Abstract
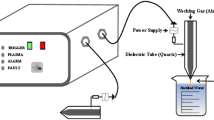
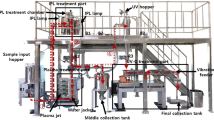
The contamination of barley kernel by Fusarium fungi constitutes a serious problem for malting-related industries. Deoxynivalenol (DON) is a secondary metabolite produced by Fusarium fungi. DON can affect dopaminergic receptors in the human brain; it may cause symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, headache, and fever. The aims of this study were to evaluate the DON destruction effect of the intense pulsed light (IPL) and plasma-activated water (PAW) treatments in raw and germinating barley and assess the feasibility for disinfection in the malt industry. Both non-thermal methods degraded DON concentration in germinating barley. IPL treatment significantly reduced (p < 0.05) the DON level of germinating barley samples by 35.5% after 180 pulses in 60 s, and the PAW treatment effectively degraded the DON level by 34.6% in germinating barley in the first 5 min. However, higher barley quality remained for PAW treatment (germination rate: 81–100%) than for the IPL treatment (germination rate: 41–60%). For the raw barley samples, although significant reduction (30.9%) was achieved after 180 pulses of IPL treatment, noticeable quality (germination rate: 20–40%) alteration was observed. Significantly less DON degradation was achieved by the PAW treatment on raw barley than the germinating barley for all times. Overall, these findings suggested that PAW and IPL might potentially be used to reduce DON levels in some malt-related industry applications, and PAW was recommended as a better method than IPL to maintain the barley quality.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson, D., James, D., House, C., & Nyachoti, M. (2005). Reduction of deoxynivalenol in barley by treatment with aqueous sodium carbonate and heat. Mycopathologia, 160(4), 297–301.
Arjunan, K. P., Friedman, G., Fridman, A., & Clyne, A. M. (2011). Nonthermal dielectric barrier discharge plasma induces angiogenesis through reactive oxygen species. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 9(66), 147–157.
Atalla, M. M., Hassaneini, N. M., Elbeih, A. A., & Youssef, Y. A. (2004). Effect of fluorescent and UV light on mycotoxin production under different relative Humidities in wheat grains. International Journal of Agriculture & Biology, 6(6), 1006–1012.
Brenn, S. Z., Cichna, M. M., & Bohm, M. (2007). Selective sample cleanup by reusable sol-gel immunoaffinity columns for determination of deoxynivalenol in food and feed samples. Analytical Chemistry, 79(2), 710–717.
Bretz, M., Beyer, M., Cramer, B., Knecht, A., & Humpf, H. U. (2006). Thermal Degradation of the Fusarium Mycotoxin Deoxynivalenol. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 54(17), 6445–6451.
Burlica, R., Grim, R., Shih, K., Balkwill, D., & Locke, B. (2010). Bacteria inactivation using low power pulsed gliding arc discharges with water spray. Plasma Processes and Polymers, 7(8), 640.
Chen, D., Wiertzema, J., Peng, P., Cheng, Y., Liu, J., Mao, Q., Ma, Y., Anderson, E., Chen, P., Baumler, D. J., Chen, C., Vickers, Z., Feirtag, J., Lee, L., & Ruan, R. (2018). Effects of intense pulsed light on Cronobacter sakazakii inoculated in non-fat dry milk. Journal of Food Enigneering, 238, 178–187.
Ellis, R. H., & Roberts, E. H. (1980). The influence of temperature and moisture on seed viability period in barley (Hordeum distichum L.). Annals of Botany, 45(1), 31–37.
Elmnasser, N., Guillou, S., Leroi, F., Orange, N., Bakhrouf, A., & Federighi, M. (2007). Pulsed-light system as a novel food decontamination technology: A review. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 53(7), 813–821.
EFSA (2004). Opinion of the scientific panel on contaminants in the food chain on a request from the commission related to deoxynivalenol (DON) as undesirable substance in animal feed. European Food Safety Authority, 73, 1–41.
Filatova, I., Azharonok, V., Lushkevich, V., Zhukovsky, A., Gadzhieva, G., & Spasi, K. (2013). Plasma seeds treatment as a promising technique for seed germination improvement. 31st International Conference on Phenomena in Ionized Gases, Granada, Spain.
