Abstract
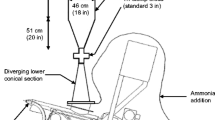
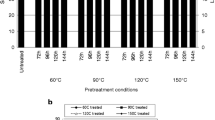
Soaking in aqueous ammonia at moderate temperatures was investigated as a method of pretreatment for enzymatic hydrolysis as well as simultaneous saccharification and cofermentation (SSCF) of corn stover. The method involves batch treatment of the feedstock with aqueous ammonia (15–30 wt%) at 40–90°C for 6–24 h. The optimum treatment conditions were found to be 15 wt% of NH3, 60°C, 1 : 6 of solid-to-liquid ratio, and 12 h of treatment time. The treated corn stover retained 100% glucan and 85% of xylan, but removed 62% of lignin. The enzymatic digestibility of the glucan content increased from 17 to 85% with 15 FPU /g-glucan enzyme loading, whereas the digestibility of the xylan content increased to 78%. The treated corn stover was also subjected to SSCF test using Spezyme-CP and recombinant Escherichia coli (KO11). The SSCF of the soaking in aqueous ammonia treated corn stover resulted in an ethanol concentration of 19.2 g/L from 3% (w/v) glucan loading, which corresponds to 77% of the maximum theoretical yield based on glucan and xylan.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang, V. S. and Holtzapple, M. T. (2000), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 84–86, 5–37.
Cowling, E. B. and Kirk, Ti. K. (1976), Biotechnol. Bioeng. Symp. 6, 95–123.
Dulap, C. E., Thomson, J., and Chiang, L. C. (1976), AIChE. Symp. Ser. 158, 7258.
Lee, D., Yu, A. H. C., and Saddler, J. N. (1995), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 45, 328–336.
Mooney, C. A., Mansfield, S. D., Touhy, M. G., and Saddler, J. N. (1998), Bioresour. Technol. 64, 113–119.
Schwald, W., Brownell, H. H., and Saddler, J. N. (1988), J. Wood Chem. Tech. 8(4), 543–560.
Kim, S. B. (1986), PhD. Dissertation, Auburn University.
Kim, T. H. and Lee, Y. Y. (2005), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 121–124, 1119–1132.
Hahn-Hägerdal, B., Jeppsson, H., Olsson, L., and Mohagheghi, A. (1994), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 41, 62–72.
Ohta, K., Beall, D. S., Mejia, J. P., Shanmugam, K. T., and Ingram, L. O. (2004), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57, 893–900.
NREL (1996), Chemical Analysis and Testing Laboratory. Analytical Procedures (CAT), National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, CO.
Iyer, P. V., Wu, Z. W., Kim, S. B., and Lee, Y. Y. (1996), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 57–58, 121–132.
Kim, T. H., Kim, J. S., Sunwoo, C., and Lee, Y. Y. (2003), Bioresour. Technol. 90, 39–47.
Converse, A. O. (1993), Substrate Factors Limiting Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Biotechnology in Agriculture No. 9, in CAB Int’l, Oxford, UK, 93–106.
Kim, S. B. and Lee, Y. Y. (1996), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 57–58, 147–156.
Kim, T. H. and Lee, Y. Y. (2006), Bioresour. Technol. 97, 224–232.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, T.H., Lee, Y.Y. Pretreatment of corn stover by soaking in aqueous ammonia at moderate temperatures. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 137, 81–92 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-007-9041-7
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-007-9041-7