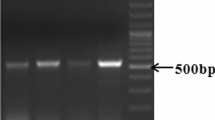
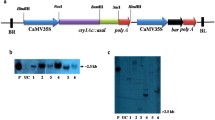
Abstract
Plant lectins have been reported as transgenic resistance factors against a variety of insect pests. Herein, homologous analysis demonstrated that Zephyranthes grandiflora agglutinin (ZGA) exhibited high similarity with other monocot mannose-binding lectins (MBLs). Phylogenetic analysis revealed that it had taxonomical relationships with insecticidal MBLs. Subsequently, a plasmid expression vector pBI121 containing zga gene (pBIZGA) was constructed using the zga sequence, under the control of CaMV35S promoter and nos terminator. pBIZGA was then integrated into the genome of Nicotiana tabacum L. Polymerase chain reaction and Southern blot analysis demonstrated that this zga gene was integrated into the plant genome. Western blotting and agglutinating activity analysis also showed that transgenic tobacco plants expressed different levels of ZGA. Carbohydrate inhibition analysis indicated that recombinant ZGA and the native shared the same carbohydrate-binding specificity. Moreover, genetic analysis confirmed Mendelian segregation (3:1) of the transgenic in T1 progenies. In planta bioassays on T0 plants and their progenies indicated that expressed ZGA had an effect on reducing the survivability and fecundity of tobacco aphids (Myzus nicotianae). These findings demonstrate that the novel zga gene of ZGA can be expressed in crop plants susceptible to various sap-sucking insects.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- pBIZGA:
-
expression vector pBI121 containing zga gene
- ZGA:
-
Zephyranthes grandiflora agglutinin
- CaMV35S:
-
35S cauliflower mosaic virus promoter
- zga :
-
Zephyranthes grandiflora agglutinin gene
- MBLs:
-
mannose-binding lectins
- GNA:
-
Galanthus nivalis agglutinin
- ZCA:
-
Zephyranthes candida agglutinin
- gna :
-
Galanthus nivalis agglutinin gene
- ASAL:
-
Allium sativum leaf agglutinin
- WGA:
-
wheat germ agglutinin
- 6-BA:
-
6-benzylaminopurine
- ConA:
-
concanavalin A
- T0:
-
the first generation of transgenic plants
- T1:
-
the first progenies of T0
References
Sharon, N., & Lis, H. (1989). Lectins as cell recognition molecules. Science, 246(4927), 227–234. doi:10.1126/science.2552581.
Goldstein, I. J., Hughes, R. C., Monsigny, A., Osawa, T., & Sharon, N. (1980). What should be called a lectin? Nature, 285, 66. doi:10.1038/285066b0.
Huang, G. L., Huang, H. L., Zhang, H. C., & Wang, P. G. (2006). Structure-function relations of carbohydrates by neoglycolipid arrays. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 133(3), 211–215. doi:10.1385/ABAB:133:3:211.
Goldberg, R. B., Barker, S. J., & Perez-Grau, L. (1989). Regulation of gene expression during plant embryogenesis. Cell, 56(2), 146–160. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(89)90888-X.
Howard, I. K., Sage, H. J., & Horton, C. B. (1972). Studies on the appearance and location of hemagglutinins from a common lentil during the life cycle of the plant. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 149, 323–326. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(72)90328-1.
Brill, L. M., Evans, C. J., & Hirsch, A. M. (2001). Expression of MsLEC1- and MsLEC2-antisense genes in alfalfa plant lines causes severe embryogenic, developmental and reproductive abnormalities. The Plant Journal, 25, 453–461. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.00979.x.
Liu, B., Xu, X. C., Cheng, Y., Huang, J., Liu, Y. H., Liu, Z., et al. (2008). Apoptosis-inducing effect and structural basis of Polygonatum cyrtonema lectin and chemical modification properties on its mannose-binding sites. BMB Reports, 41(5), 369–375.
Liu, B., Cheng, Y., Zhang, B., Bian, H. J., Bao J. K. Polygonatum cyrtonema lectin induces apoptosis and autophagy in human melanoma A375 cells through a mitochondria-mediated ROS–p38–p53 pathway. Cancer Letter, doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2008.09.042.
