Abstract
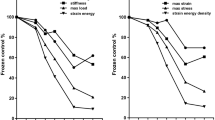
Ionizing radiation could supplement tissue bank screening to further reduce the probability of diseases transmitted by allografts if denaturation effects can be minimized. It is important, however, such sterilization procedures be nondetrimental to tissues. We compared crosslinking and free radical scavenging potential methods to accomplish this task in tendon tissue. In addition, two forms of ionizing irradiation, gamma and electron beam (e-beam), were also compared. Crosslinkers included 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide (EDC) and glucose, which were used to add exogenous crosslinks to collagen. Free radical scavengers included mannitol, ascorbate, and riboflavin. Radioprotective effects were assessed through tensile testing and collagenase resistance testing after irradiation at 25 kGy and 50 kGy. Gamma and e-beam irradiation produced similar degenerative effects. Crosslinkers had the highest strength at 50 kGy, EDC treated tendons had 54% and 49% higher strength than untreated, for gamma and e-beam irradiation respectively. Free radical scavengers showed protective effects up to 25 kGy, especially for ascorbate and riboflavin. Crosslinked samples had higher resistance to collagenase and over a wider dose range than scavenger-treated. Of the options studied, the data suggest EDC precrosslinking or glucose treatment provides the best maintenance of native tendon properties after exposure to ionizing irradiation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akkus O, Belaney RM, Das P. Free radical scavenging alleviates the biomechanical impairment of gamma radiation sterilized bone tissue. J Orthop Res. 2005;23:838–845.
Block SS. Disinfection, Sterilization, and Preservation, 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA and London, England: Lea and Febiger; 1991.
Cai L, Koropatnick J, Cherian MG. Roles of vitamin C in radiation-induced DNA damage in presence and absence of copper. Chem Biol Interact. 2001;137:75–88.
Caruso AB, Dunn MG. Functional evaluation of collagen fiber scaffolds for ACL reconstruction: cyclic loading in proteolytic enzyme solutions. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2004;69:164–171.
Cheung DT, Perelman N, Tong D, Nimni ME. The effect of gamma-irradiation on collagen molecules, isolated alpha-chains, and crosslinked native fibers. J Biomed Mater Res. 1990;24:581–589.
Dziedzic-Goclawska A, Kaminski A, Uhrynowska-Tyszkiewicz I, Stachowicz W. Irradiation as a safety procedure in tissue banking. Cell Tissue Bank. 2005;6:201–219.
Fuga L, Kragl M, Getoff N. Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) and a mixture of vitamin B2 and C affects MMC efficiency in aerated media under irradiation. Anticancer Res. 2004;24:4031–4034.
Garrett RH, Grisham CM. Biochemistry, 2nd ed. Fort Worth, TX: Saunders College Publishing; 1999.
Grieb TA, Forng RY, Bogdansky S, Ronholdt C, Parks B, Drohan WN, Burgess WH, Lin J. High-dose gamma irradiation for soft tissue allografts: High margin of safety with biomechanical integrity. J Orthop Res. 2006;24:1011–1018.
Hernigou P. Allograft sterility as exemplified by human immunodeficiency virus and sterilization by irradiation. J Arthroplasty. 2000;15:1051–1058.
Kohlhaas M, Spoerl E, Schilde T, Unger G, Wittig C, Pillunat LE. Biomechanical evidence of the distribution of cross-links in corneas treated with riboflavin and ultraviolet A light. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006;32:279–283.
Konopacka M, Widel M, Rzeszowska-Wolny J. Modifying effect of vitamins C, E and beta-carotene against gamma-ray-induced DNA damage in mouse cells. Mutat Res. 1998;417:85–94.
Li X, Trout JM, Jenkins MC, Palmer R, Fayer R. Effects of gamma radiation on viability of Encephalitozoon spores. J Parasitol. 2002;88:812–813.
Lietman SA, Tomford WW, Gebhardt MC, Springfield DS, Mankin HJ. Complications of irradiated allografts in orthopaedic tumor surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;375:214–217.
Monboisse JC, Borel JP. Oxidative damage to collagen. EXS. 1992;62:323–327.
Nguyen H, Morgan DA, Forwood MR. Sterilization of allograft bone: is 25 kGy the gold standard for gamma irradiation? Cell Tissue Bank. 2007;8:81–91.
Ohan MP, Dunn MG. Glucose stabilizes collagen sterilized with gamma irradiation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2003;67:1188–1195.
Powell HM, Boyce ST. EDC cross-linking improves skin substitute strength and stability. Biomaterials. 2006;27:5821–5827.
Reddy GK. Glucose-mediated in vitro glycation modulates biomechanical integrity of the soft tissues but not hard tissues. J Orthop Res. 2003;21:738–743.
Russell AD. Principles, Practice of Disinfection, Preservation, and Sterilization, 2nd ed. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Scientific Publications; 1992.
Salehpour A, Butler DL, Proch FS, Schwartz HE, Feder SM, Doxey CM, Ratcliffe A. Dose-dependent response of gamma irradiation on mechanical properties and related biochemical composition of goat bone-patellar tendon-bone allografts. J Orthop Res. 1995;13:898–906.
Smith RA, Ingels J, Lochemes JJ, Dutkowsky JP, Pifer LL. Gamma irradiation of HIV-1. J Orthop Res. 2001;19:815–819.
Suarez LS, Richmond JC. Overview of procurement, processing, and sterilization of soft tissue allografts for sports medicine. Sports Med Arthrosc. 2007;15:106–113.
Vangsness CT Jr, Garcia IA, Mills CR, Kainer MA, Roberts MR, Moore TM. Allograft transplantation in the knee: tissue regulation, procurement, processing, and sterilization. Am J Sports Med. 2003;31:474–481.
Weadock KS, Miller EJ, Keuffel EL, Dunn MG. Effect of physical crosslinking methods on collagen-fiber durability in proteolytic solutions. J Biomed Mater Res. 1996;32:221–226.
Wissink MJ, van Luyn MJ, Beernink R, Dijk F, Poot AA, Engbers GH, Beugeling T, van Aken WG, Feijen J. Endothelial cell seeding on crosslinked collagen: effects of crosslinking on endothelial cell proliferation and functional parameters. Thromb Haemost. 2000;84:325–331.
Wollensak G, Spoerl E, Seiler T. Stress-strain measurements of human and porcine corneas after riboflavin-ultraviolet-A-induced cross-linking. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003;29:1780–1785.
Zbikowska HM, Nowak P, Wachowicz B. Protein modification caused by a high dose of gamma irradiation in cryo-sterilized plasma: protective effects of ascorbate. Free Radic Biol Med. 2006;40:536–542.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
One or more of the authors (MGD) have received funding from the Musculoskeletal Transplant Foundation Peer Reviewed Scientific Grants Program (January–December 2005).
About this article
Cite this article
Seto, A., Gatt, C.J. & Dunn, M.G. Radioprotection of Tendon Tissue via Crosslinking and Free Radical Scavenging. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466, 1788–1795 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-008-0301-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-008-0301-9