Abstract
Background
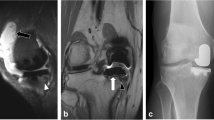
Little is known about intraarticular pathology following THA prior to the radiographic appearance of osteolysis, primarily due to imaging limitations. MRI has recently been applied to imaging the postarthroplasty hip with the ability to detect periarticular bony and soft tissue pathology; specifically, it is able to detect abnormal synovial patterns and focal bone loss well before the radiographic appearance of osteolysis.
Questions/purposes
We therefore used MRI to determine the incidence of early reactive synovitis and osteolysis in asymptomatic patients after THA, and whether there is an association between these MRI findings and clinical outcomes or radiographic wear measurements at this early stage.
Methods
We recruited 31 patients (33 hips) who underwent routine noncemented THA with one of three types of bearing surfaces: metal-on-cross-linked polyethylene (n = 7), ceramic-on-ceramic (n = 12), and ceramic-on-cross-linked polyethylene (n = 14). Patients underwent specialized MRI at a minimum of 12 months (mean, 23 months; range, 12–37 months) after surgery. MR images were analyzed for the presence of synovitis or osteolysis. WOMAC scores, patient assessment questionnaires, and radiographic wear measurements were correlated with MRI findings.
Results
Reactive synovitis was observed in 13 of 33 patients (39%) and focal osteolysis in one of 33 (3%). The presence of synovitis did not correlate with pain, activity level, patient satisfaction or clinical outcome scales, nor did it correlate with radiographic wear measurements at early followup.
Conclusions
Our observations suggest reactive synovitis is common yet asymptomatic at short-term followup. We do not know either the etiology or the long-term implications of these observations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellamy N, Buchanan WW, Goldsmith CH, Campbell J, Stitt LW. Validation study of WOMAC: A health status instrument for measuring clinically important patient relevant outcomes to antirheumatic drug therapy in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. J Rheumatol. 1988;15:1833–1840.
Bragdon CR, Greene ME, Freiberg AA, Harris WH, Malchau H. Radiostereometric analysis comparison of wear of highly cross-linked polyethylene against 36- vs 28-mm femoral heads. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22:125–129.
Cahir JG, Toms AP, Marshall TJ, Wimhurst J, Nolan J. CT and MRI of hip arthroplasty. Clin Radiol. 2007;62:1163–1171.
Chang JD, Kamdar R, Yoo JH, Hur M, Lee SS. Third-generation ceramic-on-ceramic bearing surfaces in revision total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:1231–1235.
Claus AM, Engh CA Jr, Sychterz CJ, Xenos JS, Orishimo KF, Engh CA Sr. Radiographic definition of pelvic osteolysis following total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85:1519–1526.
Clohisy JC, Calvert G, Tull F, McDonald D, Maloney WJ. Reasons for revision hip surgery: a retrospective review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;429:188–192.
Cooper HJ, Ranawat AS, Potter HG, Foo LF, Jawetz ST, Ranawat CS. Magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis and management of hip pain after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:661–667.
Coumbaras M, Le Hir P, Sautet A, Jomaah N, Tubiana JM, Arrivé L. Reactive synovitis: MRI features with arthroscopic correlation. J Radiol. 2005;86:481–486.
Digas G, Kärrholm J, Thanner J, Malchau H, Herberts P. The Otto Aufranc Award: Highly cross-linked polyethylene in total hip arthroplasty. Randomized evaluation of penetration rate in cemented and uncemented sockets using radiostereometric analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2004;429:6–16.
D’Antonio JA, Manley MT, Capello WN, Bierbaum BE, Ramakrishnan R, Naughton M, Sutton K. Five-year experience with Crossfire® highly cross-linked polyethylene. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;441:143–150.
Dorr LD,Wan Z, Shahrdar C, Sirianni L, Boutary M, Yun A. Clinical performance of a Durasul highly crosslinked polyethylene acetabular liner for total hip arthroplasty at five years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87:1816–1821.
Duffy P, Sher JL, Partington PF. Premature wear and osteolysis in an HA-coated, uncemented total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86:34–38.
Endo M, Tipper JL, Barton DC, Stone MH, Ingham E, Fisher J. Comparison of wear, wear debris and functional biological activity of moderately crosslinked and non-crosslinked polyethylenes in hip prostheses. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2002;216:111–122.
Engh CA Jr, Sychterz CJ, Young AM, Pollock DC, Toomey SD, Engh CA Sr. Interobserver and intraobserver variability in radiographic assessment of osteolysis. J Arthroplasty. 2002;17:752–759.