Wong, J. H., & Ng, T. B. (2005). Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 439, 91–98. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2005.05.004.
Macedo, M. L. R., Damico, D. C. S., Freire, M. G. M., Toyama, M. H., Marangoni, S., & Novello, J. C. (2003). Purification and Characterization of an N-Acetylglucosamine-Binding Lectin from Koelreuteria paniculata Seeds and Its Effect on the Larval Development of Callosobruchus maculatus (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) and Anagasta kuehniella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 51(10), 2980–2986.
Luo, Y. T., Xu, X. C., Wei, L. J., Li, J., Sun, Y. S., Liu, Z., et al. (2007). A novel mannose-binding tuber lectin from Typhonium divaricatum (L.) Decne (family Araceae) with antiviral activity against HSV-II and anti-proliferative effect on human cancer cell lines. Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 40, 358–367.
Kumar, P. R. (1999). Rapeseed-mustard research in India: 21st century strategies, new horizons for an old crop. Rapeseed congress. Canberra, Australia: Regional Inst. Ltd.
Patel, S. R., Awasthi, A. K., & Tomar, R. K. S. (2004). Assessment of yield losses in mustard (Brassica juncea L.) due to mustard aphids (Lipapahis erysimi Kalt.) under different thermal environment in eastern central India. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 2(1), 1–15.
Watanabe, T., & Kitagawa, H. (2000). Photosynthesis and Translocation of Assimilates in Rice Plants Following Phloem Feeding by the Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens (Homoptera: Delphacidae). Journal of Economic Entomology, 93, 1192–1198.
Zheng, Y. Z., Lan, W. S., Qiao, C. L., Mulchandani, A., & Chen, W. (2007). Decontamination of vegetables sprayed with organophosphate pesticides by organophosphorus hydrolase and carboxylesterase (B1). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 136(3), 233–241.
Rao, K. V., Rathore, K. S., Hodges, T. K., Fu, X., Stoger, E., et al. (1998). Expression of snowdrop lectin (GNA) in transgenic plants confers resistance to rice brown planthopper. The Plant Journal, 15(4), 469–477.
Jain, D., Udayasuriyan, V., Arulselvi, P. I., Dev, S. S., & Sangeetha, P. (2006). Cloning, characterization, and expression of a new cry2Ab gene from Bacillus thuringiensis strain 14-1. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 128(3), 185–194.
Rahbe, Y., Deraison, C., Bonade-Bottino, M., Girard, C., Nardone, C., & Jouanin, L. (2003). Effects of the cysteine protease inhibitor oryzacystatin (OC-I) on different aphids and reduced performance of Myzus persicae on (OC-I) expressing transgenic oilseed rape. Plant Science, 164, 441–450.
Schuler, T. H., Poppy, G. M., Kerry, B. R., & Denholm, I. (1998). Insect-resistant transgenic plants. Trends in Biotechnology, 16, 168–175.
Hossain, M. A., Maiti, M. K., Basu, A., Sen, S., Ghosh, A. K., & Sen, S. K. (2006). Transgenic Expression of Onion Leaf Lectin Gene in Indian Mustard Offers Protection against Aphid Colonization. Crop Science, 46, 2022–2032.
Hilder, V. A., Powell, K. S., Gatehouse, A. M. R., Gatehouse, J. A., Gatehouse, L. N., Shi, Y., et al. (1995). Expression of snowdrop lectin in transgenic tobacco plants results in added protection against aphids. Transgenic Research, 4, 18–25.
Down, R. E., Gatehouse, A. M. R., Hamilton, W. D., & Gatehouse, J. A. (1996). Snowdrop lectin inhibits development and decrease fecundity of the glasshouse potato aphid (Aulacorthum solani) when administered in vitro and via transgenic plants both in laboratory and glasshouse trials. Journal of Insect Physiology, 42, 1035–1045.
Wu, C. F., Li, J., An, J., Chang, L. Q., Chen, F., & Bao, J. K. (2006). Purification, Biological Activities, and Molecular Cloning of a Novel Mannose-Binding Lectin from Bulbs of Zephyranthes candida Herb (Amaryllidaceae). Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 48(2), 223–231.
