Abstract
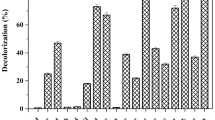
A combined biological (augmented membrane bioreactor (MBR)) and photochemical (photocatalysis and ozonation) treatment has been proposed for bromoamine acid (BAA) removal in dyeing wastewater. It was demonstrated that the color and chemical oxygen demand removal in the sequential augmented MBR was about 90% and 50%, respectively. By ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis, it was found that the introduced strain QYY was maintained as the predominant species and the diversity of the system was relatively low throughout the operation. Photocatalysis and ozonation processes were efficient to treat the effluents from MBR with high color and total organic carbon removal more than 90% within 120 min. Therefore, the hybrid treatment system is a possible way to achieve the complete mineralization of BAA.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pearce, C. I., Lloyd, J. R., & Guthrie, J. T. (2003). The removal of color from textile wastewater using whole bacterial cells: a review. Dyes and Pigments, 58, 179–196. doi:10.1016/S0143-7208(03)00064-0.
Pandey, A., Singh, P., & Iyengar, L. (2007). Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 59, 73–84. doi:10.1016/j.ibiod.2006.08.006.
Forgacs, E., Cserhátia, T., & Oros, G. (2004). Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: a review. Environment International, 30, 953–971. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2004.02.001.
Sendelbach, L. E. (1989). A review of the toxicity and carcinogenicity of anthraquinone derivatives. Toxicology, 57, 227–240. doi:10.1016/0300-483X(89)90113-3.
Qu, Y. Y., Wang, J., Zhou, J. T., & Xing, L. L. (2005). Decolorization of bromoamine acid by a newly isolated strain of Sphingomonas xenophaga QYY and its resting cells. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 27, 104–109. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2005.08.005.
Qu, Y. Y., Zhou, J. T., Wang, J., Fu, X., & Xing, L. L. (2005). Microbial community dynamics in bioaugmented sequencing batch reactors for bromoamine acid removal. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 246, 143–149. doi:10.1016/j.femsle.2005.04.006.
Qu, Y. Y., Zhou, J. T., Wang, J., Song, Z. Y., Xing, L. L., & Fu, X. (2006). Bioaugmentation of bromoamine acid degradation with Sphingomonas xenophaga QYY and DNA fingerprint analysis of augmented systems. Biodegradation, 17, 83–91. doi:10.1007/s10532-005-3544-0.
Hu, J., Zhou, J. T., Sun, L. Y., & Yang, S. (2004). Pretreatment of bromoamine acid wastewater by combined TiO2/UV and ozone. Industrial Water Treatment (China), 24, 34–36.
Gogate, P. R., & Pandit, A. B. (2004). A review of comparative technologies for wastewater treatment II: hybrid methods. Advances in Environmental Research, 8, 553–597. doi:10.1016/S1093-0191(03)00031-5.
Gomez, C., Rodriguez, J., Freer, J., Lizama, C., Zaror, C., & Mansilla, H. D. (2007). Coupling of photocatalytic and biological reactors to remove EDTA-Fe from aqueous solution. Environmental Technology, 28, 123–127. doi:10.1080/09593332808618781.
Essam, T., Amino, M. A., Ei, T. O., Mattiasson, B., & Guieysse, B. (2007). Sequential photochemical-biological degradation of chlorophenols. Chemosphere, 66, 2201–2209. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.08.036.
Mufiel, B., Wafa, A., Vincent, U., & Thierry, H. (1999). DNA extraction from activated sludge. Current Microbiology, 38, 315–319. doi:10.1007/PL00006809.
APHA.Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater (1995). (20th ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Xing, L. L. (2005). Study on the treatment of bromoamine acid wastewater by the bioaugmented membrane bioreactor. Master Dissertation of Dalian University of Technology.
Idil, A. A., Emine, U. C., & Baris, K. (2007). Integrated photochemical and biological treatment of a commercial textile surfactant: process optimization, process kinetics and COD fractionation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 146, 453–458. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.04.069.
Parra, S., Sarria, V., Malato, S., Péringer, P., & Pulgarin, C. (2000). Photochemical versus coupled photochemical-biological flow system for the treatment of two biorecalcitrant herbicides: metobromuron and isoproturon. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 27, 153–168. doi:10.1016/S0926-3373(00)00151-X.
L’Amour, R. J. A., Azevedo, E. B., Leite, S. G. F., & Dezotti, M. (2007). Removal of phenol in high salinity media by a hybrid process (activated sludge + photocatalysis). Separation and Purification Technology, doi:10.1016/j. seppur. 2007.08.008.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 50608011) and the State Key Lab of Urban Water Resource and Environment in Harbin Institute of Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, Yy., Yang, Q., Zhou, Jt. et al. Combined MBR with Photocatalysis/Ozonation for Bromoamine Acid Removal. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 159, 664–672 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8501-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8501-z