Fine, F., & Gervais, P. (2004). Efficiency of pulsed UV light for microbial decontamination of food powders. Journal of Food Protection, 67(4), 787–792.
Gemma, O. O., & Olga, M. B. (2010). Pulsed light treatments for food preservation. A Review. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 3, 13–23.
Heisel, S. (1996). Report of subcommittee on Deoxynivalenol in barley and malt. Journal of the ASBC, 54, 268–270.
Hoang, H. H., Sechet, J., Bailly, C., Leymarie, J., & Corbineau, F. (2014). Inhibition of germination of dormant barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) grains by blue light as related to oxygen and hormonal regulation. Plant, Cell and Environment, 37(6), 1393–1403.
Hojnik, N., Cvelbar, U., Kalcher, G. T., Walsh, J. L., & Krizaj, I. (2017). Mycotoxin decontamination of food: Cold atmospheric pressure plasma versus “classic” decontamination. Toxins, 9(5), 151.
Hua, G., Li, G. X., Cheng, Y., & Chen, D. J. (2015). Meng, D., et al. primary study on influencing factors of rice seed germination rate. Agricultural Science & Technology, 16(6), 1126–1129.
Kabak, B. (2009). The fate of mycotoxins during thermal food processing. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 89(4), 549–554.
Krishnamurthy, K. (2006). Decontamination of milk and water by pulsed UV-light and infrared heating. ProQuest, 12, 410.
Liao, L. B., Chen, W. M., & Xiao, X. M. (2007). The generation and inactivation mechanism of oxidation–reduction potential of electrolyzed oxidizing water. Journal of Food Engineering, 78(4), 1326–1332.
Los, A., Ziuzina, D., Akkermans, S., Boehm, D., Patrick, J. C., & Impeb, J. V. (2018). Paula Bourkea. Improving microbiological safety and quality characteristics of wheat and barley by high voltage atmospheric cold plasma closed processing. Food Research International, 106, 509–521.
Ma, R. N., Feng, H. Q., Li, F. T., Liang, Y. D., Zhang, Q., Zhu, W. D., et al. (2012). An evaluation of antioxidative protection for cells against atmospheric pressure cold plasma treatment. Applied Physics Letters, 100(12), 123701–123704.
Ma, R. N., Wang, G. M., Tian, Y., Wang, K. L., Zhang, J., & Fang, J. (2015). Non-thermal plasma-activated water inactivation of foodborne pathogen on fresh produce. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 300, 643–651.
Ma, R., Yu, S., Tian, Y., Wang, K., Sun, C., Li, X., Zhang, J., Chen, K., & Fang, J. (2016). Effect of non-thermal plasma-activated water on fruit decay and quality in postharvest Chinese bayberries. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 9(11), 1825–1834.
Mahalingam, R. (2017). Shotgun proteomics of the barley seed proteome. BMC Genomics, 18(1), 44.
Maksimovic, J. D., Zhang, J. Y., Zeng, F. Y., Zivanovic, B. D., Shabala, L., et al. (2013). Linking oxidative and salinity stress tolerance in barley: Can root antioxidant enzyme activity be used as a measure of stress tolerance. Plant and Soil, 365(1–2), 141–155.
Mishra, S., Dixit, S., Dwivedi, P. D., Pandey, H. P., & Das, M. (2014). Influence of temperature and pH on the degradation of deoxynivalenol (DON) in aqueous medium: Comparative cytotoxicity of DON and degraded product. Food Additives & Contaminants: Part A, 31(1), 121–131.
Moreau, M., Lescure, G., Agoulon, A., Svinareff, P., Orangeaand, N., & Feuilloley, M. (2013). Application of the pulsed light technology tomycotoxin degradation and inactivation. Journal of Applied Toxicology, 33(5), 357–363.
Numanoglu, E., Gokmen, V., & Uygun, U. (2011). Thermal degradation of deoxynivalenol during maize bread baking. Food Additives & Contaminants, 29(3), 423–430.