Sauvion, N., Rahbe, Y., Peumans, W. J., Van Damme, E. J. M., Gatehouse, J. A., & Gatehouse, A. M. R. (1996). Effects of GNA and other mannose binding lectins on development and fecundity of the peach-potato aphid Myzus persicae. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 79, 285–293.
Yao, J. H., Pang, Y. Z., Qi, H. X., Wan, B. L., Zhao, X. Y., Kong, W. W., et al. (2003). Transgenic tobacoo expressing Pinellia ternate agglutinin confers enhanced resistance to aphids. Transgenic Research, 12, 715–722.
Sadeghi, A., Broeders, S., De Greve, H., Hernalsteens, J. P., Peumans, W. J., Van Damme, E. J. M., et al. (2007). Expression of garlic leaf lectin under the control of the phloem-specificpromoter Asus1 from Arabidopsis thaliana protects tobacco plants against the tobacco aphid (Myzus nicotianae). Pest Management Science, 63, 1215–1223.
Mochida, O., Wahyu, A. & Surjani, T. K. (1979). Some Considerations on Screening Resistant Cultivars/lines of Rice Plant to the Brown Planthopper, Nilparvata lugens (Stal) (Hom, Delphacidae). Los Banos, Philippines: International Rice Research Institute, pp. 1–9.
Dahal, G., Hibino, H., & Aguiero, V. M. (1997). Population characteristics and tungro transmission by Nephotettix virescens (Hemiptera: Cicadellidea) on selected resistant rice cultivars. Bulletin of Entomological Research, 87, 387–395.
Kanrar, S., Venkateshwari, J., Kirti, P. B., & Chopra, V. L. (2002). Transgenic Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) with resistance to mustard aphid (Lipaphis erysimi Kalt.). Plant Cell Reports, 20, 976–981.
Bandyopadhyay, S., Roy, A., & Das, S. (2001). Binding of garlic (Allium sativum) leaf lectin to the gut receptors of homopteran pests is correlated to its insecticidal activity. Plant Science, 161, 1025–1033.
Banerjee, S., Hess, D., Majumder, P., Roy, D., & Das, S. (2004). The Interactions of Allium sativum Leaf Agglutinin with a Chaperonin Group of Unique Receptor Protein Isolated from a Bacterial Endosymbiont of the Mustard Aphid. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279(22), 23782–23789.
Bao, J. K., Wu, C. F., An, J., et al. (2004). Molecular Cloning and Analysis of a Monocot Mannose-binding Agglutinin from Zephyranthes Grandiflora(Family Amaryllidaceae). Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 21(5), 812–816.
Thompson, J. D., Higgins, D. G., & Gibson, T. J. (1994). CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Research, 22, 4673–4680.
Kumar, S., Tamura, K., & Nei, M. (2004). MEGA3: Integrated software for Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis and sequence alignment, Brief. Briefings in Bioinformatics Advance Access, 5, 150–163.
Tamura, K., Dudley, J., Nei, M., & Kumar, S. (2007). MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) Software Version 4.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24, 1596–1599.
Horsch, R. B., Fry, J., Hoffmann, N., Neidermeyer, J., Rogers, S. G., & Fraley, R. T. (1988). Leaf disc transformation. Plant molecular biology manual A5 pp. 1–9. Dordtrecht, Netherlands: Kluwer.
Murashige, T., & Skoog, F. (1962). Revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Plant Physiology, 15, 473–479.
Graham, G. C. (1994). A simplified method for the preparation of fungal genomic DNA for PCR and RAPD analysis. Biotechniques, 16, 49–50.
Lee, R. W. H., Strommer, J., Hodgins, D., Shewen, P. E., Niu, Y. Q., & Lo, R. Y. C. (2001). Towards development of an edible vaccine against bovin pneumonic pasteurellosis using transgenic clover expressing a Mannheimia haemolytica A1 leukotoxin 50 fusion protein. Infection and Immunity, 69(9), 5786–5793.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., & Randall, R. J. (1951). Protein measurement with the follin pheol reagent. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 193(1), 265–275.
Oda, Y., & Minami, K. (1986). Isolation and characterization of a lectin from tulip bulbs, Tulipa gesneriana. European Journal of Biochemistry, 159, 239–245.