Garvin KL, Hartman CW, Mangla J, Murdoch N, Martell JM. Wear analysis in THA utilizing oxidized zirconium and crosslinked polyethylene. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009; 467:141–145.
Geerdink CH, Grimm B, Vencken W, Heyligers IC, Tonino AJ. The determination of linear and angular penetration of the femoral head into the acetabular component as an assessment of wear in total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90:839–846.
Geller JA, Malchau H, Bragdon C, Greene M, Harris WH, Freiberg AA. Large diameter femoral heads on highly cross-linked polyethylene: minimum 3-year results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;447:53–59.
Goosen JHM, Castelein RM, Verheyen CCPM. Silent osteolysis associated with an uncemented acetabular component: A monitoring and treatment algorithm. Curr Orthop. 2005;19:288–293.
Greene JW, Malkani AL, Kolisek FR, Jessup NM, Baker DL. Ceramic-on-ceramic total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:15–18.
Harris WH. The problem is osteolysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995;311:46–53.
Hozack WJ, Mesa JJ, Carey C, Rothman RH. Relationship between polyethylene wear, pelvic osteolysis, and clinical symptomatology in patients with cementless acetabular components: a framework for decision making. J Arthroplasty. 1996;11:769–772.
Ingram JH, Stone M, Fisher J, Ingham E. The influence of molecular weight, crosslinking and counter roughness on TNF-Alpha production by macrophages in response to ultra high molecular weight polyethylene particles. Biomaterials. 2004;25:3511–3522.
Kido K, Fujioka M, Takahashi K, Ueshima K, Goto T, Kubo T. Short-term results of the S-ROM-A femoral prosthesis operative strategies for Asian patients with osteoarthritis. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:1193–1199.
Kim YH. Comparison of polyethylene wear associated with cobalt-chromium and zirconia heads after total hip replacement: a prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87:1769–1776.
Kim YH, Kim JS, Choi YW, Kwon OR. Intermediate results of simultaneous alumina-on-alumina bearing and alumina-on-highly cross-linked polyethylene bearing total hip arthroplasties. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:885–891.
Kraay MJ, Thomas RD, Rimnac CM, Fitzgerald SJ, Goldberg VM. Zirconia versus Co-Cr femoral heads in total hip arthroplasty: Early assessment of wear. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;453:86–90.
Krushell RJ, Fingeroth RJ, Cushing MC. Early femoral head penetration of a highly cross-linked polyethylene liner vs a conventional polyethylene liner: a case-controlled study. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20:73–76.
Langton DJ, Jameson SS, Joyce TJ, Hallab NJ, Natu S, Nargol AVF. Early failure of metal-on-metal bearings in hip resurfacing and large-diameter total hip replacement: A consequence of excess wear. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92:38–46.
Leung SB, Egawa H, Stepniewski A, Beykirch S, Engh CA Jr, Engh CA Sr. Incidence and volume of pelvic osteolysis at early follow-up with highly cross-linked and noncross-linked polyethylene. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22:134–139.
Looney RJ, Boyd A, Totterman S, Seo GS, Tamez-Pena J, Campbell D, Novotmy L, Olcott C, Martell J, Hayes FA, O’Keefe RJ, Schwartz EM. Volumetric computerized tomography as a measurement of periprosthetic acetabular osteolysis and its correlation with wear. Arthritis Res. 2001;4:59–63.
Malchau H, Potter HG. How are wear-related problems diagnosed and what forms of surveillance are necessary? J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2008;16(suppl):s14–s19.
Marshall A, Ries MD, Paprosky W. How prevalent are implant wear and osteolysis, and how has the scope of osteolysis changed since 2000? J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2008;16(suppl):S1–S6.
Martell JM, Berkson E, Berger R, Jacobs J. Comparison of two and three-dimensional computerized polyethylene wear analysis after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85:1111–1117.
McCalden RW, MacDonald SJ, Rorabeck CH, Bourne RB, Chess DG, Charron KD. Wear rate of highly cross-linked polyethylene in total hip arthroplasty. A randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:773–782.
Ollivere B, Darran C, Barker T, Nolan J, Porteous MJ. Early clinical failure of the Birmingham metal-on-metal hip resurfacing is associated with metallosis and soft tissue necrosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009;91:1025–1030.
