Abstract
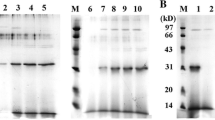
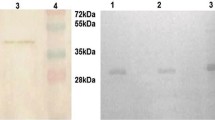
To develop more potent thrombolytic agents with fibrinolytic and antiplatelet aggregation activity, staphylokinase (Sak) variant Y1-Sak, a recombinant mutant of the Staphylococcus aureus protein Sak, was constructed. Y1-Sak formed an insoluble inclusion body when overexpressed in Escherichia coli strain JF1125. To obtain an optimized refolding process, dilution refolding was used to optimize refolding conditions. The results revealed that additive l-arginine and refolding temperature played critical roles in the refolding of Y1-Sak. Subsequently, two refolding methods, gel filtration and reverse dilution, were investigated to refold Y1-Sak. The results indicated that the fibrinolytic activity and recovery of Y1-Sak from gel filtration were lower than those from reverse dilution. Reverse dilution refolding successfully reduced the side reaction of refolding with the help of l-arginine, and the fibrinolytic activity and recovery of Y1-Sak were significantly improved. Functional analysis revealed that refolded Y1-Sak by reverse dilution possessed fibrinolytic and antiplatelet aggregation activities. Moreover, the immunogenicity of Y1-Sak was significantly reduced.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Sak:
-
staphylokinase
- Y1-Sak:
-
a staphylokinase variant in which N-terminal 15 amino acid residues were deleted and Ser16, Lys74, Glu75, Arg77, Lys109, Phe 111 was substituted with Lys, Ala, Ala, Ala, Arg, and Asp
- rt-PA:
-
recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator
- CV:
-
column volumes
- IBs:
-
inclusion bodies
- Gu-HCl:
-
guanidine–HCl
- RGD:
-
Arg-Gly-Asp
References
Tsumoto, K., Ejima, D., Kumagai, I., & Arakawa, T. (2003). Protein Expression and Purification, 28, 1–8.
Middelberg, A. P. J. (2002). Trends in Biotechnology, 20, 437–443.
De Bernardez Clark, E. (2001). Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 12, 202–207.
Singh, S. M., & Panda, A. K. (2005). Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 99, 303–310.
Li, M., Su, Z. G., & Janson, J. C. (2004). Protein Expression and Purification, 33, 1–10.
Swietnicki, W. (2006). Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 17, 367–372.
De Bernardez Clark, E., Schwarz, E., & Rudolph, R. (1999). Methods in Enzymology, 309, 217–236.
Collen, D. (1998). Nature Medicine, 4, 279–284.
Laroche, Y., Heymans, S., Capaert, S., De Cock, F., Demarsin, E., & Collen, D. (2000). Blood, 96, 1425–1432.
Su, H. B., Zhang, Y. G., He, J. T., Mo, W., Zhang, Y. L., Tao, X. M., et al. (2004). Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica, 36, 336–342.
Leach, J. K., Patterson, E., & O’Rear, E. A. (2004). Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 2, 1548–1555.
Ojima, I., Chakravarty, S., & Dong, Q. (1995). Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 3, 337–360.
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E. F., & Sambrook, J. (1982). Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual (1st ed.). New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory.
He, J., Wang, G., Li, G., Zhao, B., Mo, W., & Song, H. (2006). Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry, 45, 43–49.
Yang, J. T., Wu, C. S. C., & Martinez, H. M. (1986). Methods in Enzymology, 130, 208–269.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, J., Wang, G., Xu, R. et al. Refolding of a Staphylokinase Variant Y1-Sak by Reverse Dilution. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 151, 29–41 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8150-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8150-2