electron donor and 170.5 μM and 4.29 nM/mg protein/min, respectively, in presence of sodium pyruvate as electron donor. Ca2+ enhanced the enzyme activity while Hg2+, Cd2+, Ba2+, and Zn2+ inhibited the enzyme activity. Among the various immobilization matrices screened, calcium alginate beads seemed to be the most effective one. Though immobilized enzyme system was able to reduce Cr(VI), the performance was not very encouraging in continuous mode of operation.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves, M. M., Ceca, C. G. G., Carvalho, R. G. D., Castanheira, J. M., Periera, M. C. S., & Vasconcelos, L. A. T. (1993). Water Research, 27, 1333–1338. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(93)90220-C.
Shen, H., & Wang, Y. T. (1993). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 59, 3771–3777.
Volesky, B., & Holan, Z. R. (1995). Biotechnology Progress, 11, 235–250. doi:10.1021/bp00033a001.
Philip, L., Iyengar, L., & Venkobachar, C. (1998). Journal of Environmental Engineering, 124, 1165–1170. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(1998)124:12(1165).
Guha, H., Jayachandran, K., & Maurrasse, F. (2001). Environmental Pollution, 115, 209–218. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(01)00108-7.
Schmieman, E. A., Yonge, D. R., Rege, M. A., Petersen, J. N., Turick, C. E., Johnstone, D. L., et al. (1998). Journal of Environmental Engineering, 124, 449–455. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(1998)124:5(449).
Chirwa, E. N., & Wang, Y. T. (2000). Water Research, 34, 2376–2384. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(99)00363-2.
Smith, W. A., Apel, W. A., Petersen, J. N., & Peyton, B. M. (2002). Bioremediation Journal, 6, 205–215. doi:10.1080/10889860290777567.
Wang, Y., & Xiao, C. (1995). Water Research, 29, 2467–2474. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(95)00093-Z.
Chen, J. M., & Hao, O. J. (1997). Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology (Oxford, Oxfordshire), 69, 70–76. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4660(199705)69:1<70::AID-JCTB665>3.0.CO;2-4.
Philip, L., Iyengar, L., & Venkobachar, C. (1999). International Journal of Environment and Pollution, 11, 202–210. doi:10.1504/IJEP.1999.002258.
Chirwa, E. N., & Wang, Y. T. (2001). Water Research, 35(8), 1921–1932. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00472-3.
Dermou, E., Velissariou, A., Xenos, D., & Vayenas, D. V. (2007). Desalination, 211, 156–163. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2006.02.090.
Zakaria, Z. A., Zakaria, Z., Surif, S., & Ahmad, W. A. (2007). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 148, 164–171. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.02.029.
Park, C. H., Keyhan, M., Wielinga, B., Fendorf, S., & Matin, A. (2000). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66, 1788–1795. doi:10.1128/AEM.66.5.1788-1795.2000.
Camargo, F. A., Okeke, B. C., Bento, F. M., & Frankenberger, W. T. (2003). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 62, 569–573. doi:10.1007/s00253-003-1291-x.
Megharaj, M., Avudainayagam, S., & Naidu, R. (2004). Current Microbiology, 47, 51–54. doi:10.1007/s00284-002-3889-0.
Bae, W. C., Lee, H. K., Choe, Y. C., Jahng, D. J., Lee, S. H., Kim, S. J., et al. (2005). Journal of Microbiology (Seoul, Korea), 43, 21–27.
Elangovan, R., Abipsha, S., Rohit, B., Philip, L., & Chandraraj, K. (2006). Biotechnology Letters, 28(4), 247–252. doi:10.1007/s10529-005-5526-z.
Pal, A., Dutta, S., & Paul, A. K. (2005). Current Microbiology, 51, 327–330. doi:10.1007/s00284-005-0048-4.
Garbisu, C., Alkorta, I., Llama, M. J., & Serra, J. L. (1998). Biodegradation, 9, 133–141. doi:10.1023/A:1008358816529.
McLean, J., & Beveridge, T. J. (2001). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67, 1076–1084. doi:10.1128/AEM.67.3.1076-1084.2001.
White, C. A., & Kennedy, J. F. (1985). In A. Wiseman (Ed.), Handbook of enzyme biotechnology pp. 147–380. Chichester: Horwood.
Munjal, N., & Sawhney, S. K. (2002). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 30, 613–619. doi:10.1016/S0141-0229(02)00019-4.
Mabbett, A. N., Yong, P., Farr, J. P. G., & Macaskie, L. E. (2004). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 87, 104–109. doi:10.1002/bit.20105.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., & Randall, R. J. (1951). The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 193, 265–275.
APHA (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Lovley, D. R., & Phillips, E. J. P. (1994). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 60, 726–728.
Ishibashi, Y., Cervantes, C., & Silver, S. (1990). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 56, 2268–2270.
Campos, J., Martinez-Pacheco, M., & Cervantes, C. (1995). Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 68, 203–208. doi:10.1007/BF00871816.
Bopp, L. H., & Ehrlich, H. L. (1988). Archives of Microbiology, 150, 426–431. doi:10.1007/BF00422281.
Wang, P. C., Mori, T., Toda, K., & Ohtake, H. (1990). Journal of Bacteriology, 172, 1670–1672.
Wang, P., Mori, T., Komori, K., Sasatsu, M., Toda, K., & Ohtake, H. (1989). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 55, 1665–1669.
Bhinde, J. V., Dhakephalkar, P. K., & Paknikar, K. M. (1996). Biotechnology Letters, 18, 667–672. doi:10.1007/BF00130763.
Farrell, S. O., & Ranallo, R. T. (2000). Experiments in biochemistry. a hands-on approach. Orlando: Saunders College Publications.
Losi, M. E., Amrhein, C., & Frankenberger, W. T. (1994). Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 36, 91–121.
Camargo, F. A., Bento, F. M., Okeke, B. C., & Frankenberger, W. T. (2004). Biological Trace Element Research, 97, 183–194. doi:10.1385/BTER:97:2:183.
Hiraoka, B. Y., Fukasawa, K., & Harada, M. (1987). Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 73, 111–115. doi:10.1007/BF00219425.
Kwak, Y. H., Lee, D. S., & Kim, H. B. (2003). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 69, 4390–4395. doi:10.1128/AEM.69.8.4390-4395.2003.
Opperman, D. J., Piater, L. A., & Heerden, E. V. (2008). Journal of Bacteriology, 8, 3076–3082.
Birke, R. L., & Lombardi, J. R. (1988). In R. J. Gale (Ed.), Surface enhanced Raman scattering in spectroelectrochemistry: theory and practice. Plenum, New York.
Longo, M. A., Novella, I. S., García, L. A., & Díaz, M. (1992). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 14, 586–590. doi:10.1016/0141-0229(92)90131-7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elangovan, R., Philip, L. & Chandraraj, K. Hexavalent Chromium Reduction by Free and Immobilized Cell-free Extract of Arthrobacter rhombi-RE . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160, 81–97 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8515-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8515-6