Pandit H, Glyn-Jones S, McLardy-Smith P, Gundle R, Whitwell D, Gibbons CLM, Ostlere S, Athanasou N, Gill HS, Murray DW. Pseudotumours associated with metal-on-metal hip resurfacings. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90:847–851.
Pedersen DR, Brown TD, Hillis SL, Callaghan JJ. Prediction of long-term polyethylene wear in total hip arthroplasty, based on early wear measurements made using digital image analysis. J Orthop Res. 1998;16:557–563.
Potter HG, Montgomery KD, Padgett DE, Salvati EA, Helfet DL. Magnetic resonance imaging of the pelvis: new orthopaedic applications. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995;319:223–231.
Potter HG, Nestor BJ, Sofka CM, Ho ST, Peters LE, Salvati EA. Magnetic resonance imaging after total hip arthroplasty: evaluation of periprosthetic soft tissue. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86:1947–1954.
Puri L, Wixson RL, Stern SH, Kohli J, Hendrix RW, Stulberg SD. Use of helical computed tomography for the assessment of acetabular osteolysis after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84:609–614.
Rasquina VJ, Ranawat CS, Cervieri CL, Rodríguez JA. The press-fit modular total knee system with a posterior-cruciate substituting design: a concise followup of a previous report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88:1006–1010.
Rhodes LA, Keenan AM, Grainger AJ, Emery P, McGonagle D, Conaghan PG. The relationship between limited MRI section analyses and volumetric assessment of synovitis in knee osteoarthritis. Clin Radiol. 2005;60:1295–1299.
Roman free to share software version V1.70. The Institute of Orthopaedics Web site. Available at: http://www.Keele.ac.uk/depts/rjah/. Accessed October 28, 2009.
Saleh KJ, Holtzman J, Gafni A, Saleh L, Davis A, Resig S, Gross AE. Reliability and intraoperative validity of preoperative assessment of standardized plain radiographs in predicting bone loss at revision hip surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83:1040–1046.
Schmalzried TP, Callaghan JJ. Wear in total hip and knee replacements. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999;81:115–136.
Sugimoto H, Hirose I, Miyaoka E, Fujita A, Kinebuchi Y, Yamamoto W, Itoh Y. Low-field-strength MR imaging of failed hip arthroplasty: association of femoral periprosthetic signal intensity with radiographic, surgical, and pathologic findings. Radiology. 2003;229:718–723.
Sychterz CJ, Engh CA Jr, Yang A, Engh CA. Analysis of temporal wear patterns of porous-coated acetabular components: distinguishing between true wear and so-called bedding-in. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999;81:821–830.
Sychterz CJ, Yang AM, McAuley JP, Engh CA. Two-dimensional versus threedimensional radiographic measurements of polyethylene wear. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;365:117–123.
Urban JA, Garvin KL, Boese CK, Bryson L, Pedersen DR, Callaghan JJ, Miller RK. Ceramic-on-polyethylene bearing surfaces in total hip arthroplasty: seventeen to twenty-one-year results. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83:1688–1694.
Walde TA, Weiland DE, Leung SB, Kitamura N, Sychterz CJ, Engh CA Jr, Claus AM, Potter HG, Engh CA Sr. Comparison of CT, MRI, and radiographs in assessing pelvic osteolysis: a cadaveric study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;437:138–144.
Weiland DE, Walde TA, Leung SB, Sychterz CJ, Ho S, Engh CA, Potter HG. Magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of periprosthetic acetabular osteolysis: a cadaveric study. J Orthop Res. 2005;23:713–719.
White LM, Kim JK, Mehta M, Merchant N, Schweitzre ME, Morrison WB, Hutchison CR, Gross AE. Complications of Total Hip Arthroplasty: MR Imaging – Initial Experience. Radiology. 2000;215:254–262.
Willert HG, Buchhorn GH, Fayyazi A, Flury R, Windler M, Koster G, Lohmann CH. Metal-on-metal bearings and hypersensitivity in patients with artificial hip joints: a clinical and histomorphological study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87:28–36.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
One of more of the authors (HJC, ASR, HGP, LFF, CSR) have received funding from The Hip Society for this project.
Each author certifies that his or her institution approved the human protocol for this investigation and that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research, and that informed consent for participation in the study was obtained.
This work was performed at Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, NY, and the Hospital for Special Surgery, New York, NY.
Aided by a grant from the Hip Society.
About this article
Cite this article
Cooper, H.J., Ranawat, A.S., Potter, H.G. et al. Early Reactive Synovitis and Osteolysis after Total Hip Arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468, 3278–3285 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1361-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1361-1