Schardl, C. L., Byrd, A. D., Benzion, G., Altschuler, M. A., Hildebrand, D. F., & Hunt, A. G. (1987). Design and construction of a versatile system for the expression of foreign genes in plants. Gene, 61, 1–11.
Van Damme, E. J. M., Smeets, K., Torrekens, S., Van Leuven, F., Goldstein, I. J., et al. (1992). The closely related homomeric and heterodimeric mannose-binding lectins from garlic are encoded by one-domain and two-domain lectin genes, respectively. European Journal of Biochemistry, 206, 413–420.
Sadeghi, A., Smagghe, G., Broeders, S., Hernalsteens, J. P., de Greve, H., Peumans, W. J., et al. (2008). Ectopically expressed leaf and bulb lectins from garlic Allium sativum L.) protect transgenic tobacco plants against cotton leafworm (Spodoptera littoralis). Transgenic Research, 17, 9–18.
Edwards, G. A., Hepher, A., Clerk, S. P., & Boulter, D. (1991). Pea lectin is correctly processed, stable and active in leaves of transgenic potato plants. Plant Molecular Biology, 17, 89–100.
McCafferty, H. R. K., Moore, P. H., & Zhu, Y. J. (2008). Papaya transformed with the Galanthus nivalis GNA gene produces a biologically active lectin with spider mite control activity. Plant Science, 175, 385–393.
Foissac, X., Loc, N. T., Christou, P., Gatehouse, A. M. R., & Gatehouse, J. A. (2000). Resistance to green leafhopper (Nephotettix virescens) and brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens) in transgenic rice expressing snowdrop lectin (Galanthus nivalis agglutinin;GNA). Journal of Insect Physiology, 46, 573–583.
Maqbool, S. B., & Christou, P. (1999). Multiple traits of agronomic importance in transgenic indica rice plants: analysis of transgene integration patterns, expression levels and stability. Molecular Breeding, 5, 471–480.
Nagadhara, D., Ramesh, S., Pasalu, I. C., Kondala Rao, Y., Sarma, N. P., Reddy, V. D., & Rao, K. V. (2004). Transgenic rice plants expressing the snowdrop lectin gene (gna) exhibit high-level resistance to the whitebacked planthopper (Sogatella furcifera). Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 109, 1399–1405.
Dutta, I., Majumder, P., Saha, P., Ray, K., & Das, S. (2005a). Constitutive and phloem specific expression of Allium sativum leaf agglutinin (ASAL) to engineer aphid (Lipaphis erysimi) resistance in transgenic Indian mustard (Brassica juncea). Plant Science, 169, 996–1007.
Dutta, I., Saha, P., Majumder, P., Sakar, A., Chakraborti, D., Banerjee, S., et al. (2005b). The efficacy of a novel insecticidal protein, Allium sativum leaf lectin (ASAL), against homopteran insects monitored in transgenic tobacco. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 3, 601–611.
Stoger, E., Williams, S., Christou, P., Down, R. E., & Gatehouse, J. A. (1999). Expression of the insecticidal lectin from snowdrop (Galanthus nivalis agglutinin; GNA) in transgenic wheat plants: effects on predation by the grain aphid Sitobion avenae. Molecular Breeding, 5, 65–73.
Fitches, E., & Gatehouse, J. A. (1998). A comparison of the short and long term effects of insecticidal lectins on the activities of soluble and brush border enzymes of tomato moth larvae (Lacanobia oleracea). Journal of Insect Physiology, 44, 1213–1224.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Bo Liu and He-jiao Bian for their good comments on this manuscript. This work was supported in part by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Programs: no. 30270331 and no. 30670469); Director Fund of State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases (Sichuan University); The Science and Technology Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars of Sichuan Province (no. 06ZQ026-035); and the Key Technologies R&D Program of Sichuan Province (2006Z08-010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ye and Chen contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, Sh., Chen, S., Zhang, F. et al. Transgenic Tobacco Expressing Zephyranthes grandiflora Agglutinin Confers Enhanced Resistance to Aphids. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 158, 615–630 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8418-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8418-6