Oehmigen, K., Hahnel, M., Brandenburg, R., Wilke, C., Weltmann, K. D., & Woedtke, T. V. (2010). The role of acidification for antimicrobial activity of atmospheric pressure plasma in liquids. Plasma Processes and Polymers, 7(3), 250–257.
Schwarz, P. B., & Horsley, R. D. (2006). Quality risks associated with the utilization of fusarium head blight infected malting barley. Journal of ASBC, 64(1), 1–7.
Sera, B., Spatenka, P., Sery, M., Vrchotova, N., & Hruskova, I. (2010). Influence of plasma treatment on wheat and oat germination and early growth. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 38(10), 2963–2968.
Sharma, R. R., & Demirci, A. (2003). Inactivation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 on inoculated alfalfa seeds with pulsed ultraviolet light and response surface modelling. Journal of Food Science, 68(4), 1448–1453.
Tian, Y., Ma, R. N., Zhang, Q., Feng, H. Q., Liang, Y. D., Zhang, J., et al. (2014). Assessment of the physicochemical properties and biological effects of water activated by non-thermal plasma above and beneath the water surface, plasma process. Polym, 12(5), 439–449.
Traylor, M. J., Pavlovich, M. J., Karim, S., Hait, P., Sakiyama, Y., Hait, P., et al. (2011). Long-term antibacterial efficacy of air plasma-activated water. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 44, 22–27.
US FDA (2010). Guidance for Industry and FDA: Advisory Levels for Deoxynivalenol (DON) in Finished Wheat Products for Human Consumption and Grains and Grain By-Products used for Animal Feed. Available at https://www.fda.gov/Food/GuidanceRegulation/GuidanceDocumentsRegulatoryInformation/ChemicalContaminantsMetalsNaturalToxinsPesticides/ucm120184.htm. Accessed 7 Nov 2018.
Wallen, R. D., May, R., Rieger, K., Holloway, J. M., & Cover, W. H. (2001). Sterilization of a new medical device using broad spectrum pulsed light. Biomedical Instrumentation & Technology, 35(5), 323–330.
Wan, D., Huang, L. L., Pan, Y. H., Wu, Q. H., Chen, D. M., Tao, Y., et al. (2013). Metabolism, distribution, and excretion of deoxynivalenol with combined techniques of radiotracing, high-performance liquid chromatography ion trap time-of-flight mass spectrometry, and online radiometric detection. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 62(1), 288–296.
Wang, L., Shao, H. L., Luo, X. H., Wang, R., Li, Y. F., Li, Y. N., et al. (2016). Effect of ozone treatment on Deoxynivalenol and wheat quality. PLoS One, 11(1), 1–13.
Wardlaw, I. F., Dawson, I. A., Munibi, P., & Fewster, R. (1989). The tolerance of wheat to high temperatures during reproductive growth. I survey procedures and general response patterns. Journal of Agricultural Research, 40(1), 1–13.
William, A. P. (1986). Oxy-radicals and related species: Their formation, lifetimes, and Reactions. Annual Review of Physiology, 48, 657–667.
Xu, X. M., & Berrie, A. (2005). Epidemiology of mycotoxigenic fungi associated with fusarium ear blight and apple blue mold: A review. Food Additives and Contaminants, 22(4), 290–301.
Zahoranova, A., Henselova, M., Hudecova, D., Kalinakova, B., Kovacik, D., Medvecka, V., et al. (2016). Effect of cold atmospheric pressure plasma on the wheat seedlings vigor and on the inactivation of microorganisms on the seeds surface. Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing, 36(2), 397–414.
Zhang, Q., Liang, Y. D., Feng, H. Q., Ma, R. N., Tian, Y., Zhang, J., et al. (2013). A study of oxidative stress induced by non-thermal plasma-activated water for bacterial damage. Applied Physics Letters, 102(20), 203701–203704.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by a gift from Rahr Malting Co., Minnesota, USA, and University of Minnesota Center for Biorefining. Thanks to Xiang S. Yin of Rahr Malting Co. for assistance with DON analysis and others.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, D., Chen, P., Cheng, Y. et al. Deoxynivalenol Decontamination in Raw and Germinating Barley Treated by Plasma-Activated Water and Intense Pulsed Light. Food Bioprocess Technol 12, 246–254 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-018-2206-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-018-